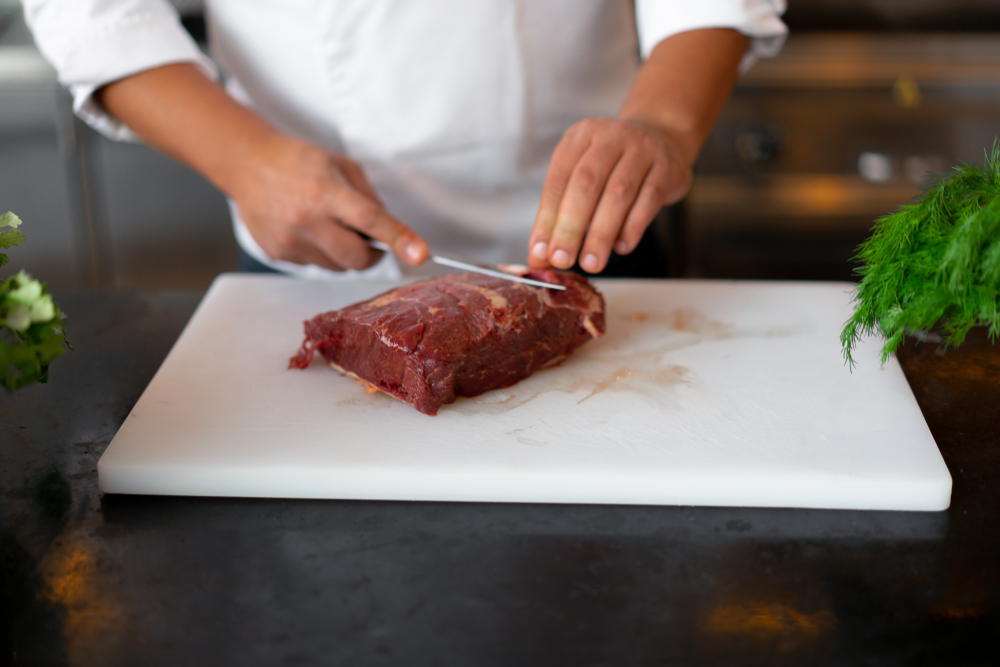
Raw meat consumption poses serious health risks despite its popularity in certain cuisines and diets. While some cultures embrace uncooked meat dishes, consuming raw meat exposes individuals to harmful pathogens that can cause severe illness. Understanding these risks helps people make informed decisions about their food choices.
Hidden dangers in raw meat
Uncooked meat harbors various harmful organisms invisible to the naked eye. Common bacteria found in raw meat include Salmonella, E. coli, and Listeria. These pathogens frequently cause food poisoning, triggering symptoms ranging from mild discomfort to severe illness.
Parasites present another significant concern, particularly in raw pork and fish. Organisms like Toxoplasma gondii, tapeworms, and roundworms can establish long-term infections with serious health consequences. Additionally, viruses such as Hepatitis E spread through raw meat, potentially causing severe liver inflammation.
Understanding infection symptoms
Foodborne illnesses from raw meat manifest through various symptoms. Initial signs often include nausea, vomiting, and stomach cramps. As infections progress, individuals may experience severe diarrhea requiring medical attention, persistent fever and chills, debilitating muscle pain, and extended fatigue.
Serious cases can lead to kidney failure, neurological complications, or death, particularly among vulnerable populations. The severity of symptoms often depends on factors such as the type of pathogen involved and the individual’s immune system strength.
Cooking versus raw consumption
Heat treatment during cooking destroys most harmful organisms in meat. The cooking process alters protein structures, making meat safer for consumption. Raw meat remains a fertile environment for bacteria and other pathogens, especially when improperly handled or stored.
Cross-contamination risks increase with raw meat handling. Using the same cutting boards or utensils for raw meat and other foods spreads bacteria throughout the kitchen. Improper storage temperatures accelerate pathogen growth, further increasing consumption risks.
Cultural preparations and precautions
Some cultures traditionally serve raw meat dishes like steak tartare, sushi, and carpaccio. These preparations typically involve strict safety protocols, including specific freezing temperatures to kill parasites and using specialty-grade meat from trusted suppliers. Rigorous sanitation practices and strict handling guidelines help minimize risks, though they cannot eliminate them entirely.
Despite these precautions, risks remain present even in carefully prepared raw meat dishes. The quality of ingredients and preparation methods significantly impact safety levels, making proper sourcing and handling crucial for these traditional dishes.
Immune system considerations
Individual immune response significantly affects reactions to raw meat consumption. While robust immune systems may handle exposure with minimal symptoms, compromised immunity leads to severe complications. Pregnant women face increased risk of Listeriosis, while elderly individuals and those with chronic illnesses may experience more severe symptoms due to weakened immune systems.
Children with developing immune systems also face higher risks from raw meat consumption. Their bodies may struggle to fight off infections effectively, leading to more serious complications and longer recovery times.
Prevention strategies
Protecting against raw meat hazards requires consistent safety practices throughout food preparation. Thorough cooking eliminates most pathogens, while proper hand washing prevents bacterial spread throughout the kitchen. Maintaining separate storage areas for raw meat prevents cross-contamination with other foods.
Temperature control plays a crucial role in food safety. Proper refrigeration slows bacterial growth, while adequate cooking temperatures ensure pathogen destruction. Regular cleaning and sanitization of preparation surfaces further reduce contamination risks.
Impact on daily life
Foodborne illnesses from raw meat significantly affect both physical and emotional well-being. Recovery often requires extended time away from work or daily activities, disrupting normal routines and responsibilities. Severe cases may need hospitalization, leading to substantial medical expenses and ongoing health concerns.
Families caring for affected members face additional challenges beyond the immediate illness. The stress of managing illness while maintaining household responsibilities creates significant burden, especially when long-term complications require extended medical support and lifestyle adjustments.
Making informed choices
Understanding raw meat risks helps individuals make better dietary decisions. While some may choose to consume raw meat dishes, knowing proper preparation methods and potential consequences allows for informed risk assessment. Using meat thermometers ensures proper cooking temperatures, while maintaining clean preparation areas reduces contamination risks.
Proper food storage and handling techniques create additional layers of protection against foodborne illness. When dining out, understanding restaurant food safety practices helps individuals make safer choices about raw meat consumption.
Long-term considerations
Raw meat consumption risks extend beyond immediate illness. Some infections lead to chronic health issues requiring ongoing medical attention. Prevention through proper food handling and cooking provides the best protection against these potential complications.
Regular education about food safety helps maintain healthy practices in homes and communities. Understanding proper meat handling, storage, and preparation creates safer eating environments while allowing people to enjoy properly prepared meals that align with their dietary preferences and health goals.
This story was created using AI technology.