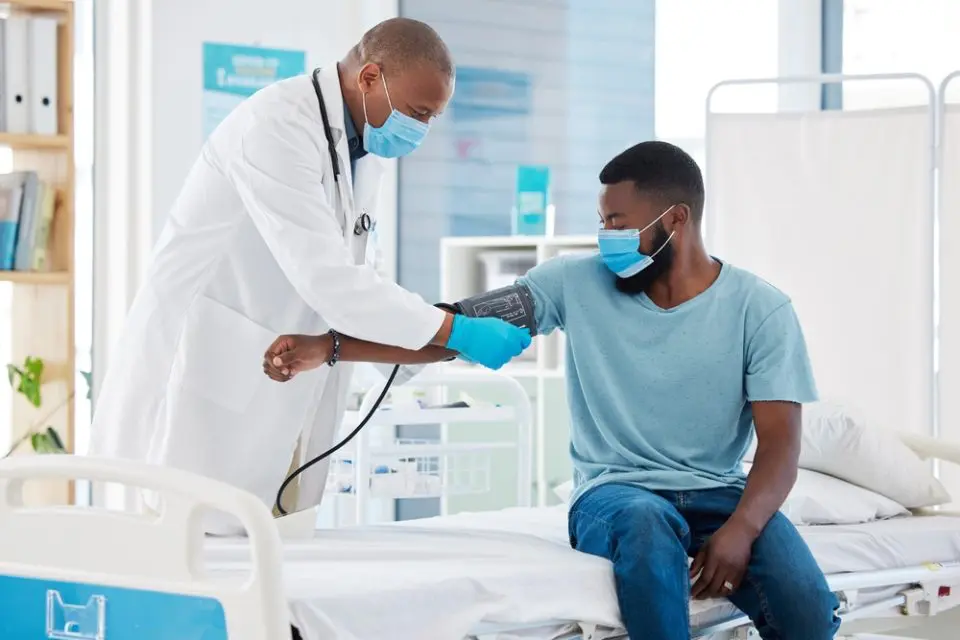
Understanding the impact of arm positioning on blood pressure readings
Recent research from Johns Hopkins University has revealed how seemingly small variations in arm positioning can significantly affect the accuracy of blood pressure measurements. This study provides valuable insights for both healthcare providers and patients, shedding light on the importance of proper technique when measuring blood pressure to avoid misdiagnoses and ensure reliable results.
Research findings on positioning impact
The study examined the effects of different arm positions on blood pressure readings, and the results were striking. The research involved testing three distinct arm positions and recording blood pressure measurements. When the arm was supported at heart level, the average baseline blood pressure readings were found to be 126/74 mmHg. However, when the arm was left unsupported, measurements showed increases of up to 6.5 mmHg in systolic readings and 4.4 mmHg in diastolic readings. This variation emphasizes the critical role that arm position plays in obtaining an accurate blood pressure reading.
Clinical implications
These findings have significant implications for clinical practice, particularly in managing patients with hypertension or those at risk for cardiovascular diseases. The accuracy of blood pressure measurements is crucial, as blood pressure readings are often used to assess cardiovascular health and guide treatment decisions. With optimal blood pressure targets being under 120/80 mmHg for reducing the risk of heart disease, small inaccuracies in measurement could lead to either over-diagnosing or under-diagnosing conditions like hypertension, affecting treatment strategies.
Improper arm positioning could easily lead to an overestimation or underestimation of a patient’s blood pressure, which can mislead healthcare professionals in making accurate diagnoses. Even minor discrepancies in blood pressure readings could result in improper treatment recommendations, potentially compromising patient care.
Measurement best practices
To obtain reliable blood pressure readings, healthcare professionals and patients need to follow best practices that include proper positioning and environmental factors. The first step is to ensure that the arm is supported at heart level. This means that the arm should be resting on a surface like a table or a pillow to ensure it is neither too high nor too low, as this can distort readings.
Correct posture is also essential for obtaining accurate readings. Both the patient and healthcare provider should ensure that the patient is sitting comfortably with their back supported, feet flat on the floor, and legs uncrossed. The wrist and forearm should be supported to prevent muscle strain, which could alter blood pressure readings.
Equally important is avoiding interference factors like caffeine consumption, physical activity, or stress just before taking a reading. These factors can cause short-term increases in blood pressure and potentially skew results. If a patient has recently consumed caffeine or engaged in physical activity, it’s best to wait at least 30 minutes before taking the measurement.
Additional measurement considerations
While arm positioning plays a central role in ensuring accurate blood pressure measurements, it is not the only factor to consider. Proper cuff size is also a crucial aspect of accurate readings. A cuff that is too small or too large for the patient’s arm size can lead to incorrect measurements. Healthcare professionals should always ensure that the cuff is appropriately sized for the patient’s arm circumference to avoid measurement discrepancies.
In addition, when assessing blood pressure, it is important to take readings on both arms to identify potential differences. Significant discrepancies between arms can indicate underlying cardiovascular issues, such as peripheral artery disease, which may require further evaluation.
Implementation strategies
To improve the accuracy of blood pressure readings, both healthcare providers and patients need to implement consistent measurement protocols. Healthcare institutions should train staff to prioritize proper arm positioning and ensure that patients are aware of the importance of following these guidelines during routine checkups.
Establishing these protocols in clinical settings can help eliminate common errors and reduce the risk of misdiagnosis. Healthcare providers should also consider using automated blood pressure monitors, which can reduce human error. However, even with automated devices, it is essential to ensure that arm positioning and other factors like cuff size are correctly addressed.
For patients taking their blood pressure at home, following the same guidelines is equally important. Using a reliable home blood pressure monitor, ensuring that the arm is supported, and avoiding interference factors can all contribute to more accurate self-monitoring.
Conclusion
This research underscores the significance of arm positioning in achieving accurate blood pressure readings. The findings from Johns Hopkins University reveal how small variations in technique can lead to major discrepancies in measurements, impacting diagnosis and treatment. By adhering to proper positioning guidelines, including supporting the arm at heart level and ensuring the correct posture, both healthcare providers and patients can significantly improve the reliability of blood pressure assessments.
As the healthcare community continues to prioritize cardiovascular health, it’s essential to recognize the critical role that accurate blood pressure measurements play in preventing and managing hypertension. By implementing consistent measurement protocols and educating patients on best practices, we can enhance diagnostic accuracy, improve treatment outcomes, and ultimately promote better health for all.