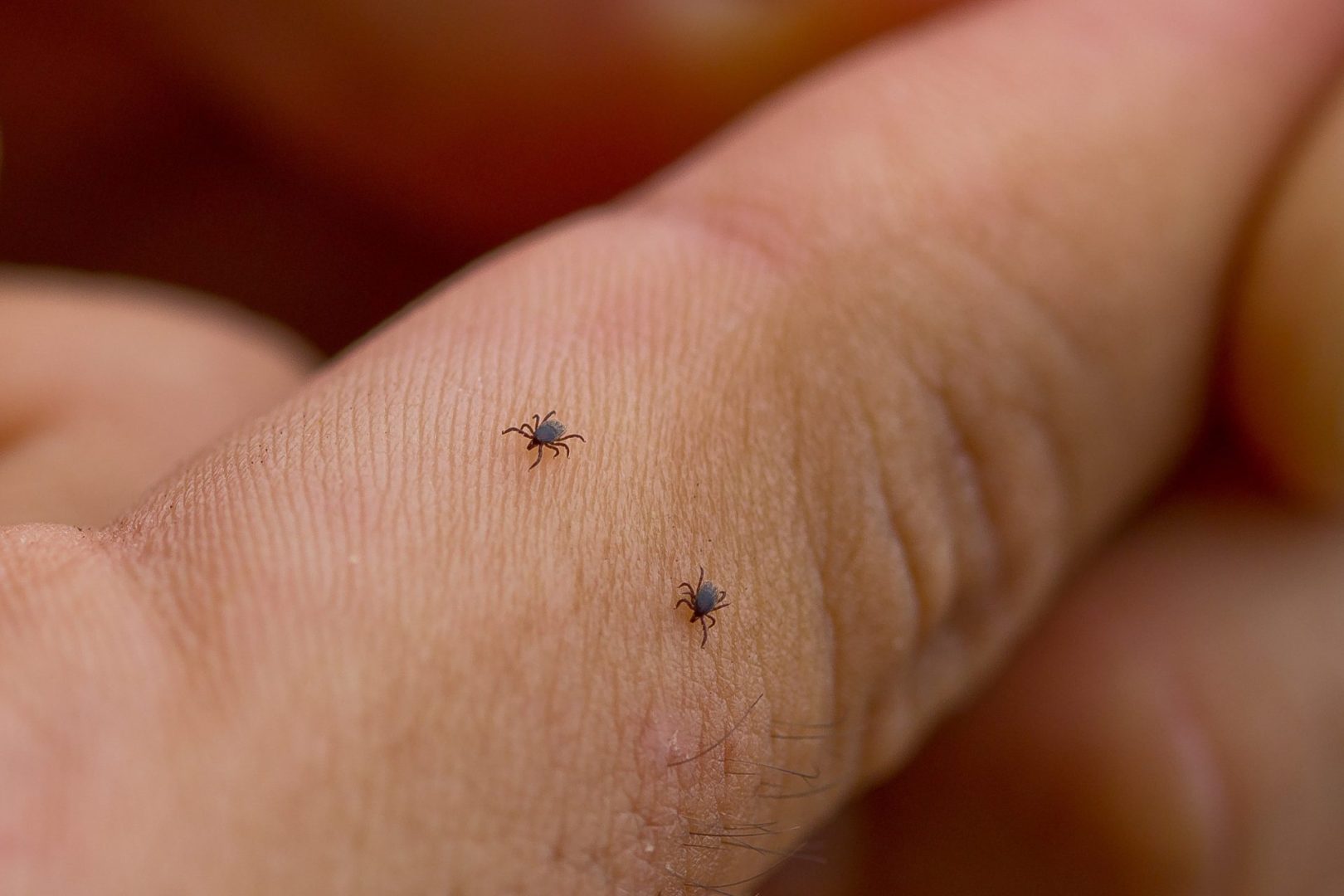
Health officials are sounding the alarm about a dramatic increase in tick-related diseases across America, with new data from the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention revealing that reported cases have quadrupled over the past two decades. This concerning trend coincides with warmer weather patterns and increased outdoor recreational activities that bring people into closer contact with tick habitats.
The CDC’s comprehensive analysis shows that what was once considered a relatively uncommon health concern has transformed into a significant public health challenge affecting thousands of Americans annually. Medical experts attribute this surge to multiple factors including climate change, suburban expansion into wooded areas, and growing participation in hiking, camping, and other outdoor pursuits.
Understanding the scope of tick-related health threats
The dramatic increase in tick-borne illnesses encompasses various diseases beyond the commonly known Lyme disease. Rocky Mountain spotted fever, ehrlichiosis, anaplasmosis, and babesiosis represent additional conditions that have contributed to the rising statistics documented by federal health authorities.
Each of these conditions presents unique challenges for both patients and healthcare providers, as symptoms often mimic common viral infections, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. The geographic distribution of these diseases has also expanded, with cases now reported in regions previously considered low-risk for tick-borne infections.
Healthcare professionals emphasize that early recognition and treatment remain crucial factors in preventing long-term health complications associated with these conditions. The window for effective intervention often closes quickly, making public awareness and prompt medical attention essential components of disease management.
Essential prevention strategies for families
Protecting yourself and your loved ones from tick-borne diseases requires a comprehensive approach that begins before venturing into areas where ticks commonly reside. The CDC recommends covering all exposed skin surfaces where ticks might attach, emphasizing the importance of long sleeves and full-length pants during outdoor activities.
The practice of tucking pant legs into socks creates an additional barrier that prevents ticks from reaching skin surfaces along the legs and ankles. While this approach might seem excessive for casual outdoor activities, medical experts stress that this simple precaution significantly reduces the likelihood of tick attachment.
Selecting appropriate clothing colors can also enhance tick detection, as these small parasites become more visible against light-colored fabrics. Additionally, treating clothing and gear with permethrin-based repellents provides extended protection that persists through multiple washing cycles.
Thorough body checks prevent dangerous infections
Post-outdoor activity inspections represent one of the most effective methods for preventing tick-borne diseases. The CDC emphasizes conducting comprehensive examinations of all family members after spending time in wooded areas or locations with tall grass vegetation.
Particular attention should focus on areas where ticks commonly attach, including the scalp, behind ears, under arms, around the waist, between legs, and behind knees. Children require especially careful examination, as their height often brings them into contact with tick-infested vegetation at different levels than adults.
The inspection process should occur as soon as possible after outdoor exposure, ideally within two hours of returning indoors. Prompt removal of unattached ticks dramatically reduces the risk of disease transmission, as most tick-borne pathogens require extended attachment periods before successful transmission occurs.
Recognizing early warning signs saves lives
The initial symptoms of tick-borne illnesses often mirror common viral infections, creating diagnostic challenges for both patients and healthcare providers. Fever, fatigue, headaches, and muscle aches typically appear within days to weeks following tick exposure, making the connection between outdoor activities and illness symptoms crucial for proper diagnosis.
These early manifestations can easily be mistaken for seasonal flu or other routine infections, leading many individuals to delay seeking medical attention. However, the window for effective antibiotic treatment often closes rapidly, making early intervention critical for preventing serious complications.
The characteristic bullseye rash associated with Lyme disease appears in only a portion of infected individuals, meaning that many cases progress without this distinctive visual indicator. Healthcare professionals stress that the absence of this rash should never provide false reassurance about potential infection status.
Geographic expansion creates new risk areas
The traditional boundaries of tick-borne disease risk have shifted significantly over the past two decades, with cases now appearing in regions previously considered safe from these infections. Climate patterns, wildlife migration, and human development have contributed to expanding the geographic footprint of disease-carrying tick populations.
States that historically reported minimal tick-borne illness cases now document hundreds of infections annually. This expansion means that individuals traveling to previously safe regions may encounter unexpected exposure risks, highlighting the importance of universal precautions regardless of geographic location.
The changing distribution patterns also challenge healthcare providers in areas with limited experience treating these conditions. Medical education and awareness campaigns have become essential tools for ensuring appropriate diagnosis and treatment across all affected regions.
Treatment timing determines long-term outcomes
Medical intervention during the early stages of tick-borne infections can prevent the development of chronic health problems that sometimes plague patients for years. Antibiotic therapy initiated within the first few weeks of infection typically results in complete recovery without lasting complications.
However, delayed treatment allows pathogens to establish deeper infections that become increasingly difficult to eliminate. Some patients develop persistent symptoms including joint pain, neurological problems, and chronic fatigue that can significantly impact quality of life.
The importance of seeking immediate medical attention following tick exposure cannot be overstated, particularly when accompanied by any combination of fever, rash, or flu-like symptoms. Healthcare providers can assess risk factors and initiate appropriate testing or preventive treatment when indicated.
Technology aids in disease prevention efforts
Modern technology has introduced new tools for tick identification and disease prevention. Smartphone applications now help users identify different tick species and assess potential disease transmission risks based on attachment duration and geographic location.
Weather monitoring services increasingly include tick activity forecasts, helping outdoor enthusiasts plan activities during periods of reduced risk. These technological advances complement traditional prevention methods and provide additional layers of protection for active families.
Research institutions continue developing improved testing methods that can detect infections earlier and more accurately than previous techniques. These advances hold promise for reducing the diagnostic delays that contribute to treatment complications and chronic health problems.
Community awareness drives prevention success
Public health campaigns focusing on tick-borne disease prevention have demonstrated measurable success in communities where implementation occurs consistently. School programs teaching children about tick identification and prevention create awareness that extends throughout entire families.
Healthcare provider education ensures that medical professionals in all geographic regions maintain current knowledge about evolving disease patterns and treatment protocols. This comprehensive approach addresses both individual prevention and healthcare system preparedness for managing increasing case loads.
The quadrupling of tick-borne illnesses over two decades represents a significant public health challenge that requires coordinated response efforts from individuals, healthcare systems, and public health authorities working together to protect community health.