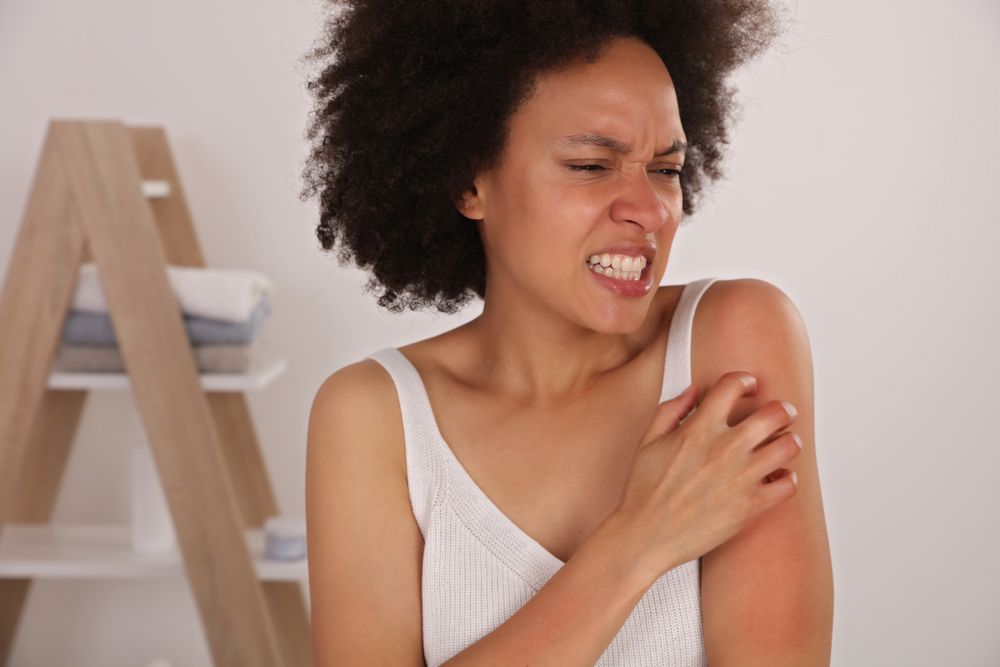
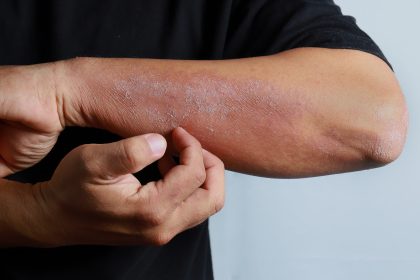
Eczema is a prevalent skin condition that affects millions of people, characterized by red, dry and itchy patches on the skin. The term “eczema” encompasses a variety of skin conditions, each with its own unique symptoms and triggers. Understanding the different types of eczema, their symptoms and treatment options is crucial for effective management.
What is eczema?
Eczema refers to a group of skin conditions that cause inflammation, redness and irritation. The most common types include:
– Atopic dermatitis
– Contact dermatitis
– Dyshidrotic eczema
– Nummular eczema
– Neurodermatitis
– Hand eczema
– Stasis dermatitis
In the U.S., over 31 million people experience eczema symptoms, making it a significant health concern. While eczema is generally manageable with topical treatments, severe cases can lead to discomfort and interfere with daily activities.
Types of eczema and their symptoms
1. Atopic dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis is one of the most common forms of eczema, often appearing on the outer parts of joints like elbows and knees. Symptoms include oozing blisters that crust over, discharge or blood from the ears, raw patches from scratching, changes in skin color and thickened skin.
Triggers include allergens, chemicals, stress and temperature changes. This condition is often linked to a compromised skin barrier, making it more susceptible to irritants.
2. Contact dermatitis
Contact dermatitis occurs when the skin reacts to irritating substances, such as nickel or certain chemicals. Symptoms include redness and warmth, scaly or thick patches and blisters that weep and crust over.
Identifying and avoiding triggers is essential for managing this type of eczema.
3. Dyshidrotic eczema
Dyshidrotic eczema causes small, itchy blisters on the hands and feet, often flaring during stress or temperature changes. Treatment may involve medicated soaks and corticosteroid creams.
4. Nummular eczema
Nummular eczema is characterized by round, coin-shaped lesions that can be itchy. Triggers include stress and dry skin. Treatments often involve topical corticosteroids and moisturizers.
Managing and treating eczema
While there is no one-size-fits-all cure for eczema, various treatment options can help manage symptoms effectively:
– Topical corticosteroids to reduce inflammation
– Moisturizers to maintain skin hydration
– Oral antihistamines for itch relief
– Biologic medications for severe cases
– Ultraviolet (UV) light therapy
In addition to medical treatments, lifestyle changes can also play a significant role in managing eczema:
– Keep fingernails short to prevent scratching
– Use a humidifier to maintain moisture in the air
– Avoid irritants like alcohol and fragrances in skincare products
– Take lukewarm baths and showers
Eczema is a complex condition that can significantly impact quality of life. Understanding the different types of eczema, their symptoms and effective treatment options is essential for those affected. If you or someone you know is struggling with eczema, consulting a health care provider can help develop a personalized treatment plan to manage symptoms and improve skin health.
For individuals with eczema, particularly those with darker skin tones, it’s important to note that symptoms may present differently. Redness may be less apparent, while skin darkening or lightening may be more noticeable. This can sometimes lead to misdiagnosis or delayed treatment, making awareness of these differences crucial for both patients and health care providers.
Stress management techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also play a role in managing eczema symptoms. Stress is a known trigger for many types of eczema, and finding effective ways to reduce stress can help minimize flare-ups.
Dietary considerations may also be important for some individuals with eczema. While research is ongoing, some studies suggest that certain foods may trigger or exacerbate eczema symptoms in some people. Keeping a food diary and working with a health care provider or nutritionist can help identify potential dietary triggers.