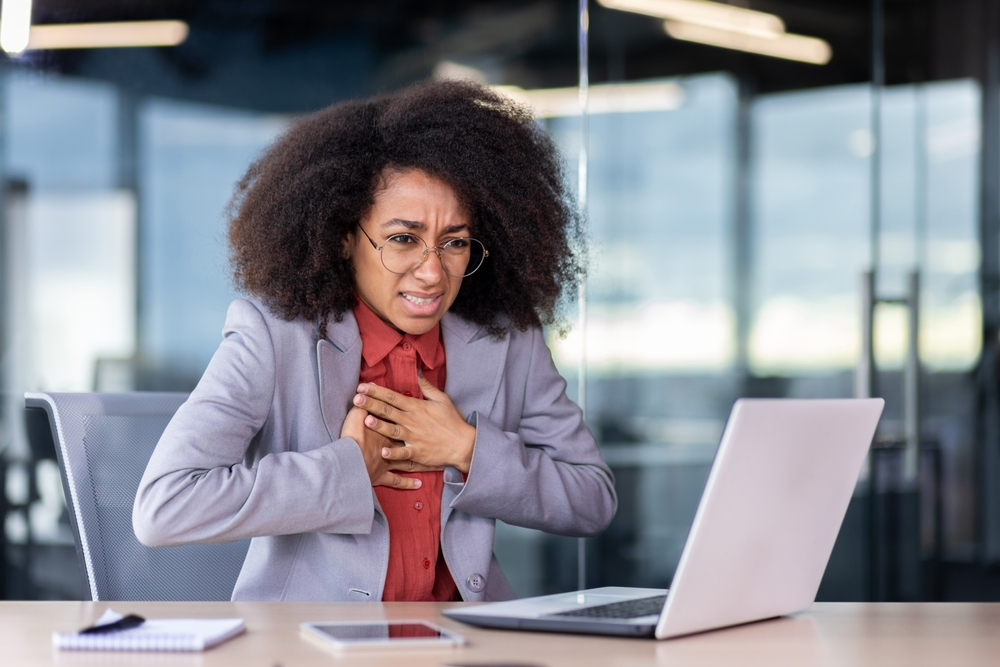
Heart attacks are often associated with physical health issues, but emotional experiences can also trigger these life-threatening events. Emotional stress has a significant impact on heart health, and certain experiences can be particularly shocking, leading to acute cardiac events. Understanding these emotional triggers is crucial for heart health and can help in preventing heart attacks.
1. Sudden loss of a loved one
The sudden loss of a loved one is one of the most emotionally devastating experiences a person can go through. The shock and grief that follow such a loss can cause a dramatic increase in stress hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These hormones can increase heart rate and blood pressure, putting immense strain on the cardiovascular system. This condition — often referred to as “broken heart syndrome” or stress cardiomyopathy — mimics the symptoms of a heart attack and can be just as dangerous.
Research has shown that the risk of a heart attack increases significantly within the first 24 hours of experiencing the sudden death of a loved one. The emotional shock can lead to arrhythmias (irregular heartbeats) and other cardiac complications, highlighting the importance of managing grief and seeking support during such times.
2. Intense anger or rage
Experiencing intense anger or rage can have immediate and severe effects on heart health. Anger triggers the body’s “fight or flight” response, leading to a surge in stress hormones. This hormonal surge can cause the heart to beat faster and blood vessels to constrict, increasing blood pressure. For individuals with underlying heart conditions, this can be particularly dangerous, as it can lead to a heart attack or other cardiovascular events.
Studies have shown that the risk of a heart attack is significantly higher in the two hours following an episode of intense anger. Learning to manage anger through techniques like deep breathing, mindfulness and stress management can help mitigate these risks.
3. Severe anxiety and panic attacks
Severe anxiety and panic attacks are other emotional experiences that can lead to heart attacks. During a panic attack, the body responds as if it is in extreme danger, with symptoms including chest pain, shortness of breath and heart palpitations. These symptoms are similar to those of a heart attack, making it difficult to distinguish between the two without medical intervention.
Chronic anxiety and frequent panic attacks can also have long-term effects on heart health. The constant state of heightened alertness can wear down the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of heart disease and heart attacks. Managing anxiety through therapy, medication and lifestyle changes is essential for reducing these risks.
4. Extreme fear or trauma
Extreme fear or traumatic experiences can have a profound impact on heart health. When a person experiences intense fear, the body’s natural response is to release a flood of stress hormones, which can lead to a rapid heart rate, elevated blood pressure and increased cardiac workload. These physiological changes can trigger a heart attack, especially in individuals with pre-existing heart conditions.
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), a condition resulting from exposure to traumatic events, has also been linked to an increased risk of heart attacks. Individuals with PTSD often experience heightened stress responses even in non-threatening situations, which can contribute to long-term heart damage. Seeking professional help to address and manage trauma is crucial for protecting heart health.
5. Overwhelming joy or excitement
While positive emotions like joy and excitement are generally beneficial for overall well-being, overwhelming joy can sometimes lead to heart attacks. This phenomenon — known as “happy heart syndrome” —occurs when an intense positive emotional experience triggers the release of stress hormones. These hormones can cause temporary changes in heart function, leading to symptoms similar to those of a heart attack.
Cases of happy heart syndrome are rare but serve as a reminder that the heart can be sensitive to extreme emotional states, whether positive or negative. Balancing emotions and maintaining a steady state of well-being is important for heart health.
Protecting your heart from emotional triggers of heart attacks
Emotional experiences can have a powerful impact on heart health, sometimes leading to severe consequences like heart attacks. The sudden loss of a loved one, intense anger, severe anxiety, extreme fear and overwhelming joy are all emotional states that can trigger acute cardiac events. Understanding these triggers and learning to manage emotional stress is crucial for protecting heart health.
If you experience symptoms of a heart attack — such as chest pain, shortness of breath or unusual fatigue — seek medical attention immediately. Additionally, practicing stress management techniques, seeking support during difficult times and maintaining a healthy lifestyle can help reduce the risk of heart attacks caused by emotional experiences.
By being aware of the emotional triggers that can affect your heart, you can take proactive steps to protect your cardiovascular health and ensure a healthier, happier life.
This story was created using AI technology.