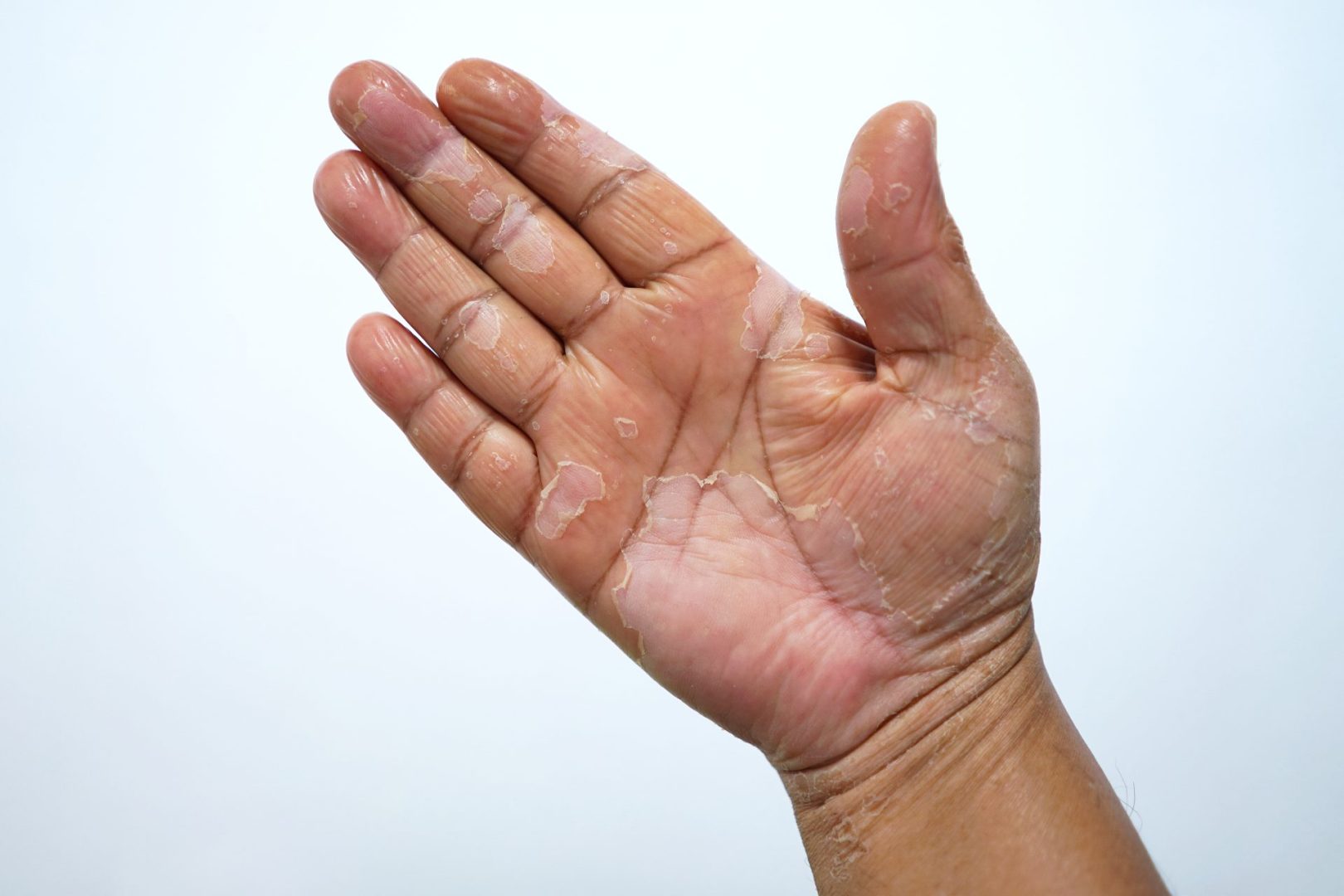
The sudden appearance of peeling skin on your hands can be both alarming and embarrassing, leaving you wondering what went wrong with your once-smooth skin. This common yet distressing condition affects millions of people worldwide, often appearing without warning and persisting despite various home remedies and over-the-counter treatments.
Hand peeling represents more than just a cosmetic concern – it serves as a visible indicator that something has disrupted your skin’s natural protective barrier. Understanding the underlying causes becomes crucial for developing an effective treatment strategy that addresses the root problem rather than merely masking symptoms.
Your hands face constant exposure to environmental aggressors, chemical irritants, and physical stressors that can compromise skin integrity in ways that other body parts rarely experience. This unique vulnerability makes hands particularly susceptible to various conditions that manifest as peeling, flaking, or scaling skin.
The complexity of hand peeling lies in its multiple potential causes, ranging from simple environmental factors to serious underlying health conditions. Identifying the specific trigger behind your hand peeling becomes essential for selecting appropriate treatments and preventing recurrence.
Many people attempt to treat hand peeling with generic moisturizers or home remedies without understanding the underlying cause, often leading to prolonged discomfort and potential complications. A systematic approach to identifying and addressing the root cause typically yields far better results than random treatment attempts.
1. Contact dermatitis wreaking havoc on your skin barrier
Contact dermatitis represents one of the most common yet overlooked causes of hand peeling, often developing gradually as your skin becomes sensitized to substances you encounter regularly. This condition occurs when your skin reacts to irritants or allergens that come into direct contact with your hands.
Irritant contact dermatitis develops when harsh chemicals, detergents, soaps, or other substances damage your skin’s protective barrier through repeated exposure. Common culprits include household cleaning products, dish soap, hand sanitizers, and industrial chemicals that strip away natural oils and disrupt normal skin function.
Allergic contact dermatitis occurs when your immune system identifies certain substances as threats, triggering inflammatory responses that lead to skin damage and peeling. Common allergens include latex, nickel, fragrances, preservatives, and certain plants that can cause delayed reactions hours or days after contact.
The cumulative effect of repeated exposure to irritants or allergens can cause progressive skin barrier damage, leading to chronic inflammation and persistent peeling that may worsen over time without proper intervention. This process often creates a cycle where damaged skin becomes more susceptible to further irritation.
Occupational exposures frequently contribute to contact dermatitis, particularly for individuals working in healthcare, food service, cleaning, manufacturing, or other industries requiring frequent hand washing or chemical exposure. The combination of multiple irritants throughout workdays can overwhelm even healthy skin barriers.
Seasonal variations in contact dermatitis may occur as people use different products, engage in various activities, or encounter different environmental conditions that expose hands to new potential irritants or allergens.
2. Chronic hand eczema creating persistent inflammation
Hand eczema, also known as hand dermatitis, represents a chronic inflammatory condition that can cause severe peeling, cracking, and scaling of hand skin. This condition often develops in individuals with personal or family histories of allergic conditions but can affect anyone under the right circumstances.
Dyshidrotic eczema specifically affects hands and feet, causing small, intensely itchy blisters that eventually burst and peel, leaving behind raw, tender skin. This particular form of eczema tends to flare during times of stress or seasonal changes and can be particularly stubborn to treat.
Atopic dermatitis affecting the hands often presents as dry, scaly patches that become inflamed and peel during flare-ups. This condition typically involves genetic factors that affect skin barrier function, making hands more susceptible to environmental triggers and irritants.
The chronic nature of hand eczema means that periods of improvement may alternate with flare-ups triggered by stress, weather changes, hormonal fluctuations, or exposure to known irritants. Managing this condition requires long-term strategies rather than quick fixes.
Secondary bacterial infections can complicate hand eczema when persistent scratching or compromised skin barriers allow harmful bacteria to penetrate deeper skin layers. These infections can worsen peeling and delay healing while creating additional treatment challenges.
The psychological impact of visible hand eczema often creates stress that can trigger further flare-ups, creating a challenging cycle that requires both physical and emotional management strategies for optimal outcomes.
3. Fungal infections silently destroying skin integrity
Fungal infections of the hands, while less common than foot infections, can cause significant peeling and scaling that often gets misdiagnosed as dry skin or eczema. These infections thrive in warm, moist environments and can spread from other body parts or through direct contact with contaminated surfaces.
Tinea manuum, the medical term for fungal infection of the hands, typically presents as scaling, peeling skin that may start on one hand before spreading to both. The infection often begins between fingers or on palms before extending to other areas of the hands.
Candida overgrowth can affect hands, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems, diabetes, or those who frequently have wet hands. This type of fungal infection often causes peeling skin along with redness and potential cracking around nail beds.
The diagnosis of fungal hand infections can be challenging because symptoms often mimic other skin conditions, leading to inappropriate treatments that may worsen the condition or delay proper healing. Antifungal treatments work specifically against fungal organisms and won’t be effective for other causes of peeling.
Risk factors for developing fungal hand infections include frequent moisture exposure, compromised immune function, existing fungal infections elsewhere on the body, and contact with contaminated surfaces in gyms, pools, or other public facilities.
The contagious nature of some fungal infections means that proper diagnosis and treatment become important not only for personal healing but also for preventing transmission to family members or close contacts.
4. Autoimmune conditions targeting hand skin
Various autoimmune conditions can manifest with hand peeling as one of their primary or secondary symptoms, often requiring specialized treatment approaches that address underlying immune system dysfunction rather than just skin symptoms.
Psoriasis affecting the hands typically presents as thick, scaly patches that peel and flake persistently. Hand psoriasis can be particularly challenging to treat due to constant use and exposure that can irritate already inflamed skin and interfere with topical treatments.
Lupus and other systemic autoimmune conditions may cause hand skin changes including peeling, particularly during disease flares or as side effects of medications used to manage these conditions. The inflammatory nature of autoimmune diseases can affect skin health throughout the body.
Dermatomyositis, a rare autoimmune condition, often presents with characteristic hand changes including peeling skin around nail beds and knuckles. This condition requires prompt medical attention as it can affect internal organs in addition to causing skin symptoms.
The systemic nature of autoimmune conditions means that hand peeling may be accompanied by other symptoms affecting different body systems, making comprehensive evaluation important for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
Treatment of autoimmune-related hand peeling often requires immunosuppressive medications or other systemic therapies rather than topical treatments alone, highlighting the importance of proper medical evaluation for persistent or severe symptoms.
5. Nutritional deficiencies undermining skin health
Specific nutritional deficiencies can compromise skin health and healing capacity, leading to persistent hand peeling that doesn’t respond well to topical treatments alone. The hands, being constantly exposed and used, often show nutritional deficiency effects more prominently than other body areas.
Essential fatty acid deficiencies can compromise skin barrier function, leading to increased water loss and susceptibility to environmental damage that manifests as peeling and scaling. These healthy fats play crucial roles in maintaining skin cell membrane integrity and inflammatory responses.
Vitamin deficiencies, particularly vitamins A, C, and E, can affect skin cell turnover, collagen production, and antioxidant protection, all of which influence skin health and healing capacity. Severe deficiencies may cause characteristic skin changes including peeling and poor wound healing.
Protein deficiency can impair skin cell production and repair processes, leading to weak, easily damaged skin that peels and doesn’t heal properly. This becomes particularly problematic for individuals following restrictive diets or those with absorption disorders.
Mineral deficiencies, including zinc, iron, and selenium, can affect various aspects of skin health including immune function, healing capacity, and protection against oxidative damage. These deficiencies often develop gradually and may not be immediately obvious.
The interconnected nature of nutrition and skin health means that addressing nutritional deficiencies often requires comprehensive dietary evaluation and potentially supplementation under professional guidance rather than random vitamin use.
6. Medication side effects disrupting normal skin function
Various medications can cause hand peeling as a side effect through different mechanisms including direct skin toxicity, immune system effects, or interference with normal skin cell production and turnover processes.
Chemotherapy drugs often cause hand-foot syndrome, a condition characterized by severe peeling, redness, and pain on palms and soles. This side effect can be dose-limiting and may require treatment modifications or supportive care measures to manage symptoms.
Antibiotics, particularly penicillins and sulfonamides, can cause allergic reactions that manifest as skin peeling, often accompanied by other symptoms like rash or itching. These reactions can range from mild to severe and may require immediate medical attention.
Blood pressure medications, particularly ACE inhibitors and diuretics, can cause skin changes in some individuals, including increased photosensitivity and altered skin healing that may contribute to peeling or other skin problems.
Topical medications, including prescription creams and ointments, can cause contact dermatitis or allergic reactions that lead to peeling, particularly when used inappropriately or for extended periods beyond recommended guidelines.
The timing relationship between medication initiation and skin symptoms often provides important clues for identifying drug-related causes of hand peeling, though some reactions may not appear until weeks or months after starting new medications.
7. Environmental factors creating cumulative skin damage
Environmental exposures can cause both acute and chronic hand peeling through various mechanisms including direct chemical damage, physical trauma, and disruption of normal skin barrier function.
Extreme weather conditions, particularly cold, dry air or excessive sun exposure, can damage hand skin and impair its ability to maintain proper moisture balance. Winter weather often causes seasonal hand peeling that may persist despite moisturizing efforts.
Chemical exposures from cleaning products, solvents, or industrial chemicals can cause immediate irritation or cumulative damage that manifests as persistent peeling. Even products labeled as mild or natural can cause problems in sensitive individuals or with frequent use.
Water exposure, particularly hot water or water with high mineral content, can strip natural oils from hand skin and disrupt normal barrier function. Frequent hand washing, while important for hygiene, can contribute to skin problems when not balanced with appropriate moisturizing.
Air pollution and environmental toxins can create oxidative stress that damages skin cells and impairs normal healing processes. Urban environments often present higher levels of these challenges compared to rural areas.
The cumulative nature of environmental damage means that protection strategies become as important as treatment approaches for maintaining healthy hand skin over time.
8. Underlying medical conditions requiring specialized attention
Various systemic medical conditions can cause or contribute to hand peeling through different mechanisms including circulatory problems, immune dysfunction, or metabolic disorders that affect skin health and healing capacity.
Diabetes can cause various skin problems including poor healing, increased infection risk, and changes in skin texture that may contribute to peeling. Blood sugar control often influences skin symptoms and healing capacity in diabetic individuals.
Thyroid disorders can affect skin health through their effects on metabolism, circulation, and immune function. Both overactive and underactive thyroid conditions can cause characteristic skin changes including alterations in texture and healing capacity.
Kidney disease can cause skin problems through accumulation of waste products that would normally be filtered out, leading to itching, dryness, and peeling that may be difficult to treat with topical measures alone.
Liver disease can affect skin health through impaired toxin processing and altered protein production that affects skin structure and function. Chronic liver conditions often present with various skin manifestations including changes in hands.
Circulatory disorders can reduce blood flow to hands, impairing nutrient delivery and waste removal that support healthy skin function. Poor circulation often makes skin more susceptible to damage and slower to heal.
The complexity of treating medically-related hand peeling often requires coordination between different healthcare providers to address both underlying conditions and skin symptoms effectively. Proper medical evaluation becomes essential for identifying and treating these conditions appropriately while managing skin symptoms.