Dark patches from eczema can last longer than the condition itself – here’s what dermatologists recommend for lasting relief
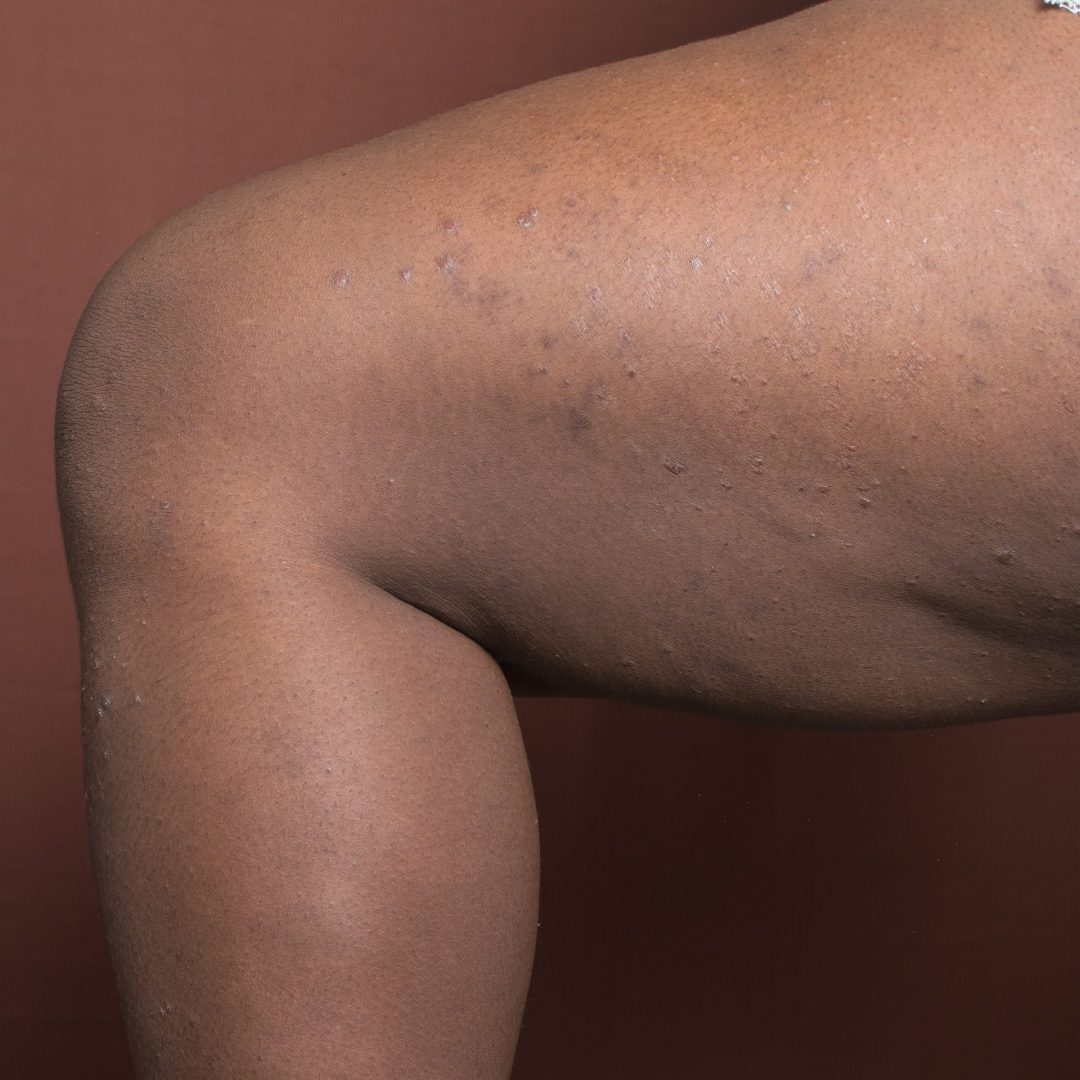
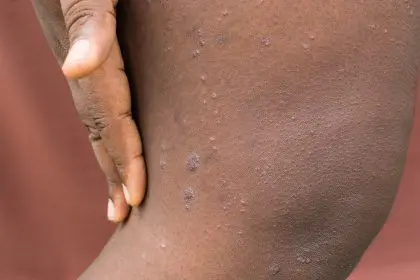
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from atopic dermatitis (commonly known as eczema) affects many individuals with melanin-rich skin, often causing more distress than the original condition. When inflammation triggers excess melanin production, the resulting dark patches can persist for months or even years after eczema symptoms subside.
The good news? Several treatment options exist specifically formulated for darker skin tones. This comprehensive guide explores the most effective therapies for fading these stubborn dark marks while protecting your skin’s natural beauty.
What happens to darker skin after eczema flares
Atopic dermatitis creates a frustrating cycle for many people with melanin-rich skin. During flare-ups, the skin becomes inflamed, dry, and intensely itchy. As this inflammation resolves, the healing process often triggers excessive melanin production – the natural pigment responsible for skin color.
This phenomenon, called post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), manifests as dark patches exactly where the eczema occurred. For individuals with naturally higher melanin levels, these dark spots appear more pronounced and can take significantly longer to fade compared to lighter skin tones.
Many patients report that these persistent dark patches cause more long-term distress than the temporary discomfort of eczema itself. The discoloration can affect self-confidence and quality of life long after the initial eczema symptoms have resolved.
The 5 most effective treatments for eczema-related dark spots
Once atopic dermatitis is under control, several treatments can significantly reduce hyperpigmentation in darker skin tones. Each option works through different mechanisms, and combining approaches often yields the best results.
- Topical retinoids accelerate skin renewal
Retinoids, derived from vitamin A, work by speeding up your skin’s natural cell turnover process. This helps your body shed the darkened skin cells faster while promoting new, evenly pigmented skin cell growth.
Research shows three specific retinoids produce excellent results for hyperpigmentation in darker skin tones after consistent three-month use:
Tretinoin helps many patients achieve nearly complete improvement in stubborn dark patches.
Adapalene reduces both the intensity and number of dark spots for approximately two-thirds of users.
Tazarotene typically lightens hyperpigmentation by about 15 percent.
While effective, retinoids may cause temporary redness or irritation, particularly when beginning treatment. Starting with lower concentrations and gradually increasing strength helps minimize side effects. Most dermatologists recommend applying retinoids at night and always using sunscreen during daytime hours.
- Hydroquinone temporarily blocks melanin production
Hydroquinone remains one of the most studied ingredients for treating hyperpigmentation in darker skin tones. This prescription agent works by temporarily inhibiting tyrosinase, an enzyme necessary for melanin production.
Both 2% and 4% hydroquinone formulations effectively reduce dark spots, especially when combined with complementary treatments like retinoids or gentle chemical exfoliants. Studies consistently show significant improvement after 8-12 weeks of consistent use.
However, dermatologists emphasize that hydroquinone should only be used for limited periods (typically 2-3 months), followed by a break. Extended use can sometimes cause ochronosis – paradoxical bluish-black discoloration – particularly in melanin-rich skin. Always use hydroquinone under professional guidance.
- Chemical peels reveal fresher, more even-toned skin
Chemical peels work by applying specific acids to the skin that dissolve the connections between dead skin cells, removing the outermost layer to reveal fresher, more evenly pigmented skin underneath.
For melanin-rich skin, several gentle to moderate-strength acids have proven particularly effective:
Salicylic acid peels can lighten post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation by approximately 32 percent after a series of treatments.
Glycolic acid treatments reduce dark spots by about half after five months of consistent use.
Phytic acid and lactic acid provide gentler options with less irritation risk while still improving skin tone.
The key to successful chemical peel treatments in darker skin tones lies in selecting the appropriate acid concentration and frequency. Too aggressive treatment risks triggering new inflammation and worsening hyperpigmentation. Seeking treatment from dermatologists specializing in skin of color ensures safer, more effective results.
- Targeted laser therapy for stubborn discoloration
Laser treatments use specific wavelengths of light to target excess melanin without damaging surrounding tissue. For darker skin tones, certain lasers work better than others.
Q-switched Nd
laser therapy stands out as particularly effective for melanin-rich skin. This advanced treatment can produce dramatic improvement in stubborn dark spots, with some patients achieving complete clearing after approximately six sessions.
However, laser treatments require exceptional expertise when performed on darker skin tones. Inappropriate settings or techniques can worsen hyperpigmentation or cause scarring. Always seek treatment from dermatologists with specific experience treating skin of color with laser technology.
- Emerging ingredients offer gentler alternatives
Beyond traditional treatments, several newer ingredients show promise for treating hyperpigmentation with potentially fewer side effects:
Azelaic acid reduces inflammation while inhibiting tyrosinase, making it ideal for treating active eczema and resulting dark spots simultaneously.
Tranexamic acid (TXA) works through multiple mechanisms to regulate melanin production, with studies showing significant improvement and excellent tolerability in darker skin tones.
Cysteamine, a naturally occurring antioxidant, has demonstrated impressive pigment-lightening effects comparable to hydroquinone but with fewer adverse reactions.
Vitamin C and niacinamide formulations brighten skin tone gradually while strengthening the skin barrier – a critical benefit for eczema-prone skin.
These gentler options often work best when incorporated into comprehensive skincare routines rather than as standalone treatments.
Prevention strategies for melanin-rich skin
While treating existing hyperpigmentation remains important, preventing new dark spots offers the best long-term strategy. These approaches help minimize the risk of developing post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation after eczema flares:
Consistent eczema management forms the foundation of prevention. Following prescribed treatment plans and maintaining a regular moisturizing routine helps control inflammation before it triggers excess melanin production.
Daily sun protection proves essential, as UV exposure significantly darkens existing hyperpigmentation and slows healing. Choose broad-spectrum sunscreens with SPF 30 or higher formulated for sensitive skin.
Protective clothing adds another defense layer. Wide-brimmed hats and UPF-rated fabrics shield vulnerable skin from sun exposure that can worsen discoloration.
Gentle skincare practices make a substantial difference. Avoiding scratching, harsh scrubbing, or picking at healing eczema prevents additional inflammation that could trigger new areas of hyperpigmentation.
Regular dermatologist consultations allow for ongoing assessment and treatment adjustment. Dermatologists can spot early signs of hyperpigmentation and recommend appropriate interventions before discoloration becomes more difficult to treat.
Finding the right dermatologist makes all the difference
For individuals with melanin-rich skin dealing with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation from atopic dermatitis, finding a dermatologist experienced in treating skin of color proves crucial. These specialists understand the unique characteristics of darker skin tones and can develop customized treatment plans that effectively address hyperpigmentation while minimizing risks.
Many academic medical centers and dermatology practices now offer specialized skin of color clinics. These dedicated centers employ dermatologists with specific training and experience treating conditions like post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation in darker skin tones.
When consulting with dermatologists, patients should feel comfortable discussing their concerns about both eczema management and resulting hyperpigmentation. Bringing photos documenting changes in skin color over time helps dermatologists assess progress and adjust treatments accordingly.
The psychological impact deserves attention too
The psychological effects of visible skin discoloration often receive less attention than physical treatments, yet they significantly impact quality of life. Many individuals with post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation report feelings of self-consciousness, decreased social confidence, and frustration with the lengthy healing process.
Support groups, both online and in-person, connect individuals experiencing similar challenges and provide valuable emotional support. Dermatology practices increasingly recognize this need and may offer resources for addressing the psychological aspects of visible skin conditions.
Patients should feel empowered to discuss these emotional impacts with healthcare providers. Comprehensive treatment plans that address both physical symptoms and psychological wellbeing typically yield the most satisfying results.
A holistic approach yields the best results
Treating hyperpigmentation from atopic dermatitis in darker skin tones requires patience and a multi-faceted approach. Combining appropriate medical treatments with preventive strategies and emotional support creates the foundation for successful management.
While complete resolution of hyperpigmentation takes time, consistent treatment typically produces gradual improvement that significantly enhances skin appearance and confidence. With proper care and expert guidance, individuals with melanin-rich skin can effectively manage both atopic dermatitis and the resulting hyperpigmentation.