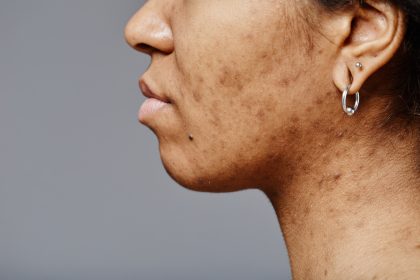
Acne affects approximately 50 million Americans annually, creating not just physical blemishes but emotional distress that can impact confidence and quality of life. While countless treatments promise clear skin, vitamin C has emerged as a multifaceted solution that addresses multiple aspects of acne simultaneously. This powerful antioxidant offers a gentler alternative to harsh chemical treatments while providing comprehensive skin benefits that extend far beyond simple blemish control.
The relationship between vitamin C and skin health involves complex biochemical processes that influence inflammation, collagen production, and cellular repair mechanisms. Understanding how this essential nutrient works at the cellular level explains why it has become a cornerstone ingredient in both professional dermatology treatments and over-the-counter skincare products designed for acne management.
Unlike many acne treatments that focus on a single mechanism, vitamin C provides multiple therapeutic benefits that work synergistically to improve overall skin health while specifically targeting the various factors that contribute to acne development and persistence. This comprehensive approach makes vitamin C particularly valuable for individuals dealing with both active breakouts and the lasting effects of previous acne episodes.
Vitamin C reduces inflammatory acne responses
Acne development involves significant inflammatory processes that create the redness, swelling, and pain associated with active breakouts. Vitamin C’s potent anti-inflammatory properties help calm these inflammatory responses, reducing the severity and duration of acne lesions while preventing the cascade of inflammatory reactions that can lead to scarring and hyperpigmentation.
The antioxidant activity of vitamin C neutralizes free radicals that contribute to inflammatory damage in acne-affected skin. These unstable molecules, produced during the body’s immune response to acne bacteria, can cause additional tissue damage beyond the initial bacterial infection. By scavenging these harmful compounds, vitamin C helps limit inflammatory damage and supports faster healing.
Vitamin C also modulates the production of inflammatory mediators, including cytokines and prostaglandins, that drive the inflammatory response in acne lesions. This regulation helps prevent the excessive inflammation that can transform minor comedones into painful, inflamed cysts that are more likely to leave permanent marks.
The anti-inflammatory effects of vitamin C extend beyond active lesions to help calm overall skin irritation and sensitivity common in acne-prone individuals. This systemic calming effect can reduce the reactive responses that often worsen acne when skin becomes irritated by environmental factors or other skincare products.
Collagen production accelerates scar healing
Acne scars develop when inflammatory processes damage the skin’s underlying structure, creating depressions, raised areas, or textural irregularities that persist long after active breakouts resolve. Vitamin C plays a crucial role in collagen synthesis, the process by which the skin rebuilds and repairs damaged tissue, making it essential for effective scar treatment and prevention.
The vitamin C-dependent enzyme hydroxylase is required for proper collagen formation, and deficiency in this nutrient directly impairs the skin’s ability to produce strong, healthy collagen fibers. By ensuring adequate vitamin C levels in skin tissue, topical applications support optimal collagen production that can help fill in depressed scars and improve overall skin texture.
Different types of acne scars respond variably to vitamin C treatment, with rolling scars and shallow boxcar scars showing the most improvement from consistent vitamin C application. The gradual rebuilding of collagen over time can soften these types of scarring, though deep ice pick scars may require additional professional treatments for significant improvement.
The timeline for scar improvement with vitamin C typically extends over months rather than weeks, as collagen remodeling is a slow process that requires consistent stimulation. Patience and persistent application are essential for achieving meaningful results in acne scar reduction through vitamin C therapy.
Hyperpigmentation fades through cellular turnover
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation represents one of the most persistent and emotionally distressing consequences of acne, often lasting months or years after active breakouts resolve. Vitamin C addresses this issue through multiple mechanisms that both prevent new pigmentation from forming and help fade existing dark spots over time.
The antioxidant properties of vitamin C help prevent the oxidative stress that triggers melanin production in response to inflammatory damage. By reducing this oxidative burden, vitamin C can prevent the formation of new dark spots while acne lesions heal, minimizing the long-term cosmetic impact of breakouts.
Vitamin C also promotes cellular turnover and renewal, helping to shed pigmented skin cells more rapidly while encouraging the growth of new, evenly pigmented skin. This acceleration of the natural skin renewal process gradually fades existing hyperpigmentation while preventing the accumulation of pigmented cells that create persistent dark spots.
The inhibition of tyrosinase, a key enzyme in melanin production, represents another mechanism by which vitamin C reduces hyperpigmentation. By interfering with this enzyme’s activity, vitamin C can reduce the production of new melanin while existing pigmentation naturally fades through normal cellular turnover processes.
Sodium ascorbyl phosphate provides stable delivery
Among the various forms of vitamin C used in skincare products, sodium ascorbyl phosphate (SAP) has gained recognition for its particular effectiveness in acne treatment and its superior stability compared to other vitamin C derivatives. This form penetrates skin effectively while remaining stable in formulations, ensuring consistent delivery of active vitamin C to target tissues.
SAP demonstrates specific antimicrobial activity against Propionibacterium acnes, the bacteria primarily responsible for inflammatory acne lesions. This direct antibacterial effect complements vitamin C’s anti-inflammatory and healing properties, providing a more comprehensive approach to acne management than antioxidant activity alone.
The pH stability of SAP allows it to be formulated in products with pH levels that are compatible with healthy skin, avoiding the irritation that can occur with highly acidic vitamin C formulations. This gentleness makes SAP particularly suitable for sensitive, acne-prone skin that may react poorly to harsh or acidic treatments.
Research has demonstrated SAP’s effectiveness in reducing both inflammatory and non-inflammatory acne lesions when used consistently over time. The combination of antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and healing properties makes this particular form of vitamin C especially well-suited for comprehensive acne management.
Professional treatments enhance vitamin C effectiveness
Microneedling combined with vitamin C application can significantly enhance the penetration and effectiveness of topical vitamin C treatments for acne scars and hyperpigmentation. The controlled micro-injuries created by professional microneedling stimulate natural healing responses while creating temporary channels that allow deeper vitamin C penetration into affected tissue.
The collagen stimulation triggered by microneedling works synergistically with vitamin C’s collagen-promoting effects, potentially accelerating scar improvement beyond what either treatment might achieve alone. This combination approach has shown particular promise for treating atrophic acne scars that have not responded adequately to topical treatments alone.
Iontophoresis represents another professional technique that uses mild electrical currents to drive vitamin C deeper into skin tissue than topical application alone can achieve. This enhanced delivery can improve results for hyperpigmentation and may provide faster improvement in overall skin texture and tone.
Professional vitamin C treatments typically use higher concentrations than over-the-counter products, potentially providing more dramatic results for severe acne scarring or persistent hyperpigmentation. However, these treatments require proper medical supervision to ensure safety and effectiveness while minimizing the risk of adverse reactions.
Comprehensive skin protection prevents future damage
Beyond its direct effects on acne and acne-related skin damage, vitamin C provides broad protective benefits that help prevent future skin problems and maintain overall skin health. UV protection, though not sufficient as a standalone sun protection method, helps reduce the photodamage that can worsen acne scars and hyperpigmentation.
The photoprotective effects of vitamin C work by neutralizing free radicals generated by UV exposure before they can cause cellular damage. While this protection supplements but does not replace proper sunscreen use, it provides an additional layer of defense against the sun damage that can make acne scars more prominent and persistent.
Vitamin C’s role in maintaining the skin barrier function helps protect against environmental irritants and pollutants that can trigger acne flares in sensitive individuals. A healthy skin barrier also promotes proper hydration and reduces the irritation that can exacerbate existing acne conditions.
The wound healing support provided by vitamin C extends beyond acne-specific benefits to help the skin recover more effectively from any type of injury or irritation. This enhanced healing capacity can reduce the likelihood that minor skin trauma will develop into significant acne lesions or scarring.
Proper application maximizes vitamin C benefits
The effectiveness of topical vitamin C for acne management depends heavily on proper application techniques and consistent use over time. Vitamin C serums should be applied to clean, dry skin before moisturizer application, allowing the active ingredient to penetrate effectively without interference from other products.
Morning and evening application, spaced approximately eight hours apart, provides optimal vitamin C delivery while allowing the skin time to utilize the antioxidant between applications. This twice-daily regimen ensures consistent availability of vitamin C for ongoing anti-inflammatory and healing processes.
The layering sequence of skincare products significantly impacts vitamin C absorption and effectiveness. Applying vitamin C serum directly to cleansed skin, followed by moisturizer and sunscreen, allows maximum penetration while maintaining proper skin hydration and protection.
Consistency in application proves more important than occasional intensive treatments, as the skin’s vitamin C levels need regular replenishment to maintain optimal antioxidant and healing activity. Missing applications can interrupt the steady supply of vitamin C needed for ongoing acne management and scar healing.
Concentration selection balances effectiveness and tolerance
Vitamin C concentrations between 10-20% provide optimal balance between therapeutic effectiveness and skin tolerance for most individuals with acne-prone skin. Lower concentrations may not provide sufficient antioxidant activity for meaningful acne improvement, while higher concentrations increase the risk of irritation without proportionally greater benefits.
Individual skin sensitivity varies significantly, making it important to start with lower concentrations and gradually increase as tolerance develops. Some individuals may achieve excellent results with 10% formulations, while others may benefit from higher concentrations once their skin has adapted to regular vitamin C use.
The formulation stability becomes increasingly important at higher vitamin C concentrations, as unstable products can cause irritation while providing little therapeutic benefit. Products packaged in dark, airtight containers help preserve vitamin C potency and reduce the risk of degradation that can cause skin irritation.
Combining high-concentration vitamin C with other active ingredients requires careful consideration to avoid over-treating the skin. Alternating vitamin C with other acne treatments or using them at different times of day can help prevent irritation while maintaining comprehensive acne management.
Dietary vitamin C supports topical treatments
While topical vitamin C application provides direct benefits for acne-prone skin, maintaining adequate dietary vitamin C intake supports overall skin health and may enhance the effectiveness of topical treatments. Vitamin C-rich foods provide the raw materials needed for collagen synthesis and antioxidant protection throughout the body, including the skin.
Citrus fruits, berries, bell peppers, and leafy greens provide abundant vitamin C that supports healthy skin function from within. These foods also provide additional antioxidants and nutrients that work synergistically with vitamin C to promote optimal skin health and healing.
The timing of vitamin C-rich food consumption may influence its availability for skin health, with consistent daily intake providing more stable tissue levels than sporadic high-dose consumption. Spreading vitamin C-rich foods throughout the day helps maintain steady antioxidant activity that supports ongoing skin repair and protection.
Cooking methods can significantly impact the vitamin C content of foods, with minimal cooking and fresh preparation preserving maximum nutrient levels. Raw or lightly cooked vegetables and fresh fruits provide optimal vitamin C bioavailability for supporting skin health from within.
Safety considerations and patch testing
While vitamin C is generally well-tolerated by most individuals, some people may experience adverse reactions including skin irritation, allergic responses, or temporary skin discoloration. Patch testing on a small area of skin helps identify potential sensitivity before applying vitamin C products to larger areas or the face.
The recommended patch testing protocol involves applying a small amount of vitamin C product to the inner forearm twice daily for one week, monitoring for any signs of irritation, redness, or allergic reaction. Absence of adverse reactions during this test period generally indicates safe use on facial skin.
Certain medications and skin conditions may increase sensitivity to vitamin C or interact with its effects, making professional consultation advisable for individuals with complex medical histories or those using prescription acne treatments. Combining vitamin C with retinoids, benzoyl peroxide, or alpha hydroxy acids requires careful monitoring to prevent over-irritation.
The yellowing of skin sometimes observed with vitamin C use typically results from product oxidation rather than actual skin discoloration and usually resolves with discontinuation of the oxidized product. Using fresh, properly stored vitamin C products minimizes this cosmetic concern.
Long-term benefits extend beyond acne treatment
Consistent vitamin C use for acne management provides cumulative benefits that extend well beyond the resolution of active breakouts. The collagen support, antioxidant protection, and skin barrier enhancement continue to benefit skin health even after acne improves, helping maintain clear, healthy skin over time.
The prevention of premature aging through vitamin C’s antioxidant and collagen-supporting effects represents a valuable long-term benefit that becomes increasingly important with age. Early establishment of consistent vitamin C use can help prevent many signs of aging while addressing current acne concerns.
The improvement in overall skin texture, tone, and radiance that occurs with regular vitamin C use enhances the cosmetic benefits beyond simple acne control. These improvements in skin appearance often provide significant psychological benefits that extend well beyond the resolution of acne lesions.
Building healthy skincare habits around vitamin C use often leads to better overall skincare practices that support long-term skin health. The discipline required for consistent vitamin C application often translates to better adherence to other beneficial skincare practices including sun protection and gentle cleansing.
Vitamin C offers a scientifically-supported, multifaceted approach to acne management that addresses inflammation, promotes healing, and prevents long-term skin damage. Its safety profile, combined with its effectiveness for multiple aspects of acne-related skin concerns, makes it a valuable addition to comprehensive acne treatment regimens for individuals seeking gentler alternatives to harsh chemical treatments while maintaining effective results.