Living with herpes simplex virus affects millions of people worldwide, yet many remain unaware that specific triggers can be identified and avoided to dramatically reduce the frequency and severity of outbreaks. While the virus remains dormant in nerve cells between episodes, certain factors can reactivate it, leading to painful blisters, uncomfortable symptoms, and emotional distress.
Understanding these triggers empowers individuals to take control of their condition through proactive lifestyle modifications. Rather than feeling helpless against unpredictable outbreaks, people can implement targeted strategies that significantly improve their quality of life and reduce the impact of this common viral infection.
The key lies in recognizing that herpes outbreaks are not random occurrences but often result from identifiable circumstances that weaken the immune system or create conditions favorable for viral reactivation. By addressing these root causes, many people experience remarkable improvements in outbreak frequency and severity.
1. Chronic stress wreaks havoc on immune defenses
Stress stands as the most significant and controllable trigger for herpes outbreaks, yet it remains the factor most people overlook in their daily lives. When the body experiences prolonged stress, it releases cortisol and other stress hormones that suppress immune function, creating the perfect environment for the dormant herpes virus to reactivate.
The relationship between stress and herpes outbreaks creates a vicious cycle that many people find themselves trapped within. The anticipation of an outbreak causes anxiety, which elevates stress levels, which in turn increases the likelihood of another outbreak occurring. This psychological component often proves more debilitating than the physical symptoms themselves.
Modern life presents countless stress triggers that people accept as normal, including work pressure, financial concerns, relationship conflicts, sleep deprivation, and information overload from constant connectivity. These chronic stressors maintain elevated cortisol levels that continuously compromise immune surveillance, allowing the virus to emerge from dormancy more frequently.
Breaking the stress-outbreak cycle requires implementing comprehensive stress management strategies that address both immediate stressors and long-term resilience building. Regular meditation practice, even just ten minutes daily, can significantly reduce cortisol levels and improve immune function. Deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and mindfulness techniques provide immediate relief during acute stress episodes.
Physical exercise serves as one of the most effective stress-reduction tools while simultaneously boosting immune function. Moderate aerobic activity like walking, swimming, or cycling for 30 minutes daily helps metabolize stress hormones and releases endorphins that naturally elevate mood and reduce anxiety levels.
Sleep optimization plays a crucial role in stress management and immune health. Maintaining consistent sleep schedules, creating relaxing bedtime routines, and ensuring seven to nine hours of quality sleep each night helps regulate cortisol production and supports optimal immune function.
Time management skills and boundary setting can eliminate many daily stressors that contribute to chronic immune suppression. Learning to prioritize tasks, delegate responsibilities, and say no to excessive commitments creates space for relaxation and recovery that the immune system requires to function effectively.
2. Sun exposure triggers cellular damage and viral reactivation
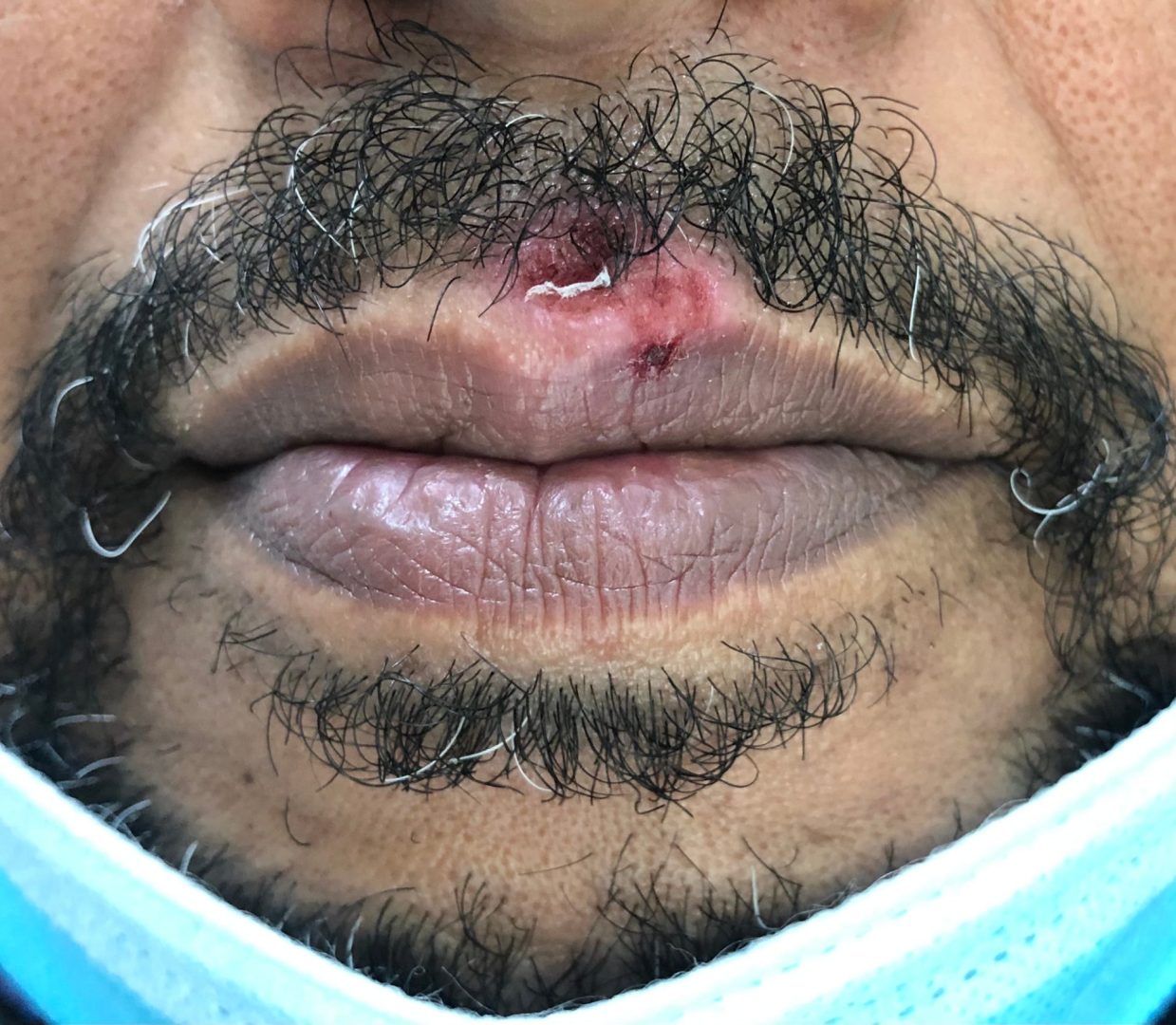
Ultraviolet radiation from sun exposure represents a well-documented trigger for herpes simplex outbreaks, particularly affecting individuals prone to cold sores around the mouth and lips. The UV rays damage skin cells and create inflammatory responses that can awaken dormant viral particles in nearby nerve endings.
Many people notice their first herpes outbreak or recurrent episodes following beach vacations, skiing trips, or extended outdoor activities without adequate sun protection. The combination of intense UV exposure, often coupled with stress from travel and disrupted routines, creates ideal conditions for viral reactivation.
The mechanism behind UV-triggered outbreaks involves cellular stress responses that compromise local immune surveillance in affected areas. When skin cells suffer UV damage, they release inflammatory mediators that can stimulate nerve pathways harboring dormant herpes virus, leading to reactivation and subsequent outbreak development.
Preventing sun-triggered outbreaks requires consistent application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with at least SPF 30 to all exposed skin areas, including lips. Lip balms containing zinc oxide or titanium dioxide provide physical barrier protection that proves more effective than chemical sunscreens for preventing cold sore outbreaks.
Protective clothing, wide-brimmed hats, and seeking shade during peak UV hours between 10 AM and 4 PM significantly reduce exposure risks. Reflective surfaces like snow, water, and sand can intensify UV exposure, requiring extra precautions during activities near these environments.
Gradual sun exposure allows skin to build protective melanin without triggering inflammatory responses that might reactivate the virus. Starting with short exposure periods and gradually increasing time spent outdoors helps prevent the sudden UV shock that often precipitates outbreaks.
Indoor tanning beds pose even greater risks than natural sunlight due to concentrated UV radiation that can trigger outbreaks more readily than outdoor sun exposure. Avoiding artificial UV sources eliminates this controllable risk factor entirely.
3. Immune system compromise from poor nutrition and lifestyle choices
A weakened immune system cannot effectively suppress herpes virus replication, leading to more frequent and severe outbreaks. Multiple lifestyle factors contribute to immune dysfunction, creating conditions that favor viral reactivation over immune control.
Nutritional deficiencies play a major role in immune compromise, with certain nutrients proving particularly important for antiviral immunity. Zinc deficiency has been linked to increased herpes outbreak frequency, as this mineral supports immune cell function and wound healing processes essential for controlling viral replication.
Vitamin D deficiency, increasingly common due to indoor lifestyles and limited sun exposure, significantly impairs immune function and increases susceptibility to viral infections. Low vitamin D levels correlate with more frequent herpes outbreaks and slower healing times.
B-complex vitamins, particularly B12, B6, and folate, support nerve health and immune function. Deficiencies in these nutrients can increase outbreak frequency and severity while prolonging healing times. Chronic alcohol consumption depletes B vitamins and directly suppresses immune function.
Excessive sugar consumption creates inflammatory conditions that impair immune responses while providing fuel for viral replication. High-glycemic foods cause blood sugar spikes that trigger inflammatory cascades, potentially reactivating dormant herpes virus.
Processed foods laden with artificial additives, preservatives, and trans fats promote systemic inflammation that compromises immune surveillance. These inflammatory compounds can trigger outbreak conditions even in the absence of other stressors.
Dehydration impairs cellular function throughout the body, including immune cells responsible for suppressing viral replication. Adequate hydration supports optimal immune function and helps flush metabolic waste products that could contribute to inflammatory conditions.
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption directly suppress immune function while creating inflammatory conditions throughout the body. These substances impair white blood cell activity and reduce the body’s ability to maintain viral suppression.
Implementing comprehensive prevention strategies
Successfully avoiding herpes triggers requires a holistic approach that addresses multiple risk factors simultaneously. Creating sustainable lifestyle changes proves more effective than attempting to eliminate single triggers in isolation.
Developing awareness of personal trigger patterns helps individuals identify their unique risk factors and timing patterns. Keeping a simple outbreak diary that tracks potential triggers, stress levels, sleep quality, and other relevant factors can reveal important connections that guide prevention efforts.
Building immune resilience through consistent healthy habits creates a foundation that can withstand occasional exposure to unavoidable triggers. This includes maintaining regular sleep schedules, eating nutrient-dense whole foods, staying adequately hydrated, and engaging in regular moderate exercise.
Stress inoculation training helps individuals develop coping skills before high-stress situations arise. Practicing relaxation techniques during calm periods builds the neural pathways needed to access these skills during actual stress events.
Social support systems play crucial roles in both stress management and maintaining healthy lifestyle habits. Connecting with understanding friends, family members, or support groups provides emotional resources that help buffer against stress-induced outbreaks.
Emergency action plans for unavoidable trigger exposure can minimize outbreak risk when prevention isn’t possible. This might include having antiviral medications available, implementing intensive stress-reduction protocols, or temporarily increasing immune-supporting supplements during high-risk periods.
Long-term benefits of trigger avoidance
Consistently avoiding known herpes triggers produces cumulative benefits that extend far beyond reduced outbreak frequency. Many people experience improved overall health, enhanced quality of life, and greater confidence in managing their condition.
Reduced outbreak frequency often leads to decreased anxiety about future episodes, creating a positive feedback loop that further reduces stress-related triggers. This psychological benefit can be as significant as the physical improvements in outbreak patterns.
The healthy lifestyle changes required for trigger avoidance typically improve multiple aspects of health simultaneously. Better stress management, improved nutrition, adequate sleep, and sun protection benefit cardiovascular health, mental well-being, and overall disease resistance.
Enhanced immune function from trigger avoidance may also reduce susceptibility to other viral infections and support faster recovery from minor illnesses. A robust immune system provides protection against numerous health challenges beyond herpes management.
Taking control of herpes triggers empowers individuals to shift from feeling victimized by their condition to actively managing their health. This sense of agency and control contributes significantly to improved mental health and overall life satisfaction.