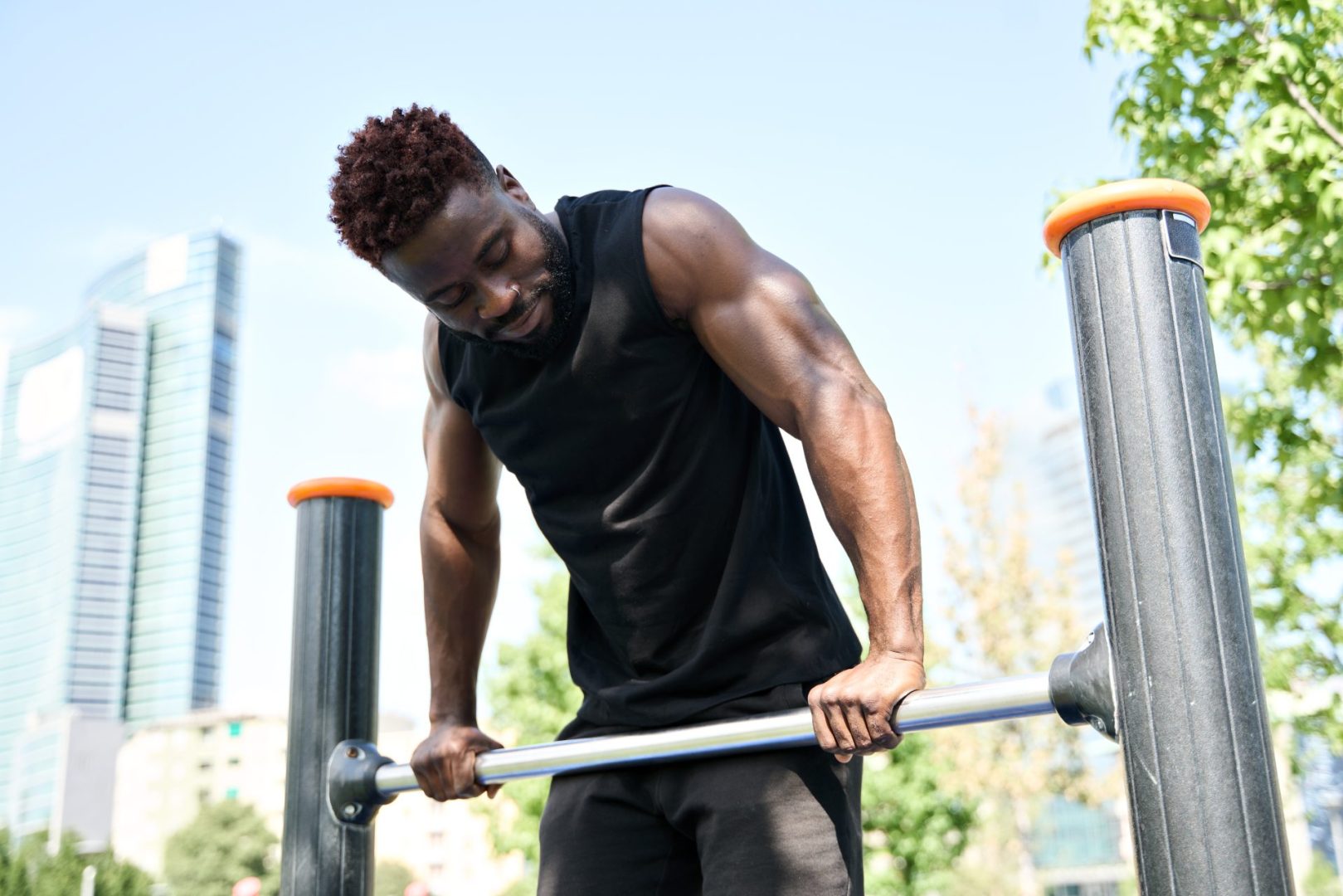
Celebrities and fitness enthusiasts alike have rediscovered the transformative power of calisthenics—a training method that uses your own body weight as resistance. This ancient approach to fitness has made a dramatic comeback, with everyone from military specialists to Hollywood actors embracing these fundamental movements.
The appeal lies in both simplicity and effectiveness. Without requiring specialized equipment or dedicated gym space, calisthenics offers accessibility that few other training methods can match. More importantly, these exercises engage multiple muscle groups simultaneously, creating efficient workouts that maximize results in minimal time.
For those seeking defined muscles, improved strength, and enhanced athletic ability, these fundamental movements provide the foundation for total body transformation. Their scalability makes them appropriate for complete beginners and elite athletes alike.
Why bodyweight training outperforms machines
The fitness industry constantly promotes new equipment and complicated training systems, yet many physique athletes rely primarily on simple bodyweight exercises for maintaining their impressive builds. This seeming contradiction has scientific backing.
Calisthenic exercises create greater neuromuscular demands than machine-based alternatives. While machines isolate specific muscles along fixed movement paths, bodyweight exercises require stabilization from numerous muscle groups simultaneously. This integration develops functional strength that transfers directly to real-world activities.
Research published in the Journal of Strength and Conditioning Research found that participants performing bodyweight training experienced greater activation in core muscles compared to those using resistance machines, even when targeting the same primary muscle groups. This additional engagement explains the more comprehensive development seen with calisthenics.
Beyond muscle development, these movements improve coordination, balance, and body awareness—qualities that enhance athletic performance across all activities. The natural movement patterns also reduce injury risk compared to loaded exercises that can place excessive stress on joints when performed improperly.
Push-ups: The ultimate upper body sculptor
- The humble push-up stands as perhaps the most effective upper body exercise ever created. This seemingly simple movement simultaneously targets your chest, shoulders, triceps, and core in ways that few exercises can match.
The beauty of push-ups lies in their infinite variability. By simply adjusting hand positioning, elevation, or tempo, you can completely transform the exercise’s focus. Diamond push-ups shift emphasis to the triceps, wide-grip versions target the chest more directly, and elevated feet increase shoulder activation.
For beginners struggling with full push-ups, starting on an incline reduces the resistance while maintaining proper movement patterns. As strength improves, gradually decrease the incline until performing standard push-ups becomes manageable.
Advanced athletes can progress to explosive variations like clapping push-ups or add resistance with weighted vests. Alternatively, shifting to one-arm progressions dramatically increases difficulty while improving stabilization through the core and shoulder girdle.
The metabolic demand of push-ups makes them excellent for both strength building and fat burning. When performed in high-volume circuits, they elevate heart rate while continuing to challenge muscular endurance, creating the perfect environment for body composition changes.
Back development without equipment
- Nothing builds impressive back width and thickness quite like the classic pull-up. This cornerstone movement creates the V-shaped torso associated with athletic physiques while strengthening the biceps, forearms, and core.
Many beginners find pull-ups initially challenging, but progressive approaches make them accessible to everyone. Starting with assisted variations using resistance bands or partner assistance allows proper technique development before handling full bodyweight.
Hand positioning dramatically changes which muscles receive emphasis. Wide grips target the upper and outer lats, creating width, while closer grips increase bicep involvement and target the lower lats for thickness.
The eccentric (lowering) phase offers particular benefits for those building strength. Controlling your descent for 3-5 seconds creates significant muscle fiber recruitment even for those who cannot yet perform full pull-ups.
For advanced athletes, weighted pull-ups provide continuous progression. Adding resistance via weighted vests or belts ensures continued strength development, while uneven grips or towel pull-ups increase grip demands for greater forearm development.
Bodyweight squats: Lower body transformation
- Squats represent the foundation of lower body development, and their bodyweight version offers remarkable benefits without loading the spine. This functional movement patterns strengthens quadriceps, hamstrings, glutes, and core while improving mobility.
Proper form remains crucial for maximum benefit. Keeping weight in the heels, maintaining an upright chest, and achieving appropriate depth ensures full muscle recruitment while protecting the knees and lower back from unnecessary stress.
For beginners, box squats provide a confidence-building progression. Squatting to a bench or chair before standing creates a safety net while developing proper movement patterns. As confidence grows, gradually reduce the height until achieving full range of motion.
Advanced athletes can progress to Bulgarian split squats, where the rear foot elevates on a bench. This unilateral variation increases the demand on each leg individually while improving balance and addressing strength asymmetries between sides.
Jumping variations add explosive power development critical for athletic performance. Jump squats increase power output while elevating heart rate, making them excellent for both performance enhancement and calorie burning during high-intensity intervals.
Plank variations: Core strength beyond aesthetics
- While often associated with abdominal definition, planks develop fundamental core strength that supports every other movement pattern. This isometric exercise creates tension throughout the entire midsection, including deep stabilizing muscles often missed by traditional ab exercises.
The standard forearm plank establishes baseline core endurance. Maintaining a rigid position from shoulders to ankles for increasing duration builds the foundation for more advanced variations while teaching proper bracing techniques.
Side planks specifically target the obliques and quadratus lumborum, muscles essential for rotational movements and lateral stability. These muscles contribute significantly to waist definition while preventing lower back issues during lifting and sports.
Dynamic variations like plank shoulder taps and plank hip dips introduce controlled movement while maintaining stability. These progressions bridge the gap between static holds and dynamic core activities required in sports and daily life.
For maximum intensity, long-lever planks increase the challenge by extending the resistance arm. Reaching arms forward from the standard position dramatically increases the demand on all core muscles, particularly the rectus abdominis responsible for the coveted “six-pack” appearance.
Dips: The missing link for upper body definition
- Triceps dips complete the upper body development started by push-ups and pull-ups. This movement primarily targets the triceps—which comprise approximately 70% of upper arm mass—while engaging the chest, shoulders, and core.
Beginners can start with bench dips, keeping feet on the floor for support while lowering and raising the body using arm strength. This scaled version maintains the fundamental movement pattern while reducing the percentage of bodyweight being moved.
As strength improves, parallel bar dips provide the full challenge. Keeping the torso relatively upright emphasizes triceps development, while leaning forward shifts focus toward the chest for balanced development across pushing muscles.
Russian dips represent an advanced progression, where practitioners lower past the parallel position to touch the upper arms to the bars. This extended range of motion creates exceptional stretch under load, stimulating maximum muscle development.
Adding weight via vests or belts ensures continued progression for strength athletes, while slowing the tempo—particularly during the lowering phase—increases time under tension for hypertrophy-focused individuals seeking maximum muscle growth.
Creating your bodyweight transformation plan
Implementing these exercises effectively requires strategic programming rather than random application. For beginners, mastering form with appropriate progressions takes priority over high volume or intensity.
A balanced approach involves full-body training 3-4 times weekly, including all movement patterns in each session. This frequency provides sufficient stimulus for adaptation while allowing adequate recovery between workouts.
A simple starting template might include:
3 sets of push-ups (8-15 reps based on ability)
3 sets of assisted pull-ups or inverted rows (8-12 reps)
3 sets of bodyweight squats (15-20 reps)
3 sets of planks (30-60 second holds)
3 sets of bench dips (10-15 reps)
Rest periods of 60-90 seconds between sets maintain efficiency while allowing sufficient recovery for quality movement. As adaptation occurs, increase difficulty through advanced variations rather than merely adding repetitions beyond productive ranges.
For those seeking fat loss alongside muscle definition, incorporating these movements into circuit formats elevates heart rate while maintaining muscle engagement. Performing each exercise for 30-45 seconds with minimal rest between movements creates metabolic demand that accelerates calorie burning.
Advanced athletes might implement specialized training blocks focusing on specific qualities like strength, endurance, or power. Periodizing these emphasis changes prevents plateaus while continuing progression across all athletic qualities.
Nutrition fundamentals for visible results
While these exercises create the stimulus for physical transformation, nutrition determines whether muscle definition becomes visible. Without appropriate dietary support, even the most effective training program produces limited visual results.
Adequate protein intake supports muscle repair and growth following training stress. Aim for 0.7-1 gram per pound of bodyweight daily from quality sources including lean meats, dairy, eggs, and plant-based options like legumes and tofu.
Controlling overall calorie intake relative to expenditure determines whether body fat decreases to reveal developed muscles. Creating a modest caloric deficit through combination of increased activity and moderate dietary restriction produces sustainable fat loss.
Timing carbohydrate intake around workouts supports performance and recovery while minimizing fat storage. Consuming the majority of daily carbohydrates before and after training sessions provides energy when needed most.
Hydration status significantly impacts both performance and appearance. Adequate water intake supports cellular function during exercise while reducing water retention that can mask muscle definition.
The journey toward a transformed physique through calisthenics requires consistency above all else. These fundamental movements have sculpted impressive physiques for centuries, from ancient Greek athletes to modern fitness icons. By mastering these essential exercises and supporting your efforts with appropriate nutrition, you’ll develop functional strength and visible muscle definition without expensive equipment or complicated routines.