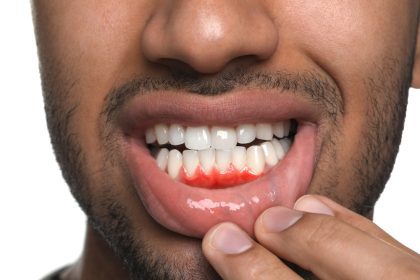
Dental bleeding can be a concerning issue, whether it occurs during brushing, flossing, or spontaneously. Understanding the root causes of dental bleeding is essential for maintaining oral health and preventing more serious conditions. One of the primary causes of dental bleeding is gum disease, also known as periodontal disease. This condition ranges from gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease, to periodontitis, a more severe form that can lead to tooth loss.
Gingivitis is characterized by red, swollen gums that bleed easily. It is often caused by poor oral hygiene, which leads to the accumulation of plaque—a sticky film of bacteria—on the teeth and gums. When plaque is not removed through regular brushing and flossing, it hardens into tartar, which further irritates the gums and exacerbates bleeding.
Other common causes of dental bleeding include aggressive brushing or flossing, using a toothbrush with hard bristles, hormonal changes (such as during pregnancy), certain medications (like blood thinners), and nutritional deficiencies, particularly a lack of vitamin C and vitamin K. Additionally, habits such as smoking can increase the risk of gum disease and dental bleeding.
Recognizing the symptoms and signs
Dental bleeding is often accompanied by other symptoms that can help identify the underlying issue. Recognizing these symptoms is crucial for seeking timely treatment and preventing further complications. Common symptoms associated with dental bleeding include:
- Swollen, red gums: Inflammation and discoloration of the gums often indicate gingivitis or periodontitis.
- Persistent bad breath: Also known as halitosis, bad breath can be a sign of plaque buildup and gum disease.
- Receding gums: When the gums pull away from the teeth, it can create pockets where bacteria thrive, leading to bleeding and infection.
- Loose teeth: Advanced gum disease can cause the supporting structures of the teeth to weaken, resulting in tooth mobility.
- Pain or discomfort: Tenderness or pain in the gums, especially when eating or brushing, is a common symptom of gum disease.
If you notice any of these signs, it’s essential to consult with a dental professional. Early intervention can prevent the progression of gum disease and preserve your oral health.
Preventive measures and treatment options
Preventing dental bleeding involves adopting a comprehensive oral hygiene routine and addressing any underlying health issues. Here are some effective preventive measures:
- Maintain good oral hygiene: Brush your teeth at least twice a day with a soft-bristled toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food particles from between your teeth and along the gumline.
- Regular dental check-ups: Visit your dentist for regular cleanings and check-ups. Professional cleanings can remove tartar that cannot be eliminated by brushing and flossing alone.
- Healthy diet: Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Ensure adequate intake of vitamin C and vitamin K to support gum health.
- Avoid tobacco products: Smoking and the use of other tobacco products can worsen gum disease and increase the risk of dental bleeding.
- Gentle brushing and flossing: Avoid aggressive brushing and flossing techniques that can damage the gums. Use gentle, circular motions when brushing and be careful not to snap the floss against the gums.
For those already experiencing dental bleeding, several treatment options are available depending on the severity of the condition. These include:
- Professional cleaning: Scaling and root planing are deep cleaning procedures that remove plaque and tartar from above and below the gumline.
- Medications: Antibiotic mouth rinses or topical gels can help control bacterial infection and reduce inflammation.
- Surgical treatments: In advanced cases, surgical procedures such as flap surgery, bone grafts, or tissue grafts may be necessary to restore gum health and prevent tooth loss.
Emotional and psychological impact of dental bleeding
Dental bleeding can have a significant emotional and psychological impact on individuals. The fear of bleeding gums can lead to anxiety about dental visits, which in turn can result in neglecting oral care. Moreover, persistent bad breath and visible gum issues can affect self-esteem and social interactions, causing embarrassment and self-consciousness.
Understanding the emotional aspects of dental health is crucial for providing comprehensive care. Dental professionals should approach treatment with empathy, addressing both the physical and emotional concerns of their patients. Encouraging open communication and providing reassurance can help alleviate anxiety and promote a positive attitude towards oral health.
Conclusion: Taking control of your oral health
Dental bleeding is a common but preventable issue. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and adopting preventive measures, you can maintain healthy gums and teeth. Regular dental check-ups and a consistent oral hygiene routine are key to preventing and managing dental bleeding. Remember, early intervention is essential for preserving your oral health and overall well-being.
If you experience dental bleeding, don’t ignore it. Consult with a dental professional to identify the cause and receive appropriate treatment. Taking proactive steps today can ensure a healthy, confident smile for years to come.
This story was created using AI technology.