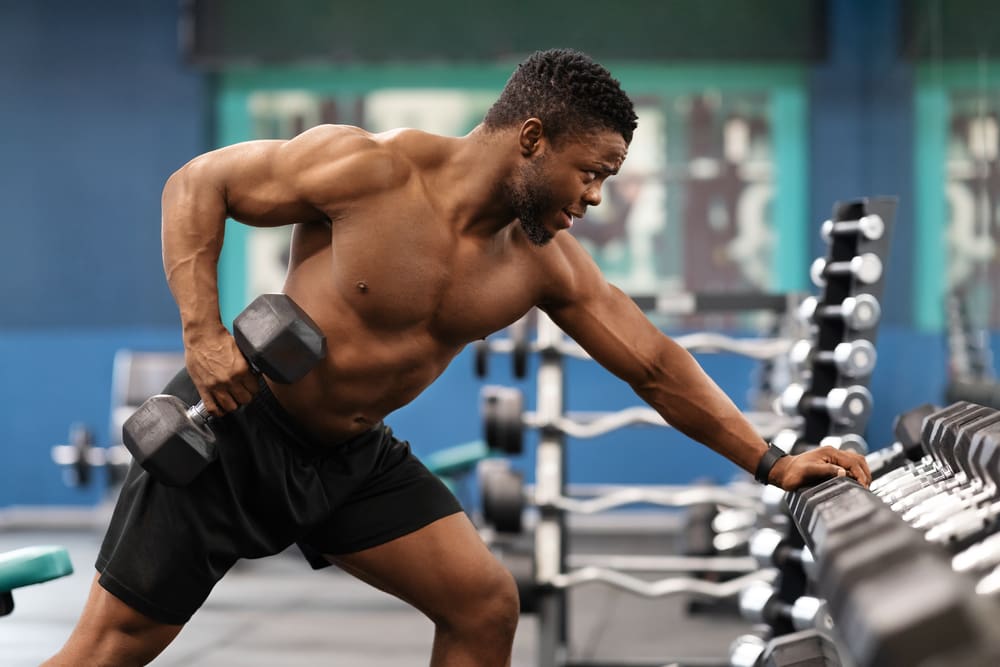
Building muscle transcends aesthetic goals, emerging as a critical component of long-term health and longevity. Recent medical studies reveal that increased muscular strength significantly reduces risks of cardiovascular disease and premature mortality, making strength training essential for overall wellness.
Understanding muscle growth
Physical therapist Shannon Ritchey explains that muscle development occurs through a process called progressive overload. When muscles experience stress beyond their normal limits, microscopic tears form in the fiber tissue. During rest periods, especially during sleep, these fibers repair and strengthen, resulting in increased muscle mass.
Protein: The building block
Successful muscle growth requires consistent protein intake throughout the day. Experts recommend consuming 1.2 grams of protein per kilogram of body weight, which can be achieved through various sources:
Lean Meats:
– Chicken breast (31g protein per 100g)
– Turkey breast (29g protein per 100g)
– Lean beef (26g protein per 100g)
– Fish like salmon (25g protein per 100g)
Plant-Based Options:
– Lentils (9g protein per 100g)
– Quinoa (4g protein per 100g)
– Spinach (3g protein per 100g)
– Broccoli (3g protein per 100g)
Nuts and Seeds:
– Almonds (21g protein per 100g)
– Pumpkin seeds (19g protein per 100g)
– Chia seeds (17g protein per 100g)
Timeline and expectations
Newcomers to strength training typically see visible results within 8-12 weeks of consistent effort, while experienced lifters may notice changes in 4-8 weeks. This process requires a caloric surplus of 200-500 calories daily, primarily from protein-rich sources.
The natural aging factor
Without intervention, muscle mass naturally decreases by 3-5 percent per decade starting around age 30. This decline accelerates after 60, making consistent resistance training crucial for maintaining strength and independence throughout life.
Training framework
Successful muscle building follows the R.E.P.S. principle: perform 6-30 repetitions per set, select compound exercises that engage multiple muscle groups, maintain consistent protein intake, and structure workouts to allow adequate recovery between sessions.
This comprehensive approach to muscle development recognizes individual variations while emphasizing scientifically proven methods. Success requires dedication to both training and nutrition, with progress measured in months rather than days or weeks.