Diabetes extends far beyond blood sugar management, affecting vital organs throughout the body. This chronic condition, affecting millions globally, requires vigilant monitoring and care to prevent serious complications. Understanding its wide-ranging effects helps individuals recognize early warning signs and take preventive action.
The impact spans multiple body systems, from cardiovascular health to nerve function, creating a complex web of potential health challenges that require careful attention and management.
Heart and blood vessel complications
The cardiovascular system bears significant strain from prolonged blood sugar elevation. High glucose levels damage blood vessels and nerves controlling the heart, increasing risks of serious conditions. Coronary artery disease develops as vessels narrow, while hypertension often accompanies diabetes, creating additional cardiovascular stress.
Warning signs include shortness of breath during routine activities, unexplained chest discomfort, and swelling in the feet or ankles. These symptoms require immediate medical attention, as they may indicate developing cardiovascular complications.
Critical kidney function
The kidneys’ filtering system faces particular challenges with diabetes. Excess blood sugar damages tiny renal blood vessels, potentially leading to diabetic nephropathy. Early detection through regular monitoring helps prevent progression to kidney failure.
Signs of kidney stress include persistent fatigue, difficulty concentrating, and changes in urination patterns. Swelling in the hands, feet, or face may indicate developing kidney problems that require medical evaluation.
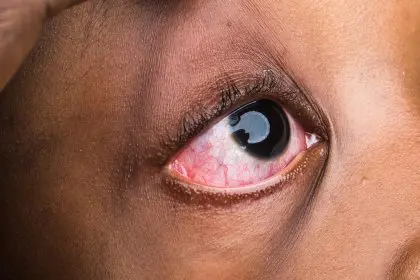
Vision and eye health
Diabetic retinopathy ranks among the leading causes of adult blindness. The condition develops when elevated blood sugar damages retinal blood vessels, causing leakage or abnormal growth. Early intervention can prevent permanent vision loss.
Changes in vision, including blurriness, floating spots, or difficulty seeing at night, warrant immediate medical attention. Regular eye examinations help detect and treat problems before they progress to severe stages.
Nervous system effects
Diabetic neuropathy affects nerves throughout the body, manifesting in various ways. Peripheral neuropathy causes tingling or numbness in extremities, while autonomic neuropathy impacts internal organ function, including digestion and blood pressure regulation.
Burning sensations, unexplained muscle weakness, or persistent digestive issues may indicate developing nerve damage. These symptoms often develop gradually but require attention to prevent worsening complications.
Skin manifestations
The skin often shows early signs of diabetes complications. Poor circulation and elevated blood sugar levels create increased vulnerability to infections and slow wound healing. Diabetic dermopathy may develop, causing distinctive skin changes.
Regular skin inspection helps identify potential problems early. Persistent wounds, unusual skin patches, or frequent infections require medical evaluation and appropriate treatment interventions.
Digestive system challenges
Diabetes affects the entire digestive tract, potentially causing gastroparesis, where the stomach empties too slowly. This condition creates nutritional challenges and requires careful dietary management.
Symptoms include frequent nausea, early satiety, and irregular digestion patterns. These challenges can impact nutrition and blood sugar control, necessitating specialized dietary approaches.
Oral health implications
Elevated blood sugar levels create an environment where oral bacteria thrive, increasing risks of gum disease and dental problems. Regular dental care becomes crucial for preventing serious complications.
Signs of oral health problems include persistent gum inflammation, unusual breath changes, and tooth mobility. Professional dental care helps manage these risks effectively.
Prevention strategies
While diabetes complications can seem daunting, proper management significantly reduces risks. Key preventive measures include:
Maintaining consistent blood sugar control through medication and lifestyle choices. Regular physical activity improves insulin sensitivity and overall health. Careful attention to diet, emphasizing whole foods and balanced nutrition. Regular medical checkups to monitor organ function and detect early problems.
Building support networks
Effective diabetes management requires comprehensive support systems. Healthcare providers, family members, and support groups all play vital roles in successful long-term care. Regular communication with healthcare teams helps ensure appropriate monitoring and timely intervention when needed.
Understanding diabetes’s multi-organ effects enables better recognition of warning signs and more effective preventive care. This knowledge, combined with proper medical support and lifestyle management, helps individuals maintain better health despite the challenges of diabetes.
This story was created using AI technology.