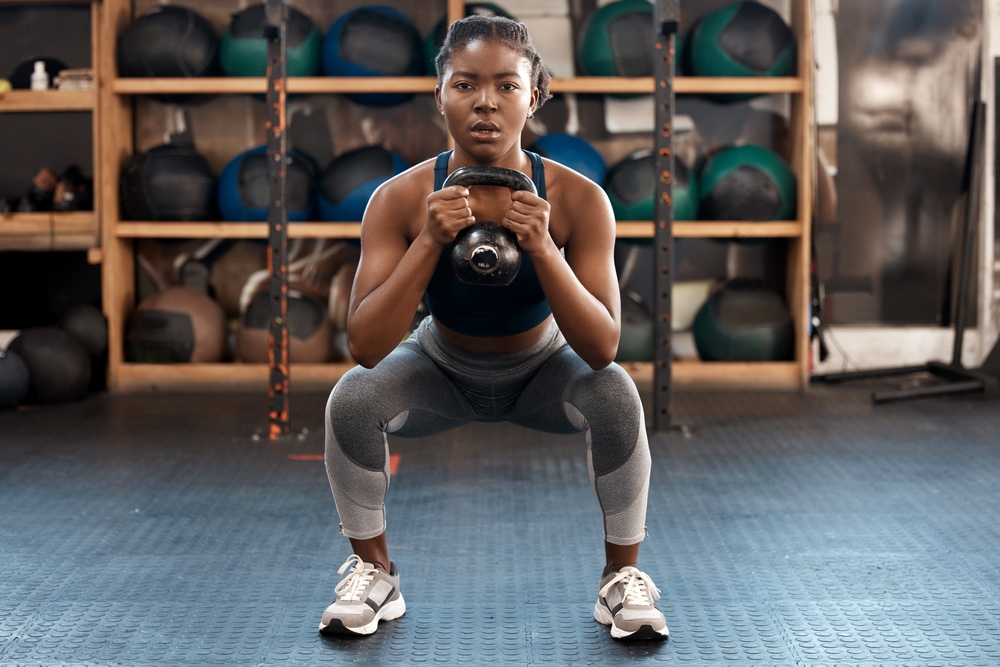
Traditional squats have dominated gym routines for decades, but fitness enthusiasts are discovering a superior alternative that transforms ordinary workouts into extraordinary results. Kettlebell squats offer a comprehensive approach to strength training that engages multiple muscle groups while delivering exceptional functional benefits.
The distinctive shape and weight distribution of kettlebells create unique challenges that standard barbells cannot replicate. This ancient training tool, originating from Russian military conditioning programs, has evolved into a cornerstone of modern fitness regimens worldwide.
The physiological transformation
Incorporating kettlebells into squat routines triggers remarkable changes throughout the body. Core muscles activate intensely to maintain stability during the movement, while smaller stabilizing muscles throughout the kinetic chain engage to support proper form. This comprehensive muscle recruitment pattern elevates metabolic rate significantly, creating an afterburn effect that continues burning calories hours after exercise completion.
The dynamic nature of kettlebell squats improves postural alignment by strengthening the posterior chain muscles responsible for spinal support. Regular practitioners often report enhanced confidence and improved physical presence as their posture naturally corrects itself through consistent training.
Discovering optimal stance mechanics
Finding the ideal squat stance requires individual assessment rather than following generic guidelines. Personal biomechanics vary significantly between individuals, making customized positioning essential for optimal performance and injury prevention.
A simple assessment involves performing three consecutive vertical jumps and observing the natural landing position. This instinctive foot placement typically represents the most efficient squat stance for each person’s unique anatomy. The kettlebell handle should align with the ankle bones when held in the goblet position, creating a stable foundation for the movement.
Weight distribution plays a crucial role in squat mechanics, with approximately 60 percent of body weight concentrated in the heels and 40 percent distributed across the forefoot. This ratio provides optimal balance between stability and power generation throughout the movement pattern.
Breathing techniques for enhanced performance
Strategic breathing patterns significantly influence squat performance and muscle activation. The inhalation phase occurs during the descent, creating intra-abdominal pressure that stabilizes the spine and prepares the body for the ascending phase.
Maintaining breath control at the bottom position for two to three seconds maximizes muscle engagement and establishes a strong foundation for the upward drive. The exhalation phase coincides with the ascent, providing additional power through increased core activation.
Strategic weight selection approaches
Kettlebell selection should align with specific training objectives rather than following arbitrary progression schemes. Endurance-focused training typically utilizes moderate weights that allow 10 to 15 repetitions with proper form maintenance.
Muscle-building protocols benefit from heavier loads that challenge the body within six to 15 repetitions. Strength development requires maximal loads that limit repetitions to five or fewer while maintaining technical proficiency.
Advanced movement variations
Tempo squats involve controlled descent and ascent phases that increase time under tension, promoting muscle growth and strength development. The extended duration challenges muscular endurance while reinforcing proper movement patterns.
Offset loading introduces unilateral challenges by holding the kettlebell in various positions, forcing the core to work harder to maintain balance and stability. This variation translates directly to real-world functional movements.
Combination movements integrate upper body exercises with squat patterns, creating compound exercises that maximize training efficiency and caloric expenditure.
Programming for optimal results
Beginner practitioners should incorporate kettlebell squats once weekly to establish movement competency and allow adequate recovery between sessions. Intermediate trainees can progress to twice-weekly sessions while maintaining focus on movement quality over training frequency.
Sessions should occur when energy levels are highest, typically early in workouts when neuromuscular coordination remains optimal. This timing ensures maximum benefit from each training session while reducing injury risk associated with fatigue.
Consistent practice combined with progressive overload principles creates sustainable improvements in strength, mobility, and overall fitness. The compound nature of kettlebell squats delivers comprehensive benefits that extend far beyond traditional lower body exercises, making them an invaluable addition to any training program.