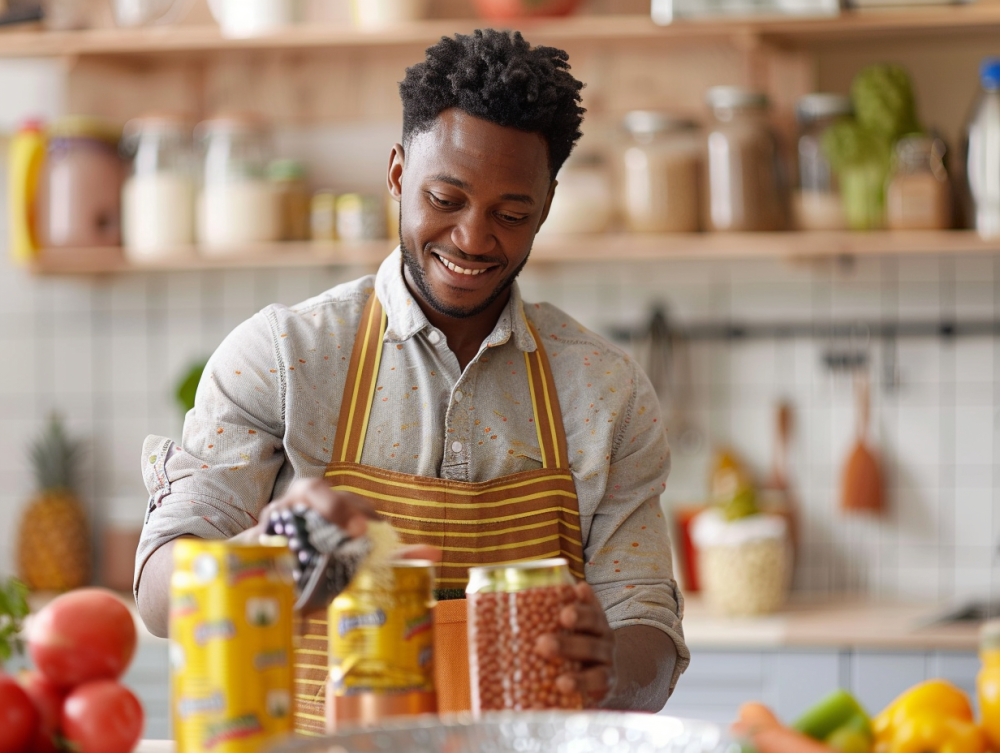
For years, canned foods have been dismissed as inferior to their fresh and frozen counterparts. Many believed that the preservation process stripped foods of essential nutrients, making them less desirable for a healthy diet. But new research challenges these long-held assumptions, revealing that canned foods are not just a convenient option but a nutritional powerhouse that can hold their own against fresh produce.
The science behind canned food nutrition
Canning is an age-old process that dates back to the early 19th century, originally developed to preserve food for military use. The technique involves sealing food in airtight containers and heating them to kill bacteria, ensuring long-term safety and freshness. Contrary to popular belief, this method does not necessarily deplete nutrients. In some cases, it enhances them.
Research shows that the canning process can increase the bioavailability of certain nutrients. For example, canned tomatoes contain higher levels of lycopene, a powerful antioxidant linked to heart health, than their fresh counterparts. Similarly, canned beans retain most of their fiber and protein, making them a reliable source of plant-based nutrition.
Why canned foods deserve a second look
Despite their long shelf life, canned foods are often just as nutrient-dense as fresh options. They undergo minimal processing beyond heating and sealing, preserving their vitamins and minerals for extended periods.
Nutrient retention: Many vegetables and legumes maintain their nutritional integrity, providing essential vitamins, fiber, and protein.
Cost-effectiveness: Canned foods are significantly cheaper than fresh or frozen alternatives, making them an accessible choice for budget-conscious consumers.
Reduced food waste: With a long shelf life, canned goods help households cut down on food spoilage, reducing overall waste.
Convenience: They require no refrigeration until opened, making them ideal for quick meals and emergency food storage.
Choosing the right canned foods
While canned foods offer numerous benefits, not all products are created equal. Consumers should be mindful of added ingredients that can impact health.
Watch the sodium: Many canned vegetables and beans contain added salt as a preservative. Opt for low-sodium or no-salt-added versions when possible.
Avoid added sugars: Some canned fruits are packed in heavy syrups that increase sugar intake. Choose fruits canned in water or natural juice instead.
Check for BPA-free packaging: Some cans contain bisphenol A (BPA), a chemical that may pose health risks. Many brands now offer BPA-free options.
By making informed choices, consumers can maximize the nutritional benefits of canned foods without unnecessary additives.
How to incorporate canned foods into your diet
Canned foods are more versatile than many people realize. They can be easily incorporated into meals without sacrificing taste or nutrition.
Canned beans: A quick and easy protein source for salads, soups, and stews.
Canned fish: Salmon, sardines, and tuna provide high-quality protein and omega-3 fatty acids, which are essential for heart and brain health.
Canned tomatoes: A base for sauces, soups, and stews, offering a rich source of antioxidants.
Canned pumpkin: A fiber-rich addition to oatmeal, smoothies, or baked goods.
Canned fruits: A convenient way to add vitamins and natural sweetness to breakfast bowls and desserts.
These simple additions can transform canned foods from basic pantry staples into key ingredients in a balanced diet.
The future of canned food nutrition
Canned foods are experiencing a resurgence, driven by changing consumer perceptions and a growing body of research supporting their nutritional value. As food insecurity and rising grocery prices continue to challenge households worldwide, the affordability and accessibility of canned foods make them a valuable dietary solution.
At the same time, innovations in food processing and packaging are making canned products healthier and more sustainable. Many brands are reducing sodium content, eliminating BPA from packaging, and focusing on cleaner ingredient lists. As consumers become more health-conscious, the demand for high-quality, nutrient-rich canned foods is expected to rise.
Canned foods are no longer just a last resort for emergencies. They are a practical, nutritious, and cost-effective option for modern diets. By understanding how to select and use them wisely, consumers can enjoy the benefits of preserved foods without compromise.