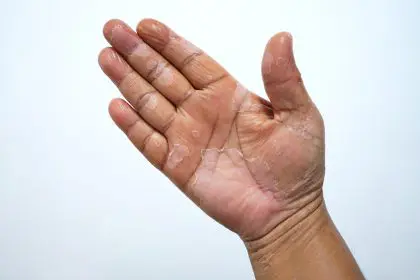
The intersection of eczema treatment and long-term health consequences has revealed an emerging crisis in skincare management. What begins as a standard treatment protocol often evolves into an unexpected battle with topical steroid withdrawal, challenging conventional approaches to eczema care. Many individuals who rely on steroid creams for relief find themselves caught in a cycle of dependency, facing severe withdrawal symptoms when attempting to discontinue their use.
Understanding the steroid withdrawal phenomenon
The hidden risks of prolonged steroid use
The widespread use of topical steroids for eczema management has unveiled a complex challenge facing patients worldwide. This condition, known as topical steroid withdrawal (TSW), presents through various symptoms that often surpass the severity of the original skin condition. As reliance on steroids grows, so does the potential for withdrawal symptoms, which can include severe redness, burning, itching, and skin peeling.
The body’s reaction to steroid dependency
Prolonged exposure to topical steroids affects the body’s natural ability to regulate inflammation. Over time, the skin adapts to these medications, and when the steroids are discontinued, the body struggles to regain balance. This sudden loss of external support results in a rebound effect, where inflammation returns with greater intensity. Many patients describe withdrawal symptoms as worse than their initial eczema, making the condition difficult to manage.
The evolution of skin complications
From temporary relief to long-term damage
Initial relief from steroid treatments frequently masks the potential for long-term complications. The progression from manageable eczema to severe withdrawal symptoms highlights the complexity of prolonged steroid use. What begins as mild, intermittent flare-ups can transform into chronic, widespread inflammation that takes months or even years to resolve.
The challenge of misdiagnosis
Many individuals experiencing withdrawal symptoms are misdiagnosed with worsening eczema, leading to increased steroid prescriptions. This cycle perpetuates dependency and delays proper treatment. Without clear diagnostic guidelines, patients often struggle to find healthcare providers who recognize the signs of TSW.
Medical perspectives and challenges
The struggle to define and diagnose TSW
The medical community’s understanding of TSW continues to evolve, presenting challenges in diagnosis and treatment. The condition lacks standardized diagnostic criteria, leading to varying approaches in recognition and management. Because withdrawal symptoms can mimic severe eczema, many doctors remain skeptical about its existence, leaving patients without proper guidance.
Conflicting treatment approaches
There is no universal treatment for TSW, and opinions on management vary widely. Some healthcare professionals advocate for gradual steroid tapering, while others recommend an immediate withdrawal approach. Patients must navigate conflicting advice while enduring severe symptoms, making it a physically and emotionally taxing experience.
Alternative treatment approaches
Exploring non-steroidal treatment options
The search for effective alternatives has led to various non-steroidal options showing promise in managing eczema without withdrawal risks. These alternatives include newer medications and traditional remedies that support skin healing through different mechanisms.
Barrier-repair therapies
Moisturizers and emollients designed to strengthen the skin barrier help reduce flare-ups and improve overall skin resilience. Ingredients such as ceramides, fatty acids, and cholesterol play a crucial role in maintaining hydration and protecting against environmental triggers.
Lifestyle modifications for long-term management
Diet, stress management, and environmental factors contribute significantly to eczema flare-ups. Identifying food sensitivities, using gentle skincare products, and managing stress can lead to noticeable improvements without the need for steroids.
Biological treatments as an emerging solution
Recent advancements in dermatology have introduced biologic medications that target the immune system to reduce inflammation. While these treatments can be expensive, they offer a promising alternative for those seeking relief without the risks associated with steroids.
Building awareness and support
The rise of online support communities
The growing recognition of TSW has sparked a movement within the skincare community. Social media platforms have become crucial spaces for sharing experiences and information, creating support networks for those affected by this condition. Many individuals who felt isolated in their struggle now find solace in connecting with others who understand their journey.
The role of patient advocacy in driving change
Advocacy groups and patient-led initiatives push for increased research, better diagnostic guidelines, and safer treatment options. These efforts encourage medical professionals to take TSW more seriously and to consider alternative treatment approaches.
Future directions in treatment
The shift toward safer skincare practices
The landscape of eczema care continues to evolve with increased understanding of TSW. Research efforts focus on developing safer alternatives and better protocols for managing existing treatments. Dermatologists are beginning to recognize the need for caution when prescribing steroids and are exploring holistic approaches to managing eczema.
The importance of informed decision-making
Patients and healthcare providers must work together to develop personalized treatment plans that consider long-term skin health. Education on the potential risks of steroid use allows individuals to make informed choices about their care.
The journey through topical steroid withdrawal represents a significant challenge in modern dermatology. Understanding these complications helps create more effective treatment approaches while supporting those affected by this condition. The future of eczema care depends on balancing effective treatment with long-term safety considerations.
As awareness grows, the medical community and patients alike work toward better solutions for managing eczema without risking severe withdrawal effects. This collaborative effort promises to reshape the approach to eczema treatment, prioritizing both immediate relief and long-term skin health. The path forward requires continued research, improved communication between healthcare providers and patients, and ongoing development of alternative treatments. Success lies in creating comprehensive care approaches that address both immediate symptoms and potential long-term consequences of treatment choices.