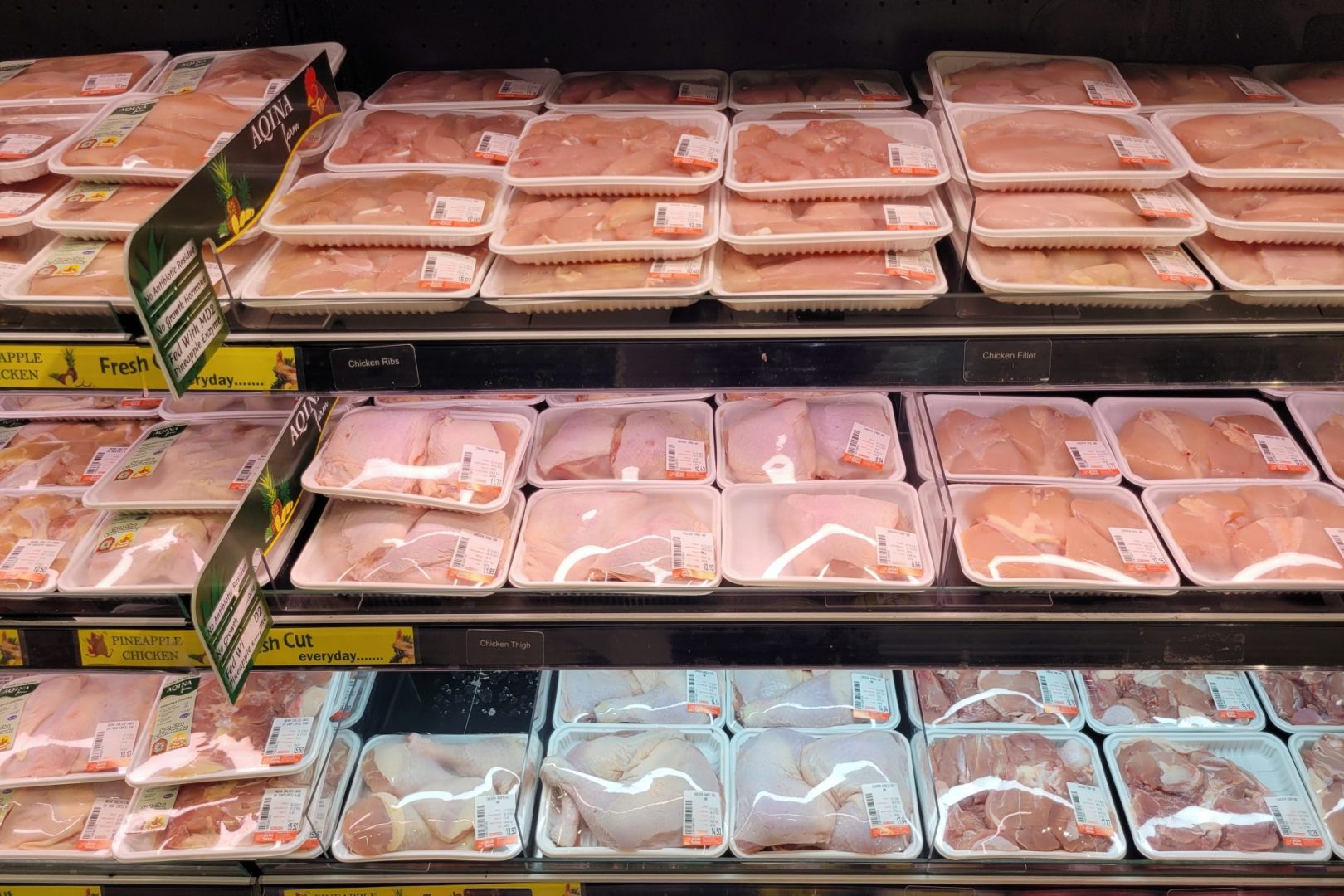
A disturbing new study has placed Pennsylvania among the most dangerous states for meat consumption, with bacterial contamination rates that should concern every family heading to their local grocery store. The Keystone State landed in the troubling fifth position on a nationwide ranking that examined the safety of retail meat products, raising serious questions about food processing standards across the commonwealth.
The comprehensive analysis conducted by Trace One researchers examined data from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration’s National Antimicrobial Resistance Monitoring System, revealing a concerning pattern of bacterial contamination in meat products sold throughout Pennsylvania. This ranking system evaluated all 50 states based on the presence of harmful bacteria in chicken and ground turkey products found on store shelves.
The research methodology focused specifically on retail meat samples, analyzing the prevalence of dangerous bacteria that can cause severe illness in consumers. Pennsylvania’s poor performance in this study suggests that residents face higher risks when purchasing meat products compared to consumers in states with better food safety records.
Understanding the dangerous bacteria threatening Pennsylvania consumers
The study examined four primary types of bacteria that pose significant health risks to consumers, each presenting unique dangers to families across Pennsylvania. These bacterial contaminants can enter meat products at various stages of the production process, from initial slaughter through final packaging and distribution.
Enterococcus bacteria serves as a key indicator of fecal contamination within meat processing facilities, suggesting inadequate sanitation practices during production. When this bacteria appears in retail meat products, it signals potential breakdowns in hygiene protocols that protect consumers from contamination. The presence of enterococcus in Pennsylvania’s meat supply indicates concerning gaps in processing facility cleanliness standards.
Escherichia coli, commonly known as E. coli, represents another critical indicator of fecal contamination and poor sanitation conditions. This bacteria can cause severe gastrointestinal illness, including potentially life-threatening complications in vulnerable populations such as young children, elderly individuals, and those with compromised immune systems. The detection of E. coli in meat products suggests serious deficiencies in processing facility sanitation protocols.
Salmonella poses particularly serious health risks as one of the leading causes of foodborne illness nationwide. This bacteria can survive in various environments and multiply rapidly under favorable conditions, making it especially dangerous for consumers. When salmonella develops resistance to antibiotics, treatment becomes significantly more challenging, potentially leading to prolonged illness and serious complications.
Campylobacter rounds out the quartet of dangerous bacteria examined in the study, representing another major cause of foodborne illness across the United States. Like salmonella, campylobacter infections can become particularly serious when the bacteria shows resistance to antibiotic treatments, limiting medical intervention options for affected patients.
How Pennsylvania compares to other states in food safety rankings
Pennsylvania’s fifth-place ranking puts the state in troubling company among the nation’s worst performers for meat safety. The study revealed that four other states demonstrated even higher rates of bacterial contamination, creating a concerning pattern across multiple regions of the country.
Georgia claimed the dubious distinction of first place, representing the worst state for bacterial contamination in meat products. The Peach State’s top ranking suggests widespread issues with meat processing standards and safety protocols that put consumers at significant risk when purchasing chicken and ground turkey products.
South Carolina secured second place in the ranking, indicating that the state’s meat processing industry faces serious challenges in maintaining adequate safety standards. The high contamination rates in South Carolina suggest systemic issues that require immediate attention from regulatory authorities and industry leaders.
Tennessee earned third place among the worst-performing states, revealing concerning patterns in meat safety across the southeastern region of the United States. The state’s poor performance indicates that consumers face elevated risks when purchasing meat products from retail outlets throughout Tennessee.
Minnesota rounded out the top four worst-performing states, demonstrating that food safety issues extend beyond any single geographic region. The inclusion of a midwestern state like Minnesota in the top five suggests that bacterial contamination problems affect diverse areas of the country with different climates and processing environments.
Critical points where contamination occurs in meat production
Understanding how bacterial contamination enters the meat supply chain helps consumers recognize the complexity of food safety challenges facing Pennsylvania and other states. The production process involves multiple stages where dangerous bacteria can infiltrate products destined for grocery store shelves.
Slaughter facilities represent the primary point where bacterial contamination typically occurs in meat production. During the slaughter process, bacteria from animal intestines and other sources can spread to meat surfaces if proper sanitation protocols are not followed rigorously. Inadequate cleaning procedures, insufficient temperature controls, and poor facility maintenance can all contribute to bacterial contamination during this critical stage.
Handling procedures throughout processing facilities create additional opportunities for bacterial contamination to occur. Workers who do not follow proper hygiene protocols, equipment that is not adequately sanitized between uses, and cross-contamination between different meat products can all introduce dangerous bacteria into the food supply chain.
Packaging operations represent the final major opportunity for bacterial contamination before products reach retail outlets. Improper packaging materials, inadequate temperature controls during packaging, and contaminated packaging equipment can all introduce bacteria into meat products just before they reach consumers.
Health implications for Pennsylvania residents
The presence of dangerous bacteria in Pennsylvania’s meat supply creates significant health risks for residents throughout the commonwealth. These bacterial contaminants can cause a range of illnesses, from mild gastrointestinal upset to life-threatening infections requiring hospitalization and intensive medical treatment.
Foodborne illnesses resulting from bacterial contamination typically develop within hours or days of consuming contaminated meat products. Symptoms often include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, abdominal cramping, and fever, which can persist for several days or weeks depending on the specific bacteria involved and the individual’s immune system response.
Vulnerable populations face particularly serious risks from bacterial contamination in meat products. Young children, elderly individuals, pregnant women, and people with compromised immune systems may experience more severe symptoms and complications from foodborne illnesses, potentially requiring emergency medical intervention and hospitalization.
The development of antibiotic-resistant bacteria strains creates additional challenges for medical professionals treating patients with foodborne illnesses. When bacteria show resistance to common antibiotics, treatment options become limited, potentially prolonging illness duration and increasing the risk of serious complications.
Protecting families from contaminated meat products
Pennsylvania consumers can take several important steps to protect their families from the risks associated with bacterial contamination in meat products. These protective measures become especially crucial given the state’s poor performance in the national food safety rankings.
Proper cooking temperatures represent the most effective defense against bacterial contamination in meat products. Using a reliable meat thermometer ensures that chicken reaches the safe internal temperature of 165 degrees Fahrenheit, while ground turkey should reach the same temperature throughout the product. These temperatures are sufficient to kill most harmful bacteria that may be present in contaminated meat.
Safe food handling practices in home kitchens help prevent cross-contamination and bacterial growth. This includes washing hands thoroughly before and after handling raw meat, using separate cutting boards for meat and other foods, and cleaning all surfaces and utensils that come into contact with raw meat products.
Proper storage techniques help minimize bacterial growth in meat products before cooking. Refrigerating meat products promptly after purchase, maintaining proper refrigerator temperatures below 40 degrees Fahrenheit, and using meat products within recommended timeframes all help reduce the risk of bacterial contamination.
Moving forward with improved food safety standards
The concerning results of this study highlight the urgent need for improved food safety standards and monitoring systems throughout Pennsylvania’s meat processing industry. Enhanced regulatory oversight, better industry compliance, and increased consumer awareness all play crucial roles in addressing these serious food safety challenges facing the commonwealth.