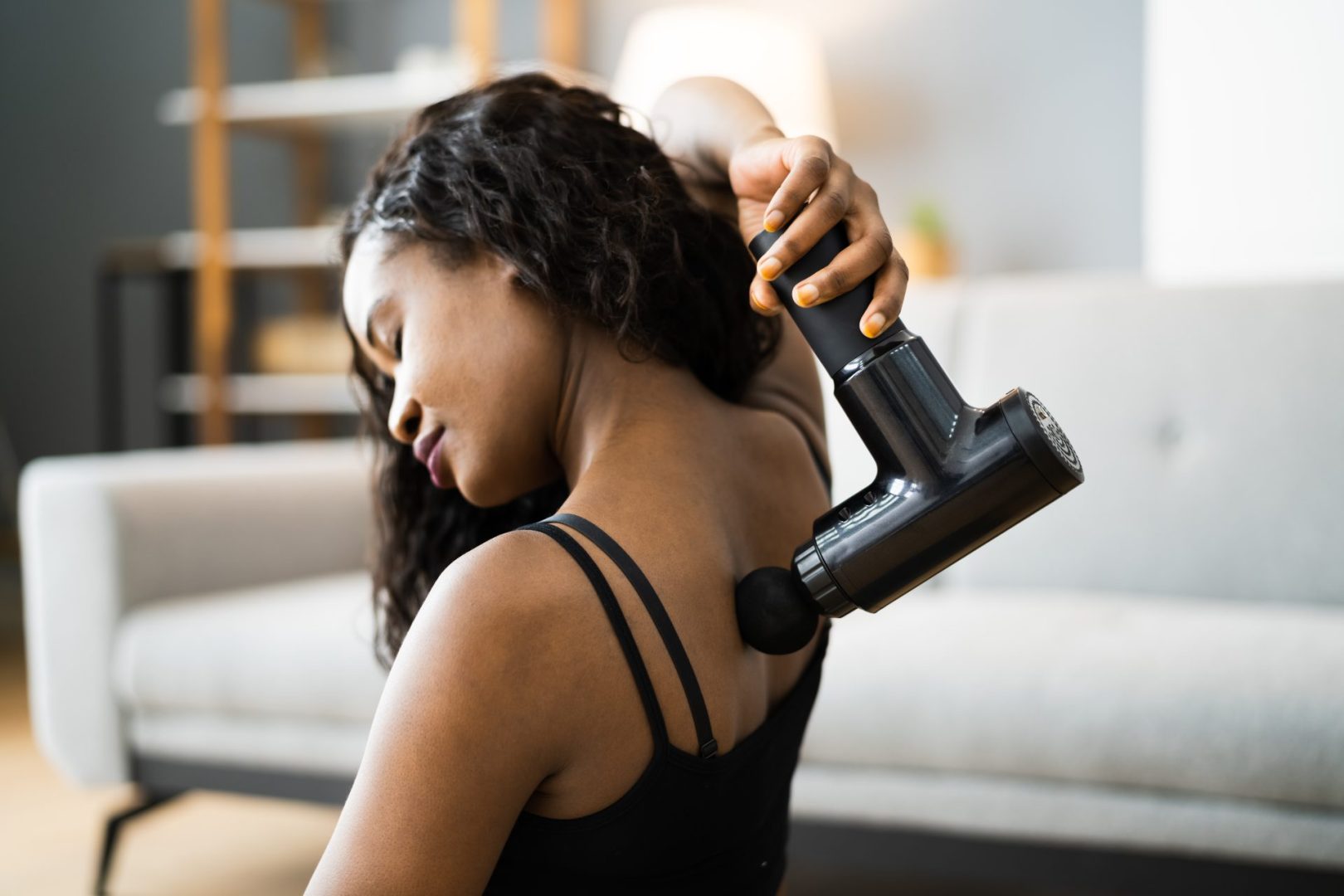
A study published in JAMA Otolaryngology has uncovered an unexpected risk of those trendy massage guns everyone loves using after workouts. While these devices can work wonders for sore muscles, using them in certain areas might literally make your head spin. This revelation comes at a time when massage guns have become increasingly popular among fitness enthusiasts and athletes, making it crucial for users to understand the potential risks associated with their use.
What’s actually happening in your inner ear
Remember those spinning cup rides at the carnival? Your inner ear works similarly, helping your brain figure out which way is up. Inside your ear are tiny calcium carbonate crystals, technically called otoconia, that help with balance, kind of like a natural level. These crystals play a vital role in your body’s balance system, helping your brain understand your position in space. The problem starts when those powerful massage gun vibrations shake these crystals loose, especially when you use the device near your head or neck. When dislodged, they can cause a variety of uncomfortable symptoms that might persist until properly treated.
Understanding BPPV and its impact
When these crystals get knocked out of place, you might experience something called benign paroxysmal positional vertigo or BPPV. Despite its complicated name, it basically means you get intense bouts of dizziness that make it feel like the room is spinning around you. Common symptoms include sudden spinning sensations, especially when moving your head, loss of balance or unsteadiness, nausea, and visual disturbances. While it sounds scary, doctors usually can fix it without surgery through a series of specific head movements.
The powerful percussive therapy that makes massage guns effective for muscle recovery can create vibrations strong enough to affect your inner ear structure. The frequency and intensity of these vibrations, particularly when used close to the head, can disturb the delicate balance system within your ears. The risk increases with higher intensity settings, prolonged use in sensitive areas, and direct contact with bones that connect to the skull. This is particularly concerning when the device is used too close to the ears or base of the skull.
Safe usage guidelines and alternatives
Medical experts now strongly advise against using massage guns anywhere near the head, neck, or spine, particularly the cervical region. This isn’t just about avoiding vertigo, it’s also about preventing potentially more serious issues like affecting blood vessels in your neck. Instead of using a massage gun for neck and head tension, healthcare professionals recommend gentler alternatives like stretching, professional massage therapy, heat therapy, or over-the-counter pain relievers when appropriate.
If you start experiencing dizziness after using a massage gun, don’t panic but don’t ignore it either. Stop using the device immediately and seek medical attention. BPPV is typically treatable through the Epley maneuver, a specific series of head movements that help reposition the displaced ear crystals. Your healthcare provider might also recommend vestibular rehabilitation therapy or modified head positions during daily activities to prevent recurrence.
The bottom line on massage gun safety
While massage guns can still be valuable recovery tools when used properly, it’s crucial to use them responsibly and understand their limitations. Focus on larger muscle groups like legs, back, and shoulders, staying well away from sensitive areas near the head and neck. If you’re dealing with persistent neck pain or tension, consult a healthcare provider who can recommend appropriate treatment options tailored to your needs.
As massage guns continue to grow in popularity, researchers are working to better understand their optimal use and potential risks. The goal is to enhance workout recovery without creating new health challenges. Stay informed about the latest research and guidelines, and always prioritize your health and safety when using any fitness or recovery equipment. Remember that when it comes to workout recovery, sometimes less is more, and it’s essential to incorporate various recovery methods rather than relying solely on any single tool or technique.