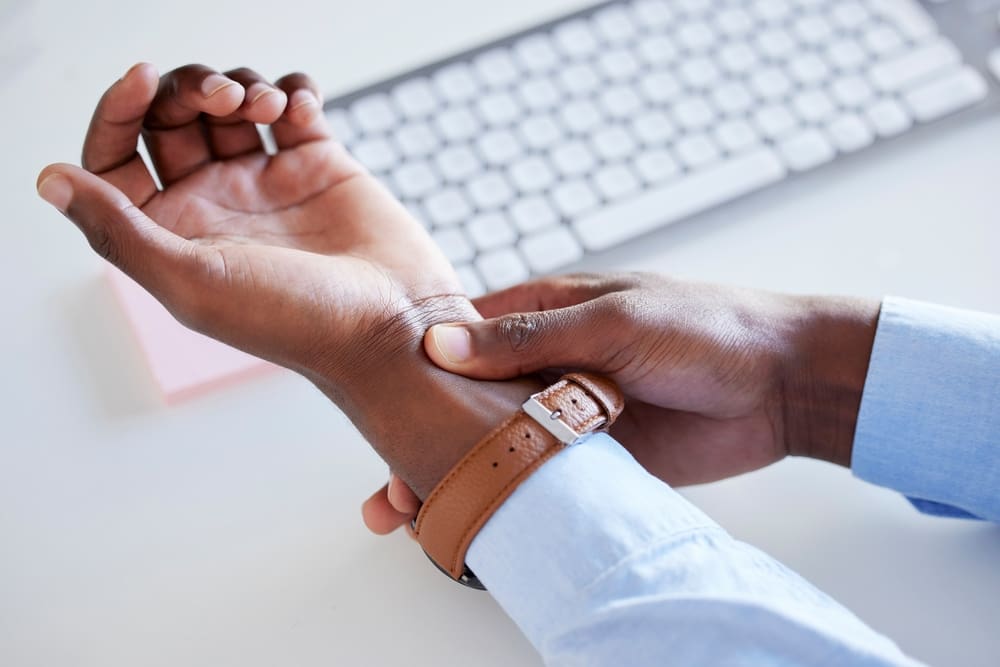
Carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) is a condition that affects millions of people worldwide, leading to pain, numbness and sometimes debilitating discomfort in the hand and arm. Understanding the reasons behind its prevalence is crucial for prevention and management. This article delves into the four primary reasons most people develop carpal tunnel syndrome, offering insights into how this condition can be addressed and mitigated.
What is carpal tunnel syndrome?
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that has garnered significant attention due to its impact on daily activities and overall quality of life. Characterized by pressure on the median nerve within the carpal tunnel of the wrist, the symptoms can range from mild discomfort to severe pain and functional impairment. The reasons for its development are multifaceted, involving anatomical, occupational and lifestyle factors. By examining the key contributors to carpal tunnel syndrome, individuals can take proactive steps to minimize their risk and manage the condition more effectively.
Repetitive hand and wrist movements
One of the most significant reasons for the development of carpal tunnel syndrome is the repetitive motion of the hand and wrist. This is particularly prevalent among individuals who engage in continuous typing, assembly line work or the use of vibrating tools. These repetitive actions can cause swelling within the carpal tunnel, exerting pressure on the median nerve.
The impact of modern workplaces
The modern workplace — with its emphasis on computer use and prolonged periods of typing — has seen a surge in cases of carpal tunnel syndrome. Ergonomic adjustments, such as keyboard trays and ergonomic mouse designs, can help mitigate the risk by ensuring the wrist remains in a neutral position, reducing strain.
Anatomical factors
Anatomical differences play a crucial role in the susceptibility to carpal tunnel syndrome. Individuals with smaller carpal tunnels are more prone to this condition due to the limited space within the tunnel, which can easily become constricted. Additionally, wrist injuries such as fractures or sprains that alter the structure of the wrist can increase the risk of developing CTS.
Recognizing individual risks
Understanding one’s anatomical risk factors is vital in taking preventative measures. For those at higher risk, regular breaks, wrist exercises and even wearing wrist splints during activities can provide significant relief and prevent the onset of symptoms.
Obesity and lifestyle factors
Lifestyle factors, particularly obesity, have a significant correlation with the incidence of carpal tunnel syndrome. Excess body weight can contribute to inflammation and fluid retention, exacerbating pressure within the carpal tunnel. Furthermore, individuals with obesity may also have associated conditions such as diabetes, which is known to increase the risk of nerve damage, including the median nerve.
The role of diet and exercise
Maintaining a healthy weight through diet and exercise is not only beneficial for overall health but can also reduce the risk of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. Activities that promote strength, flexibility and blood circulation in the wrists and hands can be particularly beneficial.
Hormonal changes and medical conditions
Hormonal changes — particularly during pregnancy, menopause or as a result of thyroid disorders — can increase the likelihood of developing carpal tunnel syndrome. These changes can lead to fluid retention and swelling, putting additional pressure on the median nerve. Similarly, conditions such as diabetes or rheumatoid arthritis, which affect the body’s ability to manage inflammation and repair nerve damage, can also elevate the risk.
Managing underlying conditions
Effectively managing underlying medical conditions is crucial in reducing the risk of carpal tunnel syndrome. Regular medical checkups, following treatment plans for chronic conditions and monitoring symptoms can help in early detection and management of CTS.
Managing and preventing carpal tunnel syndrome
Carpal tunnel syndrome is a condition that arises from a combination of factors, including repetitive motions, anatomical predispositions, lifestyle factors and underlying medical conditions. By understanding these reasons, individuals can take proactive steps to reduce their risk or manage the condition more effectively. Implementing ergonomic practices, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, recognizing individual risk factors and managing underlying medical conditions are all critical components in addressing the prevalence of carpal tunnel syndrome. While the journey to managing or preventing CTS may require dedication and adjustments, the benefits of reduced pain and improved quality of life are well worth the effort.
As we navigate through daily tasks that may put us at risk, it’s essential to remain vigilant and proactive in taking steps to protect our wrist health. Carpal tunnel syndrome, while common, is a condition that can be managed with the right knowledge and resources. By fostering an environment that prioritizes ergonomics, health and awareness, we can all work towards minimizing the impact of carpal tunnel syndrome on our lives.
This story was created using AI technology.