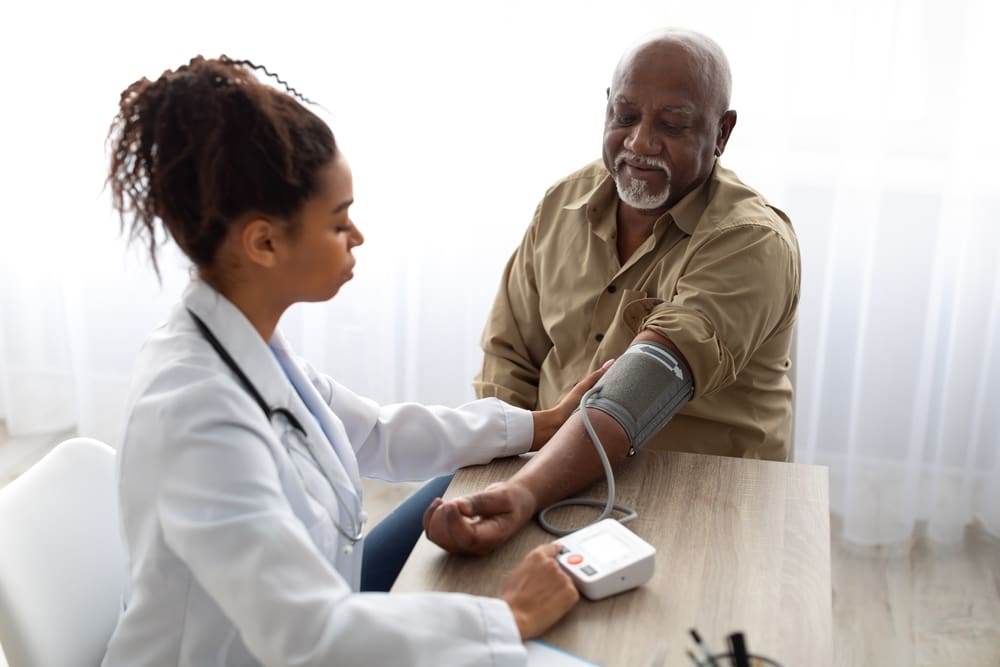
Blood pressure serves as the body’s vital barometer, quietly measuring the intricate balance of cardiovascular health every moment of every day. Medical research reveals that nearly half of American adults misunderstand their blood pressure readings, leading to potentially dangerous oversight of this critical health indicator.
Decoding the numbers
Blood pressure measurements tell a complex story through two distinct numbers, each representing different phases of the heart’s rhythm. The first number, systolic pressure, captures the force when the heart contracts, while the second number, diastolic pressure, measures the pressure between beats.
Modern medical guidelines establish five distinct categories for blood pressure readings:
- The optimal range maintains systolic pressure below 120 and diastolic below 80
- Elevated readings show systolic between 120-129 while diastolic remains below 80
- Stage 1 hypertension indicates systolic of 130-139 or diastolic of 80-89
- Stage 2 hypertension occurs with systolic above 140 or diastolic above 90
- Hypertensive crisis emerges when systolic exceeds 180 or diastolic surpasses 120
The unseen impact
High blood pressure often works silently, gradually affecting multiple organ systems without obvious symptoms. Recent studies indicate that sustained elevated pressure can lead to significant damage long before obvious signs emerge. The cardiovascular system bears the initial burden, but the effects cascade throughout the body, impacting:
The heart must work harder against increased resistance, potentially leading to enlargement and weakness over time. Recent research indicates that this added strain can age the heart up to seven years faster than normal.
Kidney function faces particular challenges as tiny blood vessels struggle against increased pressure, potentially compromising their filtering capability. Medical data suggests that approximately 30% of patients with untreated hypertension develop kidney complications within ten years.
Brain health remains particularly vulnerable to blood pressure fluctuations. Studies show that maintaining optimal pressure levels can reduce the risk of cognitive decline by up to 20% in adults over 50.
Understanding low pressure
While high blood pressure often dominates health discussions, low blood pressure presents its own set of challenges. Medical research identifies several common triggers for low pressure, including:
Dehydration remains the most frequent cause, particularly among active individuals and older adults. Studies suggest that even mild dehydration can lower blood pressure significantly.
Certain medications may inadvertently reduce blood pressure below optimal levels. Healthcare providers now recommend regular monitoring for patients taking multiple prescriptions.
Underlying health conditions sometimes manifest through unexpectedly low pressure readings, making regular medical check-ups essential for proper diagnosis.
The lifestyle connection
Managing blood pressure effectively often begins with lifestyle modifications. Recent studies highlight several key factors that significantly impact blood pressure levels:
Dietary choices play a crucial role, with sodium intake particularly significant. Research indicates that reducing sodium consumption by just 1,000 milligrams per day can lower systolic pressure by 5-6 points.
Physical activity provides multiple benefits for blood pressure regulation. Modern studies suggest that regular exercise can reduce systolic pressure by an average of 4-8 points within three months.
Stress management techniques show promising results in blood pressure control. Medical research reveals that practicing stress reduction methods for 15 minutes daily can lower systolic pressure by 3-5 points.
Modern monitoring methods
Technology has revolutionized blood pressure monitoring, making it more accessible and accurate than ever before. Smart devices now offer continuous monitoring capabilities, providing detailed insights into pressure patterns throughout the day.
Healthcare providers increasingly recommend home monitoring systems, which can detect subtle variations that might be missed during occasional office visits. These devices help identify:
- Morning surge patterns that might indicate increased cardiovascular risk
- Nighttime variations that could signal underlying health issues
- Exercise-related changes that inform activity recommendations
- Stress-induced fluctuations that guide lifestyle modifications
The path to prevention
Prevention strategies continue evolving as research reveals new insights into blood pressure regulation. Current medical guidelines emphasize:
Regular screening remains essential, with frequency determined by individual risk factors and current readings. Healthcare providers now recommend annual checks for adults with optimal pressure and more frequent monitoring for those with elevated readings.
Lifestyle modifications show increasing importance in prevention strategies. Studies demonstrate that combining multiple healthy habits can reduce the risk of developing hypertension by up to 80%.
Genetic factors play a significant role in blood pressure tendencies, making family history an important consideration in prevention planning. Medical professionals now recommend earlier screening for individuals with family histories of hypertension.
Understanding blood pressure goes beyond simply knowing the numbers. It requires awareness of personal risk factors, regular monitoring, and proactive management strategies. As medical science advances, new tools and treatments continue emerging, offering hope for better blood pressure control and improved cardiovascular health for millions of Americans.