Game-changing danger zones for blood pressure unveiled
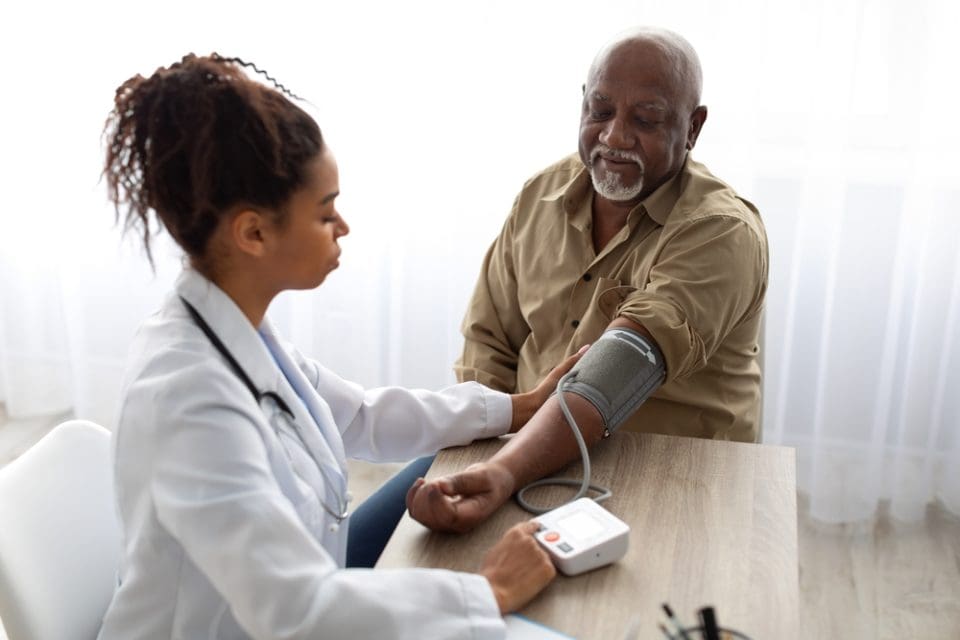
Blood pressure measurement serves as a vital indicator of cardiovascular health, offering critical insights into potential risks. Recent updates to medical guidelines have redefined the thresholds for dangerous blood pressure levels, underscoring the need for early intervention and routine monitoring. These changes could transform the way individuals approach their heart health, encouraging proactive care.
Understanding blood pressure readings
Blood pressure basics explain cardiovascular health
Blood pressure readings consist of two key numbers that reveal how well the heart and blood vessels are functioning. The systolic pressure, or the top number, measures the force of blood as the heart contracts. The diastolic pressure, or the bottom number, captures the pressure when the heart rests between beats.
Medical professionals categorize blood pressure into distinct ranges to assess potential health risks. A reading below 120/80 mm Hg is considered normal. Elevated blood pressure begins at 120-129 systolic and less than 80 diastolic, while hypertension starts at 130/80 mm Hg. Crisis levels, such as readings over 180/120 mm Hg, indicate a medical emergency requiring immediate attention.
Health implications and risk factors
Blood pressure imbalances can silently damage health
The effects of blood pressure extend far beyond a numerical scale. Persistently high blood pressure, or hypertension, can silently wreak havoc on the body. It places strain on blood vessels, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions such as heart attacks, strokes, kidney disease, and even vision loss.
Equally concerning is low blood pressure, or hypotension. While it may seem harmless, unusually low readings can cause dizziness, fainting, and fatigue. In severe cases, it might indicate underlying issues like dehydration, blood loss, or endocrine disorders, all of which require medical evaluation.
Effective management strategies
Lifestyle changes offer powerful tools for control
Maintaining healthy blood pressure levels often starts with lifestyle adjustments. A heart-friendly diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can significantly lower blood pressure. Reducing sodium intake to under 2,300 milligrams daily—or even less for some individuals—has proven particularly effective.
Physical activity also plays a vital role. Regular exercise, such as brisk walking or swimming for at least 150 minutes a week, strengthens the heart and improves circulation. Managing stress through mindfulness practices, such as yoga or meditation, further supports blood pressure control.
For individuals with high blood pressure, medication may be necessary. Healthcare providers tailor treatment plans to each person’s unique needs, ensuring effective management and minimizing potential side effects.
Monitoring and professional guidance
Consistent tracking ensures early intervention
Regular monitoring is essential for understanding and managing blood pressure. Home blood pressure monitors allow individuals to track their readings conveniently and identify patterns that may indicate emerging issues.
However, self-monitoring is only one piece of the puzzle. Routine medical check-ups provide crucial oversight, ensuring accurate interpretation of readings and adjustments to treatment plans. Physicians also help patients understand their results in the context of overall health, offering insights into any necessary lifestyle or medication changes.
Transforming cardiovascular care
New guidelines empower proactive health management
The redefined danger zones for blood pressure mark a significant shift in cardiovascular care. By encouraging earlier detection and intervention, these guidelines aim to reduce the prevalence of heart disease and related complications.
This proactive approach aligns with the broader trend toward personalized medicine. Individuals who adopt regular monitoring and preventive strategies can take charge of their cardiovascular health, potentially avoiding the long-term consequences of uncontrolled blood pressure.
A path to better heart health
The updated understanding of blood pressure readings highlights the importance of taking action early. Whether through lifestyle adjustments, consistent monitoring, or professional medical support, individuals have more tools than ever to manage their cardiovascular health.
By embracing these strategies, many people can reduce their risk of serious complications and enjoy better overall well-being. The path to a healthier heart is within reach—one step, one reading, and one lifestyle change at a time.