Pancreatic cancer is a daunting diagnosis that affects thousands of people worldwide every year. One of the most challenging aspects of this disease is its subtlety; the symptoms often mimic those of other, less severe conditions. This similarity can lead to delayed diagnosis and treatment, significantly impacting the prognosis. Understanding why pancreatic cancer symptoms resemble other diseases’ symptoms is crucial for early detection and better outcomes. This article will delve into the reasons behind this symptom overlap, explore common symptoms of pancreatic cancer, and provide insights on differentiating these symptoms from other ailments.
The anatomy and function of the pancreas
To comprehend why pancreatic cancer symptoms are easily confused with other conditions, it is essential to understand the pancreas’s role and location in the body. The pancreas is a gland behind the stomach, near the small intestine. It plays a vital role in digestion and blood sugar regulation by producing digestive enzymes and hormones like insulin.
Because of its deep location in the abdomen and its integral role in the digestive system, any disruption caused by a tumor can manifest as digestive issues or abdominal discomfort, symptoms common to many gastrointestinal diseases.
Common symptoms of pancreatic cancer
Pancreatic cancer is often referred to as a silent disease because its symptoms typically do not appear until the disease has progressed. When symptoms do present, they are usually nonspecific and can be easily attributed to other conditions. Some of the most common symptoms include:
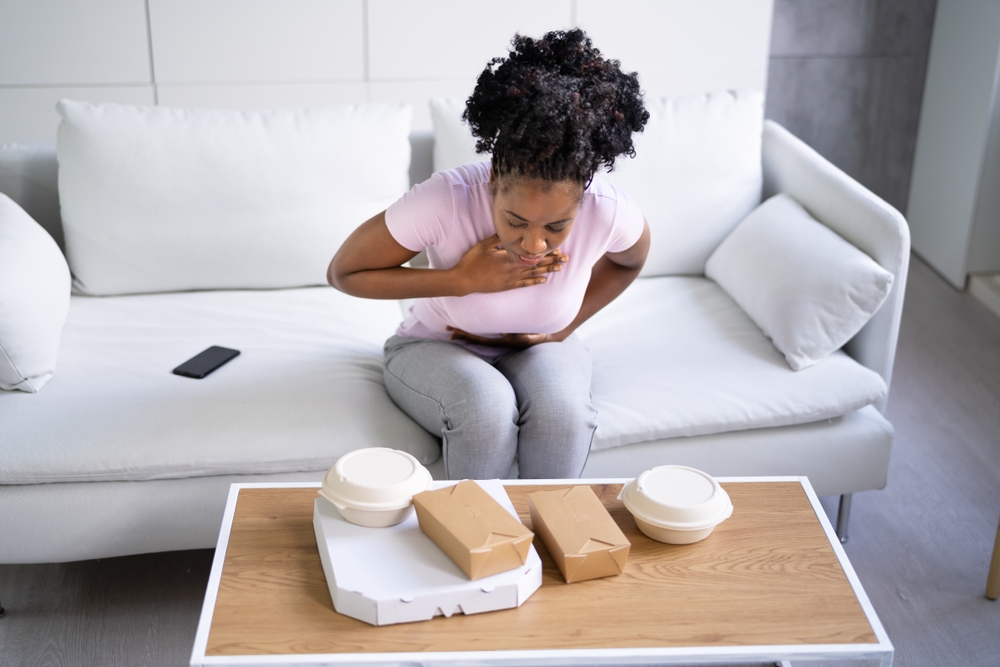
- Abdominal pain: Pain in the upper abdomen that may radiate to the back. This pain can be intermittent or constant and is often mistaken for ulcers or gallstones.
- Jaundice: Yellowing of the skin and eyes caused by the buildup of bilirubin. Jaundice is commonly associated with liver disease, which can confuse the diagnosis.
- Weight loss: Unexplained weight loss is a common symptom of many cancers, including pancreatic cancer. It can also be related to diabetes, thyroid disorders, or gastrointestinal issues.
- Nausea and vomiting: These symptoms can result from the pressure a pancreatic tumor places on the stomach, mimicking conditions like gastritis or peptic ulcer disease.
- Loss of appetite: A decreased desire to eat, which can accompany many chronic illnesses.
- Diabetes: Sudden onset of diabetes, especially in individuals with no family history of the disease, can be a sign of pancreatic cancer. This is because the pancreas is responsible for insulin production.
Overlapping symptoms with other diseases
The symptoms of pancreatic cancer overlap with those of many other diseases, making early detection challenging. Here are a few conditions with similar symptoms:
- Gallstones: Both pancreatic cancer and gallstones can cause abdominal pain, nausea, and jaundice. Gallstones block the bile duct, which can lead to similar symptoms.
- Gastritis and peptic ulcers: These conditions can cause upper abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, closely mimicking pancreatic cancer symptoms.
- Chronic pancreatitis: Chronic inflammation of the pancreas can cause pain and digestive problems similar to those seen in pancreatic cancer.
- Hepatitis and liver disease: Jaundice is a common symptom of both liver diseases and pancreatic cancer, often leading to initial misdiagnosis.
- Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS): Symptoms like abdominal pain, changes in bowel habits, and weight loss can occur in both IBS and pancreatic cancer.
Why symptoms overlap
Several factors contribute to the symptom overlap between pancreatic cancer and other diseases:
- Shared anatomical space: The pancreas is located near many other organs, including the liver, stomach, and intestines. Tumors in the pancreas can affect these organs, leading to symptoms that are not unique to pancreatic cancer.
- Common pathways of disease: Many symptoms of pancreatic cancer are due to blockages in ducts or pressure on surrounding organs, which can occur in other diseases as well.
- Hormonal and metabolic effects: The pancreas’s role in hormone production means that pancreatic cancer can affect blood sugar levels and metabolism, leading to symptoms that resemble diabetes or metabolic disorders.
Importance of early detection
Early detection of pancreatic cancer significantly improves the chances of successful treatment. However, the similarity of its symptoms to other diseases complicates this process. Here are some strategies for early detection:
- Regular check-ups: Routine medical check-ups can help monitor any unusual symptoms or changes in health.
- Awareness of risk factors: Individuals with a family history of pancreatic cancer, chronic pancreatitis, or sudden onset diabetes should be particularly vigilant.
- Advanced screening methods: Techniques like endoscopic ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can help detect pancreatic tumors earlier than traditional methods.
- Genetic testing: For those with a strong family history, genetic testing can identify mutations associated with increased pancreatic cancer risk.
Conclusion
Pancreatic cancer is a severe disease with a high mortality rate, primarily due to its late diagnosis. The overlap of its symptoms with those of other, less severe conditions contributes to this problem. Understanding why these symptoms are similar and being aware of the common signs can aid in earlier detection and better outcomes. Regular medical check-ups, awareness of personal risk factors, and advanced screening techniques are vital tools in the fight against pancreatic cancer. By staying informed and vigilant, individuals can improve their chances of catching this silent disease in its earlier, more treatable stages.
This story was created using AI technology.