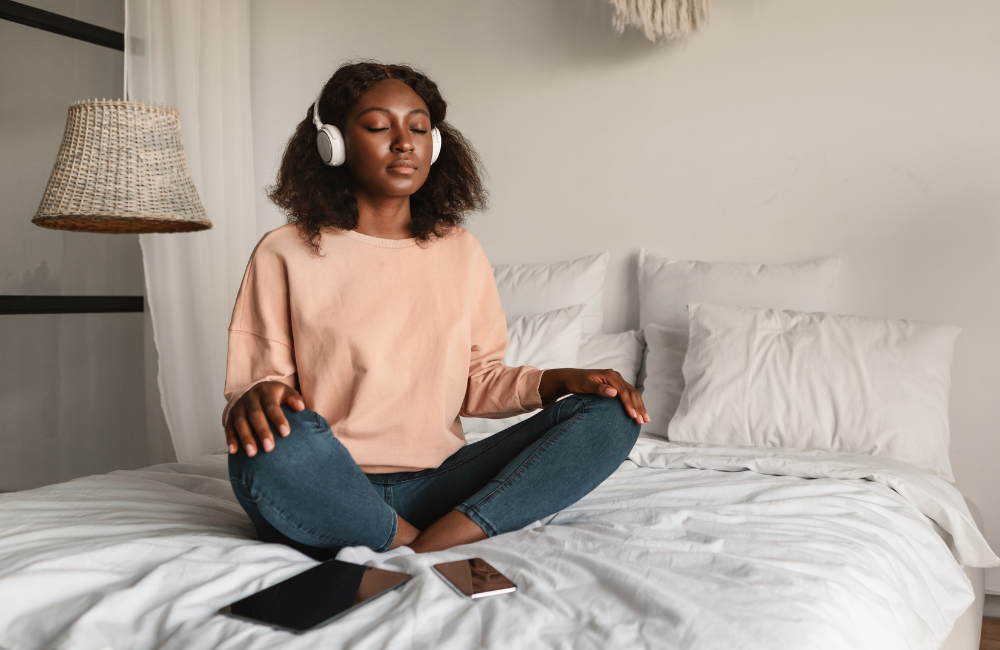
Music has long been recognized for its therapeutic properties, dating back to ancient civilizations that used rhythmic sounds for healing and spiritual connection. Today, combining music with meditation offers an accessible gateway to mindfulness for those who struggle with traditional silent practices. The harmonious integration of these two powerful modalities creates a multisensory experience that can deepen relaxation, enhance focus, and elevate mood.
1. The science behind sound
The relationship between music and our neurological systems runs remarkably deep. When we listen to music, our brains release dopamine—the same neurotransmitter associated with pleasurable experiences like eating and physical affection. Research from neuroscience laboratories has demonstrated that specific sound frequencies can alter brainwave patterns, potentially inducing states of deep relaxation similar to those achieved through traditional meditation.
Sound waves physically affect our bodies beyond our auditory system. The vibrations from music move through tissues, potentially reducing muscle tension and lowering cortisol levels. This physiological response creates an ideal foundation for meditation practices by preparing the body to enter deeper states of relaxation.
2. Guided sonic journeys
One of the most accessible approaches to music meditation involves following professionally crafted guided journeys. These audio experiences combine spoken instructions with carefully selected background compositions designed to facilitate specific meditative states. The verbal guidance provides structure for beginners while the underlying soundscapes help maintain focus and deepen the practice.
Many guided sonic journeys incorporate binaural beats—slightly different frequencies played in each ear that create a perceived third frequency in the brain. These beats can potentially entrain brainwaves to frequencies associated with meditation, making it easier to achieve focused awareness or deep relaxation even for those new to meditation.
This technique proves particularly valuable for individuals with busy minds who find traditional silent meditation challenging. The combination of verbal guidance and supportive sounds creates multiple focus points that can help prevent the mind from wandering to daily stressors or distractions.
3. Instrumental immersion technique
The instrumental immersion approach involves selecting pieces without lyrics and using them as focal points for attention. Classical compositions, ambient soundscapes, and traditional instruments like singing bowls or the hang drum create rich sonic environments for meditation without the potential distraction of words.
To practice this technique, select a piece approximately 15-20 minutes in length with minimal dramatic shifts. Begin by sitting comfortably and taking several deep breaths before starting the music. As the composition plays, notice individual instruments, rhythmic patterns, or tonal qualities rather than analyzing the music intellectually. When the mind wanders, gently return focus to a specific element of the sound.
This approach trains selective attention—the ability to focus on specific sensory input while filtering out distractions. Regular practice strengthens this cognitive skill, potentially improving concentration in other areas of life beyond the meditation session.
4. Body resonance practices
The vibrational qualities of music can be used as tools for somatic awareness during meditation. This technique involves placing attention on how different sounds physically resonate within the body rather than experiencing music solely as an auditory phenomenon.
Begin by selecting music with pronounced bass tones or resonant instruments like gongs or singing bowls. Sit or lie down comfortably and play the selection at a volume where you can physically feel the vibrations. As you listen, systematically scan through your body, noticing where you physically sense the music. Some frequencies might create sensations in the chest, while others resonate in the abdomen or even extremities.
This practice combines meditation with elements of sound healing, potentially releasing tension from areas where stress accumulates. By maintaining awareness of bodily sensations throughout the session, practitioners develop greater interoceptive awareness—the ability to perceive internal physical states—which research suggests may improve emotional regulation and stress management.
5. Creative visualization journey
Music provides a powerful scaffold for visualization practices, which combine the benefits of meditation with the creativity-enhancing effects of guided imagery. This approach uses music as an emotional backdrop for imagined scenarios that promote relaxation, inspiration, or personal growth.
Select music that evokes specific emotional qualities aligned with your meditation goals—perhaps serene natural soundscapes for relaxation or more dynamic compositions for energizing practices. Begin by establishing a relaxed state through several deep breaths, then allow the music to suggest imagery, colors, or environments. Instead of controlling the visualization rigidly, let the changing qualities of the music guide the unfolding mental landscape.
This technique leverages the brain’s natural tendency to create associations between sounds and visual or emotional experiences. The resulting state combines focused attention with creative engagement, potentially accessing subconscious material that might not emerge during more structured meditation practices.
6. Mindful music creation
Meditation need not be passive. Engaging in the creation of simple music can become a profound meditative practice itself. This approach shifts from consumption to participation, employing repetitive sound-making as a focus point for attention.
Simple instruments like frame drums, rain sticks, or even household items repurposed as percussion can serve as tools for this practice. Begin by establishing a simple, repeating pattern that can be maintained with minimal conscious effort. As you continue the rhythm, shift attention to the physical sensations of creating sound, the acoustic properties of each repetition, and the spaces between sounds.
The repetitive nature of this practice creates a state similar to mantra meditation but engages the body more actively. The combination of physical movement, sound production, and focused attention creates a multisensory anchor for awareness, making it particularly effective for people who find stillness challenging.
7. Lyrics as contemplative mantras
While instrumental music often serves as the foundation for meditation practices, carefully selected lyrical content can transform a listening session into a contemplative experience. This approach uses meaningful phrases or poetic language as focus points for reflection during meditation.
Select songs with lyrics that explore themes of presence, compassion, interconnection, or personal growth. Rather than passive listening, approach the experience as an active contemplation by focusing intently on the meaning behind the words. When particularly resonant phrases appear, mentally repeat them several times, allowing their significance to deepen.
This practice combines the traditional use of mantras in meditation with contemporary musical forms. The emotional resonance of music enhances the impact of meaningful lyrics, potentially creating profound insights or perspective shifts that might not occur through intellectual contemplation alone.
By exploring these diverse approaches to music meditation, practitioners can discover which techniques best complement their unique preferences and meditation goals. The flexibility of these methods makes meditation more accessible to individuals who might otherwise struggle with traditional approaches, opening doorways to mindfulness through the universal language of music.