If you’ve noticed changes in your skin, you’re not alone. Many people are attuned to their skin’s condition and can spot even the slightest shifts. One common issue that can arise is melasma, a skin condition that often goes unnoticed until it becomes more pronounced. This article will delve into what melasma is, its causes, who it affects, how it’s diagnosed, and the best treatment options available.
What is melasma?
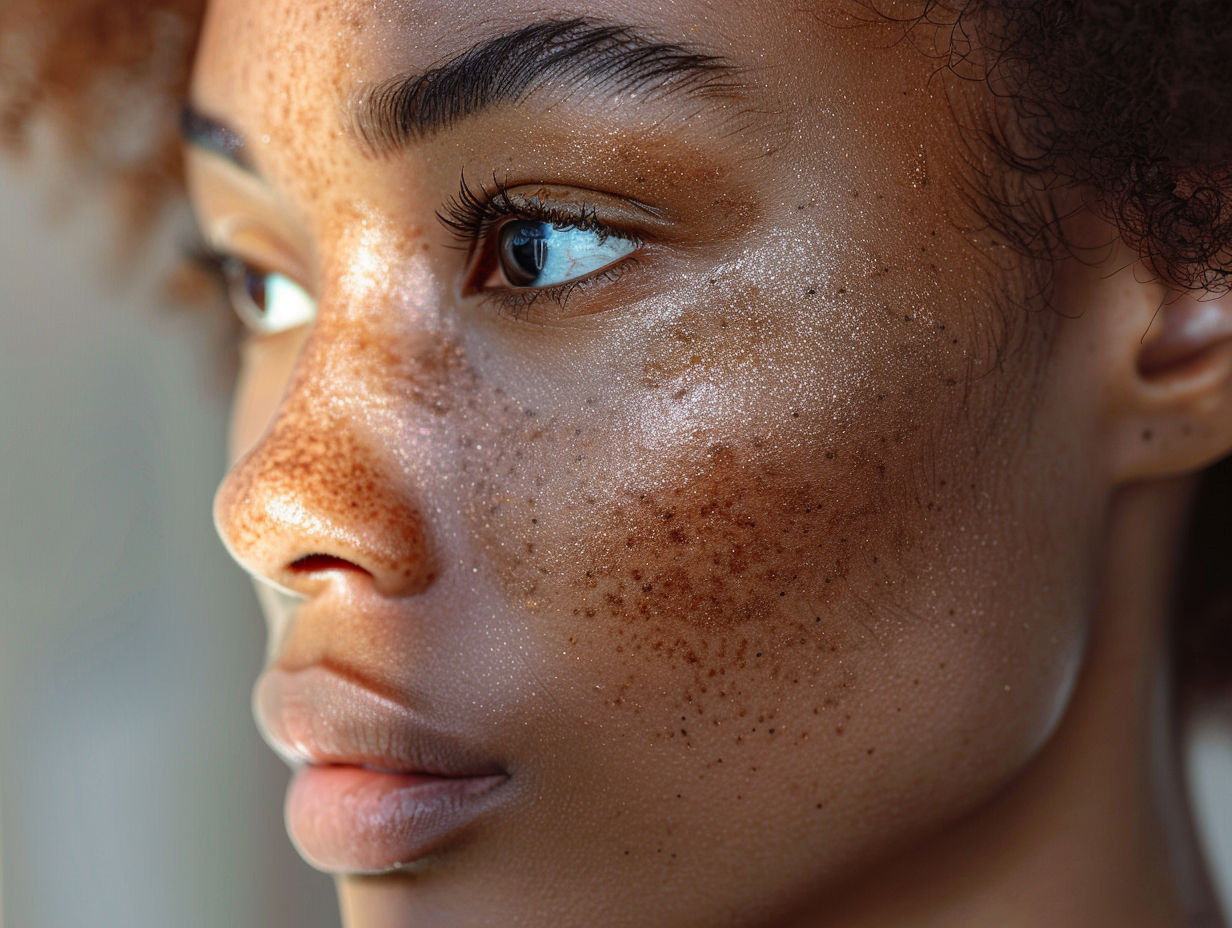
Melasma is a chronic skin condition characterized by dark, discolored patches on the face, primarily affecting areas such as the upper lip, cheeks, and forehead. It results from an overproduction of melanin, the pigment responsible for skin color. While the exact cause remains unclear, experts have identified a strong correlation between the condition and factors such as sun exposure and hormonal changes.
The condition can present in different patterns, with some people experiencing symmetrical patches across their faces while others may have more localized areas of pigmentation. Understanding these patterns helps dermatologists determine the most effective treatment approach.
Who is most affected by melasma?
Melasma can affect anyone, but it is particularly prevalent among women and individuals with darker skin tones. A study published in the Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology found that it is more common in women of childbearing age, especially those who are pregnant or taking hormonal contraceptives. This is why it is often referred to as the “mask of pregnancy.”
Several risk factors contribute to the development of melasma:
- Genetic predisposition
- Hormonal changes during pregnancy
- Use of oral contraceptives
- Thyroid disorders
- Extended sun exposure
- Living in areas with high UV radiation
The role of hormones in melasma development
Hormonal fluctuations play a significant role in the development and progression of melasma. Estrogen and progesterone levels can trigger increased melanin production, explaining why the condition often appears during pregnancy or while taking birth control pills. Understanding this hormonal connection is crucial for both prevention and treatment strategies.
The impact of lifestyle factors
Beyond hormonal influences, various lifestyle factors can affect melasma’s severity:
- Sun exposure habits
- Skincare routine
- Diet and nutrition
- Stress levels
- Sleep patterns
- Environmental pollution exposure
Diagnosis
Diagnosis typically occurs during a clinical examination. Dermatologists may use a Woods Lamp examination, which utilizes ultraviolet light to assess the depth of pigmentation. This method helps differentiate melasma from other skin conditions.
The diagnostic process often includes:
- Visual examination
- Medical history review
- Wood’s lamp examination
- Dermoscopy in some cases
- Possible skin biopsy for unclear cases
Understanding different types of melasma
Melasma can be classified into three types based on the depth of pigmentation:
- Epidermal (superficial)
- Dermal (deep)
- Mixed (combination)
Each type responds differently to treatment, making accurate diagnosis crucial for developing an effective treatment plan.
Managing and treating melasma
While there is no definitive cure for melasma, several effective management strategies exist. A comprehensive treatment plan often includes multiple approaches:
Daily sun protection
Sunscreen use is crucial for both treatment and prevention. Key considerations include:
- Using broad-spectrum SPF 30 or higher
- Selecting physical/mineral sunscreens
- Reapplying every 2-3 hours
- Wearing protective clothing and hats
- Avoiding peak sun hours
Topical treatments
Various topical treatments can help manage melasma:
- Hydroquinone (prescription strength)
- Kojic acid
- Azelaic acid
- Vitamin C serums
- Retinoids
- Tranexamic acid
Professional treatments
In-office procedures can provide additional benefits:
- Chemical peels
- Laser therapy
- Microdermabrasion
- LED light therapy
- Micro needling
- Professional skin brightening treatments
The role of skincare routine
Developing an effective skincare routine is essential for managing melasma:
Morning routine
- Gentle cleanser
- Antioxidant serum
- Moisturizer
- Broad-spectrum sunscreen
Evening routine
- Double cleansing
- Treatment products
- Moisturizer
- Prescribed topical medications
Natural remedies and lifestyle modifications
While medical treatments are essential, natural approaches can complement traditional therapies:
- Green tea extracts
- Licorice root
- Vitamin C-rich foods
- Adequate hydration
- Stress management
- Quality sleep
Prevention strategies
Preventing melasma flare-ups requires a multi-faceted approach:
- Consistent sun protection
- Hormone level monitoring
- Avoiding triggers
- Regular skin examinations
- Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
The psychological impact
Melasma can significantly affect quality of life and self-esteem. Understanding the emotional aspects is crucial for comprehensive care:
- Impact on self-image
- Social anxiety
- Professional concerns
- Relationship effects
- Support system importance
Future treatments and research
Ongoing research continues to explore new treatment options:
- Novel topical formulations
- Advanced laser technologies
- Combination therapy approaches
- Genetic research
- Preventive strategies
When to seek professional help
Consulting a dermatologist is recommended when:
- Pigmentation changes rapidly
- Over-the-counter treatments fail
- Emotional distress occurs
- Diagnosis is unclear
- Treatment guidance is needed
The importance of patient education
Understanding melasma is crucial for successful management:
- Realistic expectations
- Treatment compliance
- Trigger awareness
- Prevention strategies
- Long-term maintenance
Living with melasma
Managing melasma is an ongoing process requiring:
- Patience with treatment
- Consistent care routine
- Regular medical follow-up
- Emotional support
- Lifestyle adaptations
Looking ahead
While melasma remains a challenging condition, advances in treatment options and understanding continue to improve outcomes. Working closely with healthcare providers, maintaining consistent care routines, and staying informed about new developments can help achieve optimal results in managing this common skin condition.
Remember that everyone’s experience with melasma is unique, and what works for one person may not work for another. The key is finding the right combination of treatments and lifestyle modifications that work best for your specific situation.