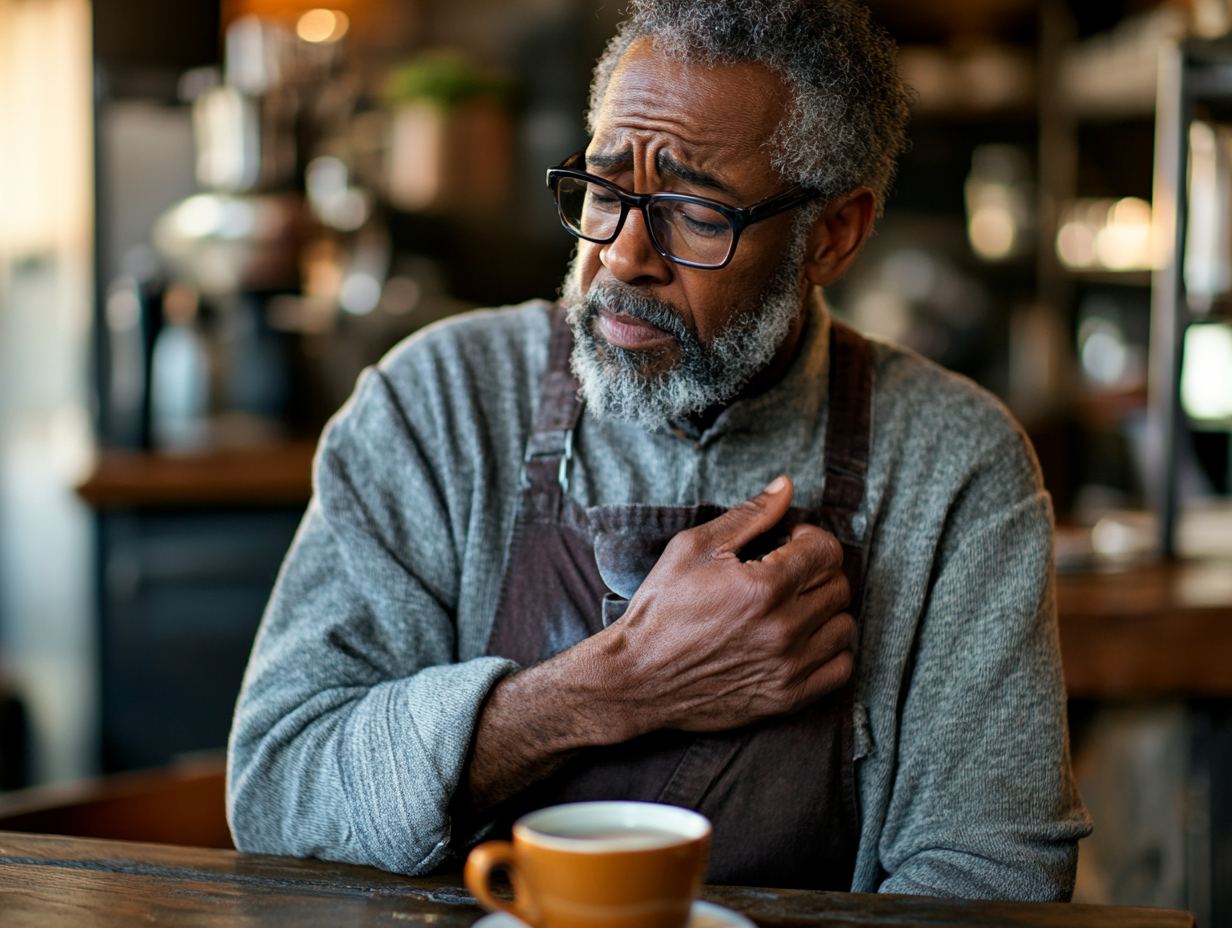
The artificial sweetener that’s been a staple in American households for decades is now facing fresh scrutiny, as emerging research casts a shadow over its supposed benefits. What was once hailed as a miracle solution for weight-conscious consumers has become the subject of concerning scientific findings that suggest a direct link between aspartame consumption and cardiovascular complications.
The sweet deception
In the pristine laboratories where mice scurry through mazes and scientists meticulously record data, a disturbing pattern has emerged. These tiny test subjects, consuming what amounts to the equivalent of three diet sodas per day, are showing signs of cardiovascular distress that could parallel human health outcomes. The revelation isn’t just about heart health – it’s about the complex web of metabolic changes that occur when we trick our bodies with artificial sweetness.
A metabolic mystery unfolds
The story begins in the mouth, where aspartame – a substance 200 times sweeter than sugar – triggers a cascade of physiological responses. Like a biochemical game of telephone, the sweetness signals travel through the body, prompting the pancreas to release insulin in anticipation of sugar that never arrives. This false alarm, repeated daily through diet sodas and sugar-free treats, may be setting the stage for a metabolic crisis.
The insulin connection
The latest research has unveiled a previously unknown mechanism: aspartame consumption triggers significant insulin spikes within mere minutes of ingestion. This isn’t a temporary blip on the metabolic radar – it’s a persistent disruption that could lead to chronic hyperinsulinemia, a condition where the body maintains abnormally high insulin levels. The implications stretch far beyond simple sugar processing, potentially affecting everything from fat storage to arterial health.
From sweetener to cardiovascular threat
The most alarming discovery centers on atherosclerosis – the buildup of fatty deposits in arterial walls. Through careful observation and analysis, researchers have documented how regular aspartame consumption may accelerate this process. The artificial sweetener appears to activate inflammatory pathways that encourage plaque formation, essentially fast-tracking the very cardiovascular problems many consumers hope to avoid by choosing sugar-free alternatives.
The hidden cost of zero calories
The illusion of a free pass – zero calories, zero sugar, zero consequences – is beginning to crumble under the weight of scientific evidence. While the FDA continues to classify aspartame as safe for consumption, the mounting research suggests a more nuanced reality. The trade-off between immediate caloric reduction and long-term cardiovascular health has become increasingly difficult to ignore.
A paradigm shift in dietary thinking
Modern nutrition science is moving away from simple calorie counting toward a more sophisticated understanding of how different substances interact with our bodies. The aspartame story exemplifies this shift, highlighting how a substance can be calorie-free yet still profoundly affect our metabolism and cardiovascular system.
The path forward
The implications of this research extend beyond individual health choices to broader questions about food policy and public health recommendations. As our understanding of artificial sweeteners evolves, so too must our approach to dietary guidelines and consumer education.
Current research indicates several key areas of concern:
The speed at which aspartame triggers insulin response suggests immediate physiological effects that could accumulate over time. The body’s insulin response to artificial sweeteners appears more complex than previously understood, with potential long-term consequences for metabolic health. The relationship between artificial sweetener consumption and cardiovascular disease risk factors presents a compelling case for reevaluating dietary recommendations.
Rethinking artificial sweeteners
The challenge now lies in translating these findings into practical dietary guidance. While complete avoidance of artificial sweeteners might not be necessary for everyone, the research suggests that moderation and awareness are crucial. The focus should shift toward embracing whole foods and natural ingredients while being mindful of both sugar and artificial sweetener consumption.
A balanced approach
The path to better health may lie in returning to fundamentals: whole foods, natural ingredients, and mindful eating practices. Rather than seeking quick fixes or artificial alternatives, consumers might benefit from developing a more nuanced understanding of nutrition and its impact on long-term health.
The emergence of this research marks a critical moment in our understanding of artificial sweeteners and their impact on human health. As the scientific community continues to unravel the complex relationships between these substances and our cardiovascular system, consumers face important decisions about their dietary choices.
The story of aspartame serves as a reminder that scientific understanding is constantly evolving, and what seems like a simple solution to dietary concerns may have unexpected long-term consequences. As we move forward, the emphasis should be on developing a deeper understanding of how our food choices affect our health, rather than seeking quick fixes or artificial alternatives.
This moment in nutritional science calls for a thoughtful recalibration of our approach to sweeteners, both natural and artificial. The goal isn’t to create panic or completely eliminate certain ingredients, but rather to foster a more nuanced understanding of their effects on our bodies and make informed choices accordingly.