Study shows combining resistance training with protein-rich diet preserves strength during rapid weight reduction
The latest generation of weight loss medications has transformed how many approach body transformation, offering unprecedented results for those struggling with excess weight. However, a common concern has emerged as these drugs gain popularity: significant muscle loss alongside fat reduction.
New research presented at the European Congress on Obesity provides welcome news for those using these medications. The study shows that with the right approach, users can shed substantial fat while preserving most of their muscle mass—a crucial factor for long-term health and mobility.
Understanding how weight loss shots work
GLP-1 medications mimic a natural gut hormone that regulates blood sugar and appetite. These injectable drugs promote weight loss through multiple mechanisms, including slowing digestion, reducing hunger signals in the brain, and altering how the body processes sugars.
The medications work primarily by making users feel fuller longer and reducing interest in food, particularly high-calorie options. This leads to significantly lower calorie intake without the extreme hunger often experienced during traditional dieting.
Currently approved medications in this category include versions that work solely on GLP-1 receptors and newer dual-action drugs that target both GLP-1 and GIP receptors, potentially offering even greater effectiveness.
The muscle preservation challenge
While these medications excel at helping people lose weight, a common side effect has been concerning health experts: the loss of lean muscle mass alongside fat. Since muscle tissue burns more calories than fat even at rest, preserving muscle is crucial for maintaining metabolism during weight loss.
Muscle also plays essential roles in overall health, including regulating blood sugar, supporting bone density, and maintaining physical independence as people age. The ability to preserve muscle during rapid weight loss represents a significant breakthrough in obesity treatment.
Early users of these medications often reported feeling weaker during their weight loss journey, leading researchers to investigate how to mitigate this effect.
Key findings from the latest research
The six-month study involved 200 adults aged 18 to 65 with BMIs of 25 kg/m² or higher. All participants received either semaglutide or tirzepatide injections alongside guidance from obesity specialists about resistance training and protein intake.
The results proved encouraging for those concerned about muscle preservation:
Women in the study reduced their average weight from 156 pounds to 137 pounds—a 12% reduction. Of this 19-pound weight loss, nearly 90% came from fat tissue while only about 1.4 pounds was muscle.
Men experienced similarly impressive results, dropping from 223 pounds to 193 pounds on average—a 13% reduction. Their composition changes showed approximately 25 pounds of fat loss with just 2.4 pounds of muscle reduction.
Perhaps most importantly, participants maintained over 95% medication adherence during the first three months and 89% after six months, demonstrating that the regimen was sustainable for most users.
The protein-training connection
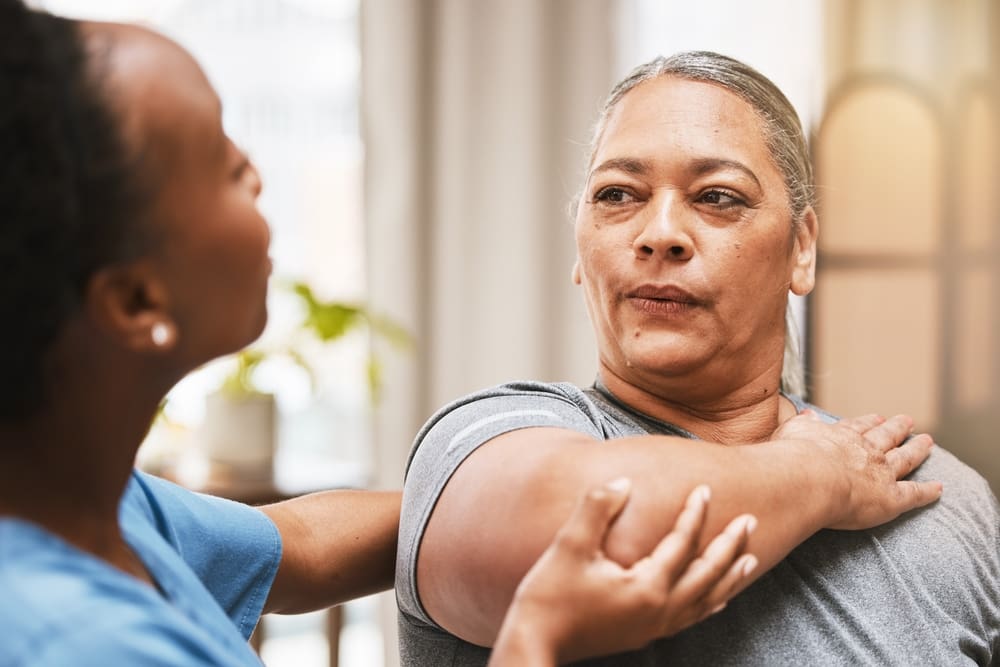
The research highlights two critical factors that appeared to make the difference in preserving muscle: consistent resistance training and adequate protein consumption.
Unlike earlier studies where participants received only the medication without specific exercise guidance, this research prescribed regular strength training sessions. The resistance work included both bodyweight exercises and weighted movements designed to stimulate muscle retention during the caloric deficit created by the medications.
Equally important was protein intake. Participants received guidance on consuming sufficient protein throughout the day, with recommendations for both quantity and timing to maximize muscle preservation.
The protein consumption appeared to provide the building blocks necessary for maintaining muscle tissue even as overall calorie intake decreased substantially. Participants were encouraged to prioritize protein at each meal, particularly after resistance training sessions.
Practical applications for medication users
For those using or considering GLP-1 medications for weight loss, the research suggests several practical strategies to minimize muscle loss:
Engage in regular resistance training at least twice weekly, focusing on major muscle groups. Even basic exercises like squats, push-ups, and resistance band work can help maintain muscle strength.
Prioritize protein consumption, aiming for amounts appropriate to body weight and activity level. Quality protein sources include lean meats, dairy, eggs, legumes, and plant-based protein supplements.
Work with healthcare providers who understand the importance of body composition, not just weight reduction. This might include fitness professionals, registered dietitians, and medical providers specializing in weight management.
Consider tracking body composition rather than just weight to ensure fat is being lost while muscle is preserved. This can be done through various methods including specialized scales, DEXA scans, or professional assessments.
Supplement with appropriate vitamins and minerals, as rapid weight loss and reduced food intake can sometimes lead to nutritional deficiencies that affect muscle function.
The future of weight management research
As the study continues, researchers are analyzing differences between specific medications and how they affect body composition. Initial findings suggest that both single and dual-action medications can be effective when combined with appropriate exercise and nutrition.
The research team is also investigating how different types of resistance training might affect results, along with variations in protein timing and sources. This ongoing work aims to develop even more effective protocols for preserving muscle during medication-assisted weight loss.
The findings represent a significant step forward in addressing one of the most common concerns about these popular medications. By demonstrating that muscle loss can be minimized with the right approach, the research opens the door to more effective, sustainable weight management strategies.
Beyond the scale: why muscle matters
The emphasis on preserving muscle highlights an important shift in how health experts approach weight management. Rather than focusing solely on total weight reduction, modern approaches prioritize body composition—the ratio of fat to muscle tissue.
Muscle tissue offers numerous health benefits beyond aesthetics:
Metabolic health: Muscle helps regulate blood sugar and improves insulin sensitivity, potentially reducing diabetes risk.
Longevity: Greater muscle mass in middle and older age correlates with longer lifespans and fewer chronic health conditions.
Functional ability: Maintaining muscle supports everyday activities and independence, particularly important as people age.
Bone health: Muscle contraction stimulates bone growth and maintenance, helping prevent osteoporosis.
Mental wellbeing: Strength training has been shown to improve mood, cognitive function, and sleep quality—all factors that support long-term weight management.
Balancing rapid results with long-term health
The finding that proper exercise and nutrition can preserve muscle during medication-assisted weight loss helps bridge the gap between quick results and sustainable health outcomes.
Many people using these medications report dramatic weight reduction—sometimes 15-20% of their starting weight within a year. While these results can profoundly improve health markers like blood pressure and blood sugar, concerns about muscle loss have tempered enthusiasm among some health professionals.
The new research suggests that with appropriate guidance, users can experience the benefits of significant weight reduction while minimizing drawbacks related to muscle loss. This balanced approach may represent the future of obesity treatment, combining effective medications with evidence-based lifestyle modifications.
For those considering or currently using weight loss medications, the message is clear: the drugs can be remarkably effective, but complementing them with resistance training and adequate protein maximizes benefits while minimizing downsides.
As research continues and clinical experience grows, the protocols for preserving muscle during medication-assisted weight loss will likely become more refined, offering even better outcomes for the millions struggling with excess weight and its health consequences.