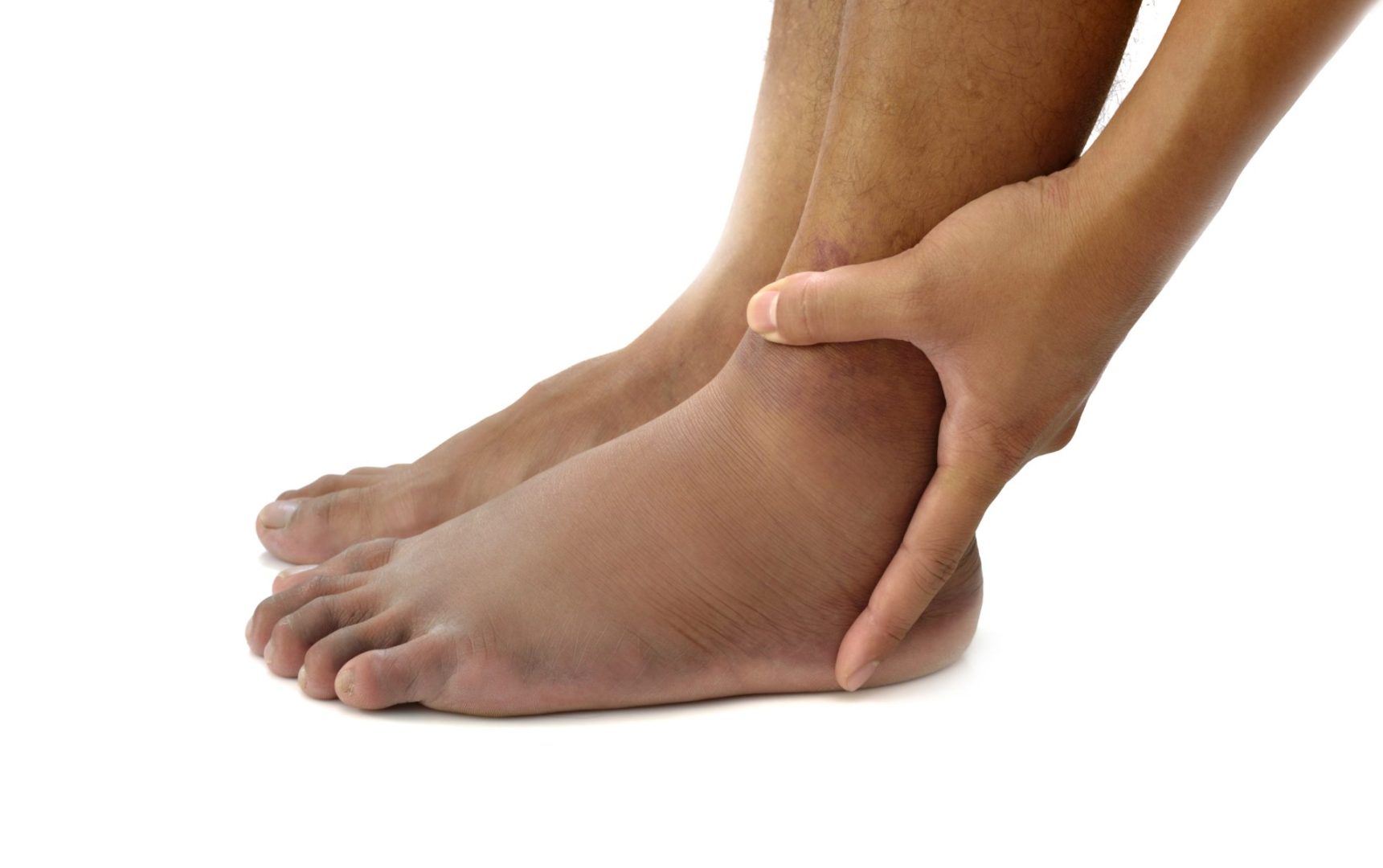
That uncomfortable tightness in your shoes at the end of a long day might seem like just another minor annoyance, but persistent foot swelling can sometimes signal something far more serious than fatigue or ill-fitting footwear. Medical experts increasingly recognize that our extremities often serve as early warning systems for significant health issues developing elsewhere in the body.
When your heart struggles to keep up
One of the most concerning causes of foot swelling relates to cardiovascular health. When the heart cannot efficiently pump blood throughout the body, fluid often accumulates in the lower extremities due to gravity’s relentless pull. This condition, congestive heart failure, affects nearly 6.2 million Americans and frequently manifests first as swelling in both feet that worsens as the day progresses.
Heart-related swelling typically affects both feet equally and often creates a distinctive pattern. 1) Pressing a finger into the swollen area might leave an indentation that slowly fills back in—a phenomenon doctors call “pitting edema.” This occurs because excess fluid has accumulated in the tissues rather than being properly circulated back to the heart.
Other warning signs accompanying heart-related foot swelling include unexpected fatigue with minimal exertion, shortness of breath (particularly when lying flat), and a persistent cough that worsens at night. The combination of these symptoms warrants prompt medical evaluation, as early intervention can significantly improve outcomes for heart failure patients.
Many people mistakenly attribute such swelling to aging or weight gain, potentially missing this crucial early warning. Regular monitoring of any changes in swelling patterns, especially when they occur alongside other cardiovascular symptoms, can literally become a life-saving habit.
Your kidneys’ distress signals
The kidneys serve as the body’s primary filtration system, carefully balancing fluids and removing waste products from the bloodstream. When these vital organs begin functioning below capacity, their reduced filtering ability often manifests as fluid retention throughout the body, frequently beginning in the feet and ankles.
Unlike heart-related swelling that typically worsens throughout the day, kidney-associated edema often appears most pronounced upon waking. 2) This morning swelling occurs because the horizontal position during sleep allows fluid to distribute more evenly throughout the body rather than pooling in the lower extremities.
Changes in urination patterns frequently accompany kidney-related swelling—either noticeably increased nighttime urination or, conversely, reduced urine output despite normal fluid intake. Many patients also report a metallic taste in the mouth, unexpected fatigue, or itchy skin that doesn’t improve with moisturizers.
Kidney disease often develops silently, with symptoms appearing only after significant damage has occurred. This makes recognizing early warning signs like foot swelling particularly crucial for those with risk factors such as diabetes, hypertension, or a family history of kidney problems. Regular screening becomes essential for these high-risk individuals.
Liver issues revealing themselves
The liver performs hundreds of essential functions, including producing albumin—a protein that helps maintain proper fluid balance throughout the body’s tissues. When liver function declines due to conditions like cirrhosis, hepatitis, or fatty liver disease, reduced albumin production can lead to fluid leaking from blood vessels into surrounding tissues.
Liver-related swelling often affects both the feet and abdomen simultaneously. 3) In advanced cases, this abdominal fluid accumulation (called ascites) may become visibly noticeable as increasing waistline expansion that doesn’t correspond to weight gain elsewhere in the body.
Other telltale signs of liver involvement include yellowing of the skin or whites of the eyes (jaundice), unexplained bruising or bleeding, chronic fatigue, and darkened urine. The combination of these symptoms with persistent foot swelling warrants thorough medical evaluation to determine the underlying liver condition.
The concerning aspect of liver-related swelling involves its gradual onset—many patients report retrospectively noticing their shoes becoming tighter over months rather than days, potentially delaying diagnosis. This slow progression makes regular self-assessment particularly important for early detection.
Blood flow problems in your veins
Unlike the previous conditions affecting both feet equally, venous insufficiency and blood clotting disorders often cause asymmetrical swelling affecting primarily one leg or foot. This one-sided presentation should always trigger heightened concern, particularly when accompanied by pain, warmth, or redness.
Venous insufficiency occurs when the one-way valves in leg veins deteriorate, allowing blood to pool rather than efficiently returning to the heart. 4) This pooling creates pressure that forces fluid into surrounding tissues, causing swelling that typically worsens with prolonged standing and improves with elevation.
A more urgent concern arises with deep vein thrombosis (DVT)—blood clots forming in the deep veins, usually in the legs. This potentially life-threatening condition requires immediate medical attention, as clots can break free and travel to the lungs, causing a pulmonary embolism. Warning signs include sudden swelling (usually in one leg), pain or tenderness, and skin that feels warm to the touch or appears reddened over the affected area.
Risk factors for these venous conditions include prolonged immobility (like during long flights), recent surgery, pregnancy, hormonal medications, and family history. Awareness of these risk factors helps individuals recognize when foot swelling might require urgent rather than routine evaluation.
When your lymphatic system falters
The lymphatic system works silently alongside your circulation, collecting excess fluid from tissues and returning it to the bloodstream. When this system becomes damaged or blocked, lymphedema develops—characterized by persistent swelling that typically doesn’t improve with elevation alone.
Unlike other causes of edema, lymphedema often creates a distinctive appearance and texture. 5) The affected limb may feel unusually heavy, and the skin might appear thicker or develop a peau d’orange (orange peel) texture due to fluid accumulation in the tissues beneath the skin surface.
Primary lymphedema stems from congenital issues with lymphatic development, while secondary lymphedema more commonly results from damage to lymph nodes or vessels. Cancer treatments represent a significant cause of secondary lymphedema, particularly when lymph nodes are removed during surgery or damaged during radiation therapy.
Early intervention proves crucial with lymphedema, as the condition typically worsens progressively without appropriate management. Specialized compression garments, manual lymphatic drainage massage, and exercise programs tailored to lymphedema can significantly improve quality of life for affected individuals.
When to seek immediate medical attention
While some degree of foot swelling after prolonged standing or during pregnancy might be expected, certain presentations warrant urgent evaluation. Seek emergency care for sudden, severe swelling in one leg, especially with pain, warmth, redness or tenderness. Swelling accompanied by difficulty breathing or chest pain requires immediate attention, as does swelling following a long period of immobility, such as a long flight or car ride. Be particularly concerned about swelling with fever or unexplained weight gain, or swelling that doesn’t improve after several days of home treatment.
Home management strategies
For milder forms of foot swelling without concerning features, several home approaches may help reduce discomfort:
Regular elevation remains one of the most effective strategies, ideally raising feet above heart level for 30 minutes several times daily. This position uses gravity to help excess fluid drain from the extremities naturally.
Compression stockings provide external pressure that helps prevent fluid accumulation, though proper fitting proves essential for effective results. These garments come in various compression levels, with higher pressures requiring professional fitting.
Salt reduction helps minimize fluid retention throughout the body, as excess sodium causes the body to hold onto water. Reading food labels and preparing meals at home makes managing sodium intake considerably easier.
Staying physically active promotes circulation that helps prevent fluid accumulation. Even simple ankle exercises or walking short distances regularly can make a significant difference in reducing swelling.
Weight management reduces stress on the circulatory system and improves overall cardiovascular health, potentially addressing one underlying factor contributing to fluid retention in many individuals.
The importance of professional evaluation
While home management strategies help with minor swelling, persistent or recurrent foot edema warrants professional medical evaluation to identify potential underlying causes. A comprehensive assessment typically includes:
Detailed medical history focusing on when swelling occurs, associated symptoms, and potential risk factors for various conditions causing edema. This context helps physicians narrow down possible causes.
Physical examination assessing the pattern, distribution, and characteristics of swelling, including whether it creates pitting when pressed and whether it affects one or both extremities.
Laboratory tests measuring kidney and liver function, along with markers of heart function and inflammation that might indicate underlying disease processes.
Imaging studies such as ultrasound to evaluate blood flow in the legs, echocardiogram to assess heart function, or more specialized tests depending on suspected underlying causes.
The diagnostic process sometimes requires patience, as identifying the root cause of foot swelling may involve ruling out multiple possibilities through sequential testing rather than finding an immediate answer.
Long-term outlook and management
For many individuals, foot swelling represents an early warning sign that, when properly addressed, leads to successful management of underlying conditions before they progress to advanced stages. This early intervention often significantly improves long-term outcomes.
Regular monitoring becomes essential for anyone with a history of foot swelling, particularly those with identified underlying conditions. Keeping a simple log noting when swelling occurs, its severity, and associated factors helps healthcare providers track patterns over time.
Consistency with prescribed treatments—whether medications, compression therapy, dietary modifications, or specialized exercise programs—makes the critical difference between successful management and progressive worsening for many conditions causing foot edema.
The seemingly simple symptom of swollen feet often serves as the body’s early warning system for serious health conditions that might otherwise remain undetected until more advanced stages. By understanding these connections and recognizing when foot swelling warrants medical attention rather than just elevation, individuals can potentially identify significant health issues at their most treatable stages.