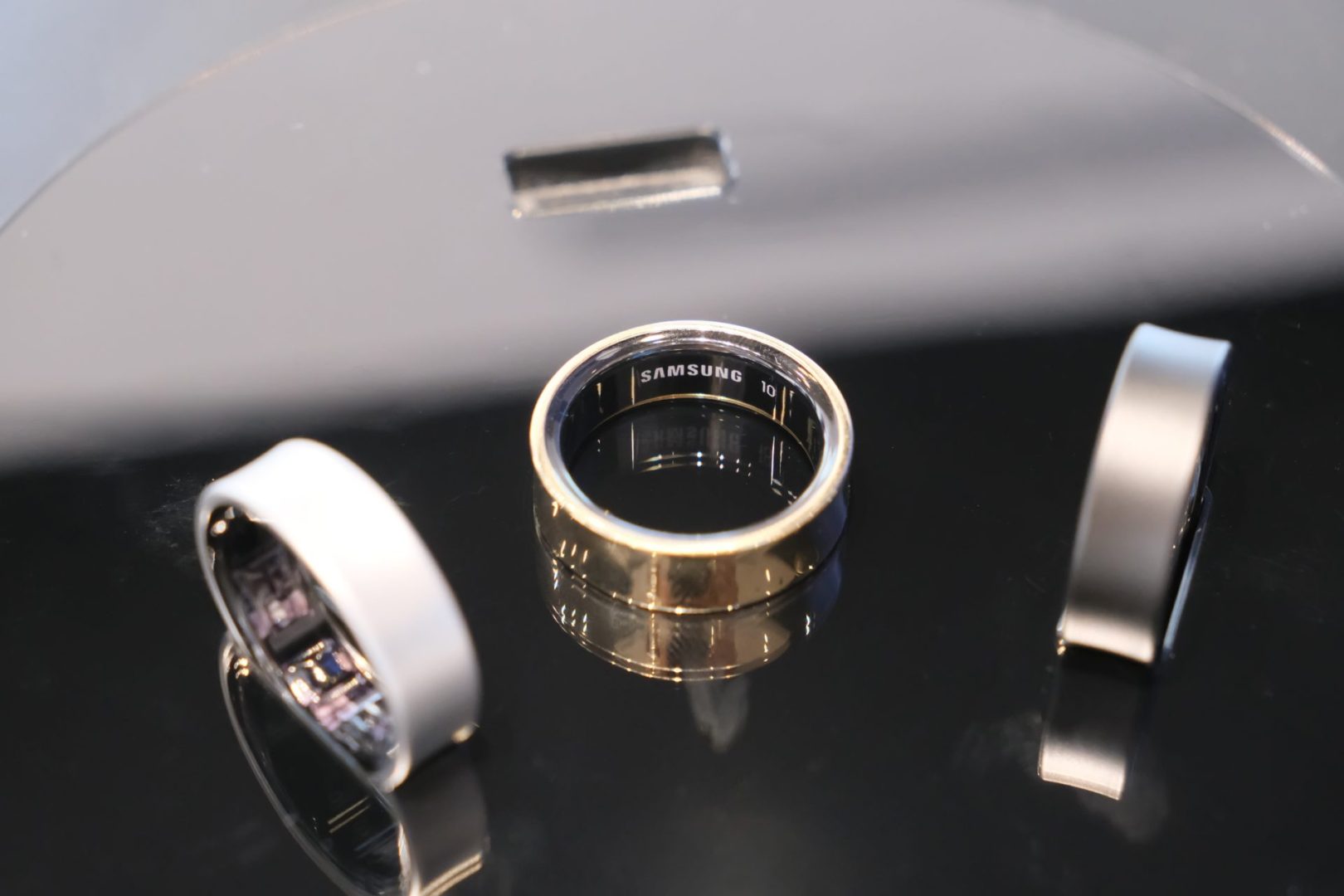
The modern landscape of reproductive health has evolved dramatically in recent years, with innovative technologies reshaping how people approach birth control. Among these advancements, a remarkable smart ring has emerged as a compelling option for those seeking non-hormonal alternatives to traditional contraceptive methods.
The rise of wearable reproductive technology
As social media feeds fill with engagement announcements and baby photos, many individuals in their thirties and beyond find themselves exploring birth control options aligned with their current life plans. The smart ring technology represents a significant departure from conventional approaches, combining sophisticated health tracking with fertility awareness in a sleek, wearable device.
This compact tracker collects comprehensive health data through embedded sensors that monitor vital metrics including heart rate, heart rate variability, body temperature, blood oxygen levels, and physical activity. What truly distinguishes this technology is its integration with fertility tracking applications designed to help users make informed decisions about their reproductive health.
The ring’s advanced temperature monitoring capabilities make it particularly valuable for those interested in fertility awareness methods. By automatically tracking subtle body temperature changes throughout the menstrual cycle, the device eliminates much of the manual work traditionally associated with these approaches.
How temperature-based fertility tracking works
Fertility awareness methods rely on understanding the body’s natural reproductive cycle to determine fertility windows. Among the most reliable indicators is basal body temperature (BBT), which typically increases slightly after ovulation occurs.
The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention notes varying effectiveness rates for different birth control methods. While hormonal implants show a failure rate of merely 0.1%, traditional fertility awareness methods range from 2% to 23% failure rates depending on consistency and proper implementation.
The smart ring technology addresses consistency challenges by automatically collecting continuous temperature data throughout the night when the body is at rest. This information synchronizes with companion applications that analyze the data and identify fertility patterns with greater precision than manual tracking methods.
After detecting the slight temperature rise that follows ovulation, the application can predict fertility windows with increasing accuracy over time as it learns individual patterns. Days identified as non-fertile appear marked in green, while potentially fertile periods appear in red, signaling when additional precautions should be taken to prevent pregnancy.
Understanding the science of fertility windows
The effectiveness of any fertility awareness method depends on a clear understanding of how conception occurs. Ovulation represents the phase in the menstrual cycle when an egg releases from the ovaries, becoming available for fertilization during a relatively brief period—typically less than 24 hours.
However, sperm can survive within the female reproductive tract for up to five days under favorable conditions. This biological reality creates a fertility window spanning approximately six days each cycle: the five days preceding ovulation plus the ovulation day itself.
Traditional tracking methods require diligent monitoring of multiple fertility indicators, including body temperature, cervical mucus changes, and cycle timing. The smart ring technology simplifies this process by automating temperature tracking and using algorithms to interpret the data.
Effectiveness comparisons with other methods
Historical criticisms of fertility awareness methods often center on their reliance on consistent user implementation. However, technological advancements have significantly improved accessibility and effectiveness rates.
According to research published in medical journals, modern fertility awareness applications can achieve effectiveness rates exceeding 93% with typical use, potentially reaching 98% with perfect adherence to guidelines. These figures compare favorably with other non-hormonal methods like condoms, which show typical use effectiveness around 87%.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists acknowledges that fertility awareness methods can achieve 95% to 99% effectiveness with perfect use. The automated data collection capabilities of smart rings potentially reduce human error factors that often decrease effectiveness rates in traditional methods.
The personal experience factor
Many users report positive experiences with smart ring technology for birth control purposes. The automatic data synchronization and user-friendly interfaces make the approach more accessible than traditional fertility awareness methods requiring manual temperature taking and charting.
The non-invasive nature of the technology appeals particularly to individuals seeking alternatives to hormonal contraceptives. Users commonly cite benefits including:
Absence of hormonal side effects that sometimes accompany birth control pills, patches, or injections Deeper insights into personal health patterns beyond fertility tracking Greater body awareness and understanding of individual cycle variations No interruptions during intimate moments, unlike barrier methods
For those with regular menstrual cycles and committed to following application guidelines, the technology can provide an effective birth control option without physical or hormonal interventions.
Considerations before choosing this method
While smart ring technology offers numerous advantages, several important factors warrant consideration before selecting this approach to birth control.
First, effectiveness relies heavily on consistent use and adherence to application guidelines. Users must commit to wearing the ring consistently during sleep hours and following recommendations regarding fertility windows.
Second, this method works best for individuals with relatively regular menstrual cycles. Those experiencing significant cycle variations may find predictions less reliable, potentially requiring longer learning periods for the algorithm.
Third, the approach provides no protection against sexually transmitted infections, unlike barrier methods such as condoms. Individuals concerned about STI prevention should consider supplementary protection methods.
Fourth, the initial investment cost exceeds that of some traditional contraceptive methods. The smart ring technology typically requires purchasing both the hardware device and subscribing to accompanying software services.
Finally, lifestyle factors including alcohol consumption, illness, or irregular sleep patterns can potentially affect temperature readings, requiring users to mark these occasions within the application for accurate analysis.
Finding the right birth control fit
Selecting appropriate birth control represents a deeply personal decision influenced by individual health factors, lifestyle considerations, and reproductive goals. The smart ring technology offers a compelling option for those seeking non-hormonal, non-invasive approaches aligned with modern technological lifestyles.
However, no single birth control method suits everyone perfectly. Alternative options range from highly effective long-term solutions like hormonal implants and IUDs to barrier methods, hormonal pills, patches, rings, and traditional fertility awareness approaches.
The ideal method balances effectiveness requirements with personal comfort, health considerations, and lifestyle compatibility. Healthcare providers can offer valuable guidance in navigating these choices based on medical history and individual circumstances.
The future of reproductive technology
The integration of wearable technology with reproductive health represents just the beginning of a technological revolution in fertility management. As algorithms improve and devices incorporate additional biomarkers, precision in fertility prediction likely will continue advancing.
Future iterations may potentially incorporate hormonal measurements, enhanced cycle prediction capabilities, and more sophisticated pattern recognition. These developments promise to further empower individuals with detailed insights into their reproductive health.
The growing market for non-hormonal contraceptive options reflects increasing consumer interest in body-aware approaches to reproductive health. As research continues advancing understanding of fertility indicators, technology-assisted methods will likely continue gaining popularity among those seeking personalized approaches to birth control.
For now, the smart ring technology offers a meaningful step forward in making fertility awareness methods more accessible and potentially more reliable for those interested in this approach to reproductive health management.