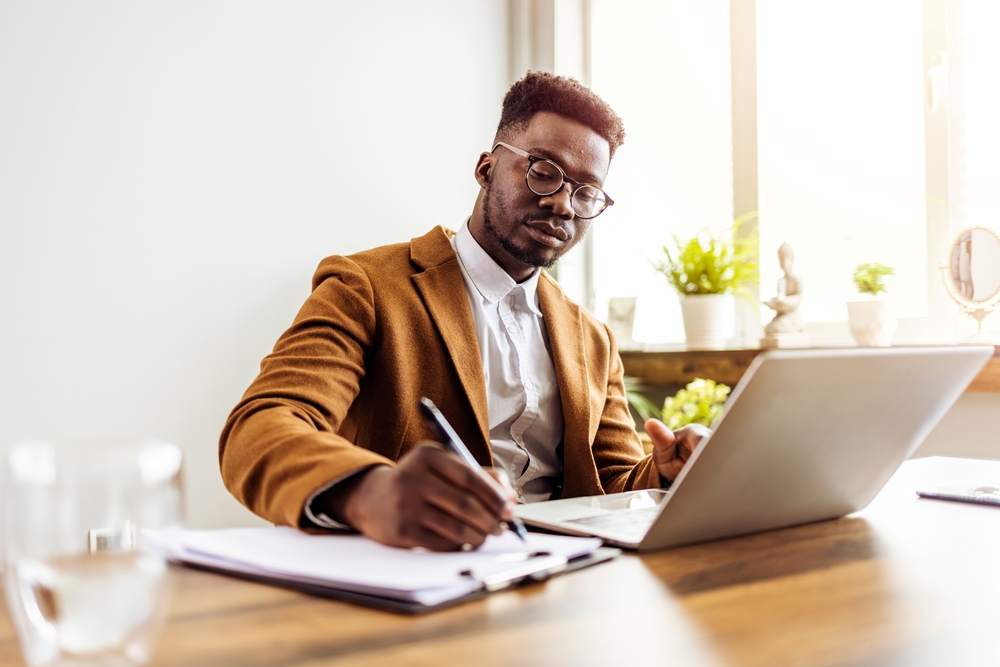
The transformation of remote work from a pandemic necessity to a permanent fixture in modern business has sparked a complex dialogue about compensation and workplace flexibility. As we venture deeper into 2025, employees find themselves navigating an increasingly challenging landscape where the comfort of home offices comes with a substantial price tag. Industry data reveals a troubling trend: remote workers face salary reductions ranging from 15% to 20% compared to their in-office colleagues, creating a significant financial divide in the workforce.
The shift toward remote work has fundamentally altered how businesses operate and how employees view their careers. Organizations worldwide are grappling with this new reality, attempting to balance operational efficiency with employee satisfaction. This transformation has led to unprecedented changes in workplace culture, team dynamics, and organizational structures.
The compensation conundrum
The growing disparity between remote and in-office salaries has emerged as a critical point of contention in today’s job market. Companies are strategically positioning remote work as a premium benefit, using it to justify reduced compensation packages. This approach has created a two-tier workforce where location dictates earning potential rather than skills or productivity. Current market analysis shows remote workers accepting substantial pay cuts, ranging from 5% to 15%, to maintain their work-from-home status.
The implications of this wage gap extend beyond immediate financial concerns. Industry experts warn about the long-term effects on career progression, retirement savings, and overall economic mobility. The practice of location-based salary adjustment has sparked debates about workplace equity and the true value of physical presence in professional settings.
Productivity paradox
Recent studies challenge the traditional notion that physical presence equals higher productivity. Remote workers consistently demonstrate equivalent or superior performance metrics compared to their office-bound counterparts. The tasks, skillsets, and workload remain identical regardless of location, yet compensation policies fail to reflect this reality. This disconnect raises questions about the long-term sustainability of location-based salary structures.
Technology adoption and digital collaboration tools have played a crucial role in maintaining and even enhancing productivity levels. Remote workers have developed new strategies for effective communication, project management, and team collaboration, often leading to innovative solutions that benefit the entire organization.
The economic impact
The financial implications of forced office returns combined with reduced wages extend beyond individual workers to affect entire economies. A comprehensive study in the UK focusing on millennial and Gen Z workers revealed startling statistics: the combination of lower wages and mandatory office attendance has resulted in a 150% decrease in productivity. This decline translates to an estimated $176 billion annual economic impact, serving as a cautionary tale for U.S. companies considering similar policies.
The broader economic consequences include increased urban-rural wage disparities, shifts in real estate markets, and changes in consumer spending patterns. Cities that once thrived on office worker populations are adapting to new economic realities, while suburban and rural areas experience unexpected growth and development.
Market dynamics and retention
Human resource experts predict a significant shift in the job market as companies grapple with remote work policies. Current data shows approximately 35% of American workers operating remotely, a slight decrease from the 46% peak during the pandemic. However, this stabilization suggests a permanent transformation in workplace norms rather than a temporary trend.
Companies that maintain rigid return-to-office policies while offering lower compensation for remote work face increasing challenges in talent acquisition and retention. The competitive landscape for skilled professionals has evolved, with workers now prioritizing flexibility and work-life balance alongside traditional benefits and compensation packages.
Future implications
Looking ahead, organizations face a critical decision point. The practice of offering reduced compensation for remote positions may trigger unintended consequences, including:
- Increased difficulty in talent acquisition
- Higher turnover rates
- Reduced employee engagement
- Diminished company loyalty
- Competitive disadvantage in the job market
- Potential legal challenges regarding pay equity
Industry analysts predict that 2025 will serve as a pivotal year for companies that have attempted to substitute competitive compensation with remote work flexibility. The sustainability of such practices remains questionable as employees become increasingly aware of their market value and workplace rights.
The future workplace will likely require a more nuanced approach to compensation and benefits. Progressive organizations are already exploring hybrid models that combine location flexibility with fair compensation structures. These innovative approaches could set new standards for workplace equity and employee satisfaction in the digital age.